2-Furoyl chloride
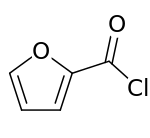 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Furan-2-carbonyl chloride | |
| Other names
2-Furancarbonyl chloride 2-Furancarboxylic acid chloride 2-Furanoyl chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
| 527-69-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 13861158 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.658 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H3ClO2 | |
| Molar mass | 130.53 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | liquid |
| Density | 1.3227 g/mL @ 20 °C |
| Melting point | −2 °C (28 °F; 271 K) |
| Boiling point | 173 °C (343 °F; 446 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Furoyl chloride is a corrosive liquid boiling at 173 °C, which is more irritating to the eyes than benzoyl chloride.[1] 2-Furoyl chloride is a useful pharmaceutical intermediate and is used in the synthesis of mometasone furoate, an antiinflammatory prodrug used in the treatment of skin disorders, hay fever and asthma.[2]
Synthesis
2-Furoyl chloride was prepared in 1924 by Gelissen by refluxing 2-furoic acid in excess thionyl chloride on a water bath.[1]
Applications
Pharmaceutical Intermediate
2-Furoyl chloride was reacted with mometasone in chilled methylene chloride solution in the presence of triethylamine. Crude mometasone 17-(2-furoate), commonly known as, mometasone furoate was obtained via filtration in 82% isolated yield.[2]
Similarly, 2-furoyl chloride was reacted with 6α,9α-difluoro-11β-hydroxy-16α-methyl-3-one androsta-1,4-diene-17β-thiocarboxylic acid in the presence of triethylamine, followed by fluoromethylation, yielding fluticasone furoate, a corticosteroid for the treatment of allergic rhinitis.[3]
Diloxanide furoate (Furamide, Amicline), a lumenal amoebicide used in the treatment of amoebiasis and amoebic dysentery, has been synthesized from the relatively simple intermediates: p-bromophenol, methylamine, dichloroacetyl chloride and 2-furoyl chloride, through an amination, acylation and esterification sequence.[4]
Reaction of 2-furoyl chloride with sodium hydrosulfide gave 2-furancarbothioic acid, an intermediate to Ceftiofur (Excenel), a third generation cephalosporin antibiotic.[5]
Acylation of the product of the reaction of 2-chloropyrazine and 1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinone oxime with 2-furoyl chloride gave mirfentanil, a fentanyl analog with analgesic activity.[6]
References
- 1 2 H. Gelissen; van Roon, J. D. (1924). "Furfuroyl peroxide". Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas et de la Belgique. 43: 59–66.
- 1 2 William Heggie, "Process for the preparation of mometasone furoate", US Patent 6,177,560 B1(2001)
- ↑ Dingjun Chu, "Method for preparation of Fluticasone furoate", CN 102558273 A 20120711 (2012)
- ↑ Wenli Zheng; Xue, Feiqun (2006). "Synthesis of diloxanide furoate". Zhongguo Yiyao Gongye Zazhi. 37 (2): 77–78.
- ↑ Xuke Zhang, "Method for preparation of Ceftiofur", CN Patent 101,108,855 A (2008)
- ↑ Jerome R. Bagley; Wynn, Richard; Rudo, Frieda; Doorley, Brian; Spencer, Kenneth; Spaulding, Theodore (1989). "New 4-(heteroanilido)piperidines, structurally related to the pure opioidagonist fentanyl, with agonist and/or antagonist properties". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 32 (3): 663–71. doi:10.1021/jm00123a028. PMID 2563773.