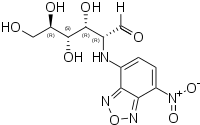
2-NBDG
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
D-Glucose, 2-deoxy-2-((7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazol-4-yl)amino)- | |
| Other names
2-NBD Glucose | |
| Identifiers | |
| 186689-07-6 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 5143305 |
| PubChem | 6711157 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H14N4O8 | |
| Molar mass | 342.2646 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-NBDG is a fluorescent tracer used for monitoring glucose uptake into living cells; it consists of a glucosamine molecule substituted with a 7-nitrobenzofurazan fluorophore at its amine group. It is widely referred to a fluorescent derivative of glucose,[1] and it is used in cell biology to visualize uptake of glucose by cells.[2] Cells that have taken up the compound fluoresce green.
2-NBDG is similar to radiolabeled glucose in that both can be used to detect glucose transport. Unlike radiolabeled glucose, 2-NBDG is compatible with fluorescence techniques such as a fluorescent microscopy, flow cytometry, and fluorimetry [2]
The compound is taken up by a variety of mammalian, plant, and microbial cells[2][3][4] In mammalian cells, the transporter for 2-NBDG is GLUT2.[5] In bacterial cells, the predominant transporter is the mannose phosphotransferase system.[4] Cells that lack these or other compatible transporters do not take up 2-NBDG.[4][6]
Similar to glucose, 2-NBDG is transported according to Michaelis-Menten kinetics. However, transport of 2-NBDG has a lower (maximum rate), and thus the rate of transport is generally slower than glucose.[4]
Once taken up, the compound is metabolized to a non-fluorescent derivative, as shown in Escherichia coli.[7] The identity and further metabolism of this non-fluorescent derivative has not been established.
References
- ↑ Yoshioka, K; Takahashi, H; Homma, T; Saito, M; Oh, K; Nemoto, Y; Matsuoka, H (1996). "A novel fluorescent derivative of glucose applicable to the assessment of glucose uptake activity of Escherichia coli". Biochim Biophys Acta. 1289 (1): 5–9. PMID 8605231.
- 1 2 3 Yamada K, Saito M, Matsuoka H, Inagaki N (2007). "A real-time method of imaging glucose uptake in single, living mammalian cells". Nat Protoc. 2 (3): 753–62. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.76. PMID 17406637.
- ↑ Etxeberria E, González P, Tomlinson P, Pozueta-Romero J (2005). "Existence of two parallel mechanisms for glucose uptake in heterotrophic plant cells". J. Exp. Bot. 56 (417): 1905–12. doi:10.1093/jxb/eri185. PMID 15911561.
- 1 2 3 4 Tao J, Diaz RK, Teixeira CR, Hackmann TJ (2016). "Transport of a Fluorescent Analogue of Glucose (2-NBDG) versus Radiolabeled Sugars by Rumen Bacteria and Escherichia coli". Biochemistry. 55 (18): 2578–89. doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01286. PMID 27096355.
- ↑ Yamada K, Nakata M, Horimoto N, Saito M, Matsuoka H, Inagaki N (2000). "Measurement of glucose uptake and intracellular calcium concentration in single, living pancreatic beta-cells". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (29): 22278–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M908048199. PMID 10748091.
- ↑ Chang HC, Yang SF, Huang CC, Lin TS, Liang PH, Lin CJ, Hsu LC (2013). "Development of a novel non-radioactive cell-based method for the screening of SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitors using 1-NBDG". Mol Biosyst. 9 (8): 2010–20. doi:10.1039/c3mb70060g. PMID 23657801.
- ↑ Yoshioka K, Saito M, Oh KB, Nemoto Y, Matsuoka H, Natsume M, Abe H (1996). "Intracellular fate of 2-NBDG, a fluorescent probe for glucose uptake activity, in Escherichia coli cells". Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 60 (11): 1899–901. doi:10.1271/bbb.60.1899. PMID 8987871.