Abexinostat
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
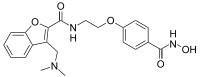
| IUPAC name
3-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]-N-{2-[4-(hydroxycarbamoyl)phenoxy]ethyl}-1-benzofuran-2-carboxamide | |
| Other names
PCI-24781; CRA-024781 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 783355-60-2 783356-67-2 (HCl) | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL2103863 |
| ChemSpider | 9924562 |
| KEGG | D10060 |
| PubChem | 11749858 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H23N3O5 | |
| Molar mass | 397.43 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Abexinostat (INN,[1] formerly PCI-24781) is an experimental drug candidate for cancer treatment.[2] It is currently under development by Pharmacyclics and is in Phase II clinical trials for B-cell lymphoma.[3] Pre-clinical study suggests the potential for treatment of different types of cancer as well.[4][5][6][7]
Abexinostat exerts its effect as a histone deacetylase inhibitor.[8][9]
References
- ↑ WHO Drug Information, Vol. 25, No. 2, 2011
- ↑ Abexinostat, NCI Cancer Dictionary
- ↑ Abexinostat HCl (PCI-24781), PanHDAC-inhibitor, Pharmacyclics
- ↑ Bhalla, S; Balasubramanian, S; David, K; Sirisawad, M; Buggy, J; Mauro, L; Prachand, S; Miller, R; Gordon, LI; Evens, AM (2009). "PCI-24781 induces caspase and reactive oxygen species-dependent apoptosis through NF-kappaB mechanisms and is synergistic with bortezomib in lymphoma cells". Clinical Cancer Research. 15 (10): 3354–65. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2365. PMC 2704489
 . PMID 19417023.
. PMID 19417023. - ↑ Lopez, G; Liu, J; Ren, W; Wei, W; Wang, S; Lahat, G; Zhu, QS; Bornmann, WG; McConkey, DJ; Pollock, RE; Lev, DC (2009). "Combining PCI-24781, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, with chemotherapy for the treatment of soft tissue sarcoma". Clinical Cancer Research. 15 (10): 3472–83. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2714. PMID 19417021.
- ↑ Rivera-Del Valle, N; Gao, S; Miller, CP; Fulbright, J; Gonzales, C; Sirisawad, M; Steggerda, S; Wheler, J; Balasubramanian, S; Chandra, J (2010). "PCI-24781, a Novel Hydroxamic Acid HDAC Inhibitor, Exerts Cytotoxicity and Histone Alterations via Caspase-8 and FADD in Leukemia Cells". International Journal of Cell Biology. 2010: 207420. doi:10.1155/2010/207420. PMC 2817379
 . PMID 20145726.
. PMID 20145726. - ↑ Yang, C; Choy, E; Hornicek, FJ; Wood, KB; Schwab, JH; Liu, X; Mankin, H; Duan, Z (2011). "Histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACI) PCI-24781 potentiates cytotoxic effects of doxorubicin in bone sarcoma cells". Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology. 67 (2): 439–46. doi:10.1007/s00280-010-1344-7. PMID 20461381.
- ↑ Buggy, JJ; Cao, ZA; Bass, KE; Verner, E; Balasubramanian, S; Liu, L; Schultz, BE; Young, PR; Dalrymple, SA (2006). "CRA-024781: A novel synthetic inhibitor of histone deacetylase enzymes with antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo". Molecular cancer therapeutics. 5 (5): 1309–17. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0442. PMID 16731764.
- ↑ Adimoolam, S; Sirisawad, M; Chen, J; Thiemann, P; Ford, JM; Buggy, JJ (2007). "HDAC inhibitor PCI-24781 decreases RAD51 expression and inhibits homologous recombination". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (49): 19482–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0707828104. PMC 2148315
 . PMID 18042714.
. PMID 18042714.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.