Aerial tramway



An aerial tramway, sky tram, cable car, ropeway or aerial tram is a type of aerial lift which uses one or two stationary ropes for support while a third moving rope provides propulsion.[1] With this form of lift, the grip of an aerial tramway cabin is fixed onto the propulsion rope and cannot be decoupled from it during operations.
Terminology
Because of the proliferation of such systems in the Alpine regions of Europe, the French and German names, téléphérique and Seilbahn, respectively, are often also used in an English language context. Cable car is the usual term in British English, as in British English the word tramway generally refers to a railed street tramway while in American English, cable car may additionally refer to a cable-pulled street tramway with detachable vehicles; e.g., San Francisco's cable cars. As such, careful phrasing is necessary to prevent confusion. It is also sometimes called a ropeway or even incorrectly referred to as a gondola lift. A gondola lift has cabins suspended from a continuously circulating cable whereas aerial trams simply shuttle back and forth on cables. In Japan, the two are considered as the same category of vehicle and called ropeway, while the term cable car means Cable car (railway) and funicular. An aerial railway where the vehicles are suspended from a fixed track (as opposed to a cable) is known as a suspension railway.
Overview
An aerial tramway consists of one or two fixed cables (called track cables), one loop of cable (called a haulage rope), and two passenger cabins. The fixed cables provide support for the cabins while the haulage rope, by means of a grip, is solidly connected to the truck (the wheel set that rolls on the track cables). An electric motor drives the haulage rope which provides propulsion. Aerial tramways are constructed as reversible systems; vehicles shuttling back and forth between two end terminals and propelled by a cable loop which stops and reverses direction when the cabins arrive at the end stations. Aerial tramways differ from gondola lifts in that gondola lifts are considered continuous systems (cabins attached onto a circulating haul rope that moves continuously).[2]
Two-car tramways use a jig-back system: A large electric motor is located at the bottom of the tramway so that it effectively pulls one cabin down, using that cabin's weight to help pull the other cabin up. A similar system of cables is used in a funicular railway. The two passenger cabins, which carry from 4 to over 150 people, are situated at opposite ends of the loops of cable. Thus, while one is coming up, the other is going down the mountain, and they pass each other midway on the cable span.
Some aerial trams have only one cabin, which lends itself better for systems with small elevation changes along the cable run.
History
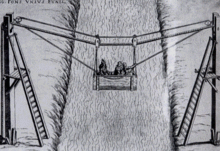
The World's first design for an aerial lift was by Croatian polymath Fausto Veranzio who designed a bicable passenger ropeway in 1616. Its closest relatives are the aerial tramway and the gondola lift.
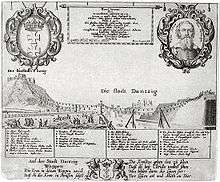
The first operational aerial tram was built in 1644 by Adam Wiebe in Gdańsk. It was moved by horses and used to move soil over the river to build defences.[3][3] It is called the first known cable lift in European history and precedes the invention of steel cables. It is not known how long this lift was used. In any case, it would be another 230 years before Germany would get the second cable lift, this newer version equipped with iron wire cable.[4] Other mining systems were developed in the 1860s by Hodgson, and Andrew Smith Hallidie. Hallidie went on to perfect a line of mining and people tramways after 1867 in California and Nevada. See Hallidie ropeway.
In mining

Cableway from abandoned coal mine in Adventdalen to Longyearbyen, Svalbard
Tramways are sometimes used in mountainous regions to carry ore from a mine located high on the mountain to an ore mill located at a lower elevation. Ore tramways were common in the early 20th century at the mines in North and South America. One can still be seen in the San Juan Mountains of the US state of Colorado. Over one thousand mining tramways were built around the world—Spitsbergen, Russia, Alaska, Argentina, New Zealand and Gabon. This experience was replicated with the use of tramways in the First World War particularly on the Isonzo Front in Italy. The German firm of Bleichert built hundreds of freight and military tramways. Strangely, Bleichert even built the first tourist tramway at Bolzano/Bozen, in then Tyrolian Austria in 1913.
Other firms entered the mining tramway business- Otto, Leschen, Breco Ropeways Ltd., Ceretti and Tanfani, and Riblet for instance. A major British contributor was Bullivant who became a constituent of British Ropes in 1924.[5][6] The perfection of the aerial tramway through mining lead to its application in other fields including logging, sugar fields, beet farming, tea plantations, coffee beans and guano mining. A resource on the history of aerial tramways in the mining industry is "Riding the High Wire, Aerial Mine Tramways in the West"
Moving people
In the beginning of the 20th century the rise of the middle class and the leisure industry allowed for investment in sight seeing machines. Prior to 1893 a combined goods and passenger carrying cableway was installed at Gibraltar. Initially its passengers were military personnel. An 1893 industry publication said of a two-mile system in Hong Kong that it "is the only wire tramway which has been erected exclusively for the carriage of individuals" (albeit workmen) Going to the Isle of Dogs by Lesser Columbus, Bullivant & Co. 1893 page 10. This item can be accessed through an original held by the North of England Institute of Mining and Mechanical Engineers. After the pioneer cable car of 1907 at mount Ulia[7][8][9][10] (San Sebastián, Spain) by Torres Quevedo others to the top of high peaks in the Alps of Austria, Germany and Switzerland resulted. They were much cheaper to build than the earlier rack railway. One of the first trams was at Chamonix, while others in Switzerland and Garmisch soon followed. From this, it was a natural transposition to build ski lifts and chairlifts. The first cable car in North America was at Cannon Mountain in Franconia, New Hampshire in 1938.[11] After the Second World War installations proliferated in Europe, America, Japan, Canada and South Africa. Many hundreds of installations have emerged in mountainous and seascape areas.
The aerial tram evolves again in latter decades—one tram in Costa Rica was built to move tourists above a rainforest, while one in Portland, Oregon, was built to move commuters. Presently, the mining role of tramways has lessened, though some still work, and moving people remains a starring role for the device.
Many aerial tramways were built by Von Roll Ltd. of Switzerland, which has since been acquired by Austrian lift manufacturer Doppelmayr. Other German, Swiss, and Austrian firms played an important role in the cable car business: Bleichert, Heckel, Pohlig, PHB (Pohlig-Heckel-Bleichert), Garaventa and Waagner-Biró (highest tower in the world: 113,6m). Now there are three groups dominating the world market: Doppelmayr Garaventa Group, Leitner Group, and Poma, the last two being owned by one person.
An escape aerial tramway is a special form of the aerial tramway that allows a fast escape from a dangerous location. They are used on rocket launching sites to offer the launch staff or astronauts a fast retreat. The tramway consists of a rope which runs from the launch tower downward to a protection shelter. On the launch supply tower several small cabs can be occupied by the launch staff or the astronauts. After a barrier is loosened these roll downward to the protection shelter. An escape aerial tramway exists on launch pads 39A and 39B at Cape Canaveral.
Some aerial tramways have their own propulsion, such as the Lasso Mule or the Josef Mountain Aerial Tramway near Merano, Italy.
Urban transport

While typically used for ski resorts, aerial tramways have been ported over for usage in the urban environment in recent times. The Roosevelt Island Tramway in New York City and the Portland Aerial Tram are examples where this technology has been successfully adapted for public transport purposes. In comparison to gondola lifts, aerial tramways provide lower line capacities, higher wait times and are unable to turn corners.[12]
Telpherage
One interesting offshoot of the aerial tram was the telpher system. This was an overhead railway, which was electrically powered. The carrier basket had a motor and two contacts on two rails. They were primarily used in English railway and postal stations. The original version was called telpherage. Smaller telpherage systems are sometimes used to transport objects such as tools or mail within a building or factory.
The telpherage concept was first publicised in 1883 and several experimental lines were constructed. It was not designed to compete with railways, but with horses and carts.[13]
The first commercial telpherage line was in Glynde, which is in Sussex, England. It was built to connect a newly opened clay pit to the local railway station and opened in 1885.[13]
Double deckers
There are aerial tramways with double deck cabins. The Vanoise Express cable car carries 200 people in each cabin at a height of 380 m (1,247 ft) over the Ponturin gorge in France. The Shinhotaka Ropeway carries 121 people in each cabin at Mount Hotaka in Japan. The CabriO cable car to the summit of the Stanserhorn in Switzerland carries 60 persons, with the upper floor accommodating 30 people in the open air.[14]
-
Pylon of Stanserhornbahn
-
Stanserhornbahn CabriO gondola entering mountain station
Records

- First – Adam Wybe construction in Gdańsk (1644). It was the first rope railway with many supports and the biggest built until the end of 19th century.
- Longest (at time of building) and years operated:
- 35 km (22 mi) 1906–1927 Chilecito – Mina La Mejicana, Argentina (34.3 km or 21.3 mi and 0.86 km or 0.53 mi branch).
- 39 km (24 mi) 1925–1950 Dúrcal – Motril, Spain (33.4 km or 20.8 mi and 5.5 km or 3.4 mi branch).
- 75 km (47 mi) 1937–1941 Asmara – Massawa, Eritrea (71.8 km or 44.6 mi and 3 km or 1.9 mi branch), technically a Funifor.[15]
- 96 km (60 mi) 1943–1987 Kristineberg-Boliden, Sweden. 13.2 km (8.2 mi) still working as Norsjö aerial ropeway.[16]
- Second longest:
- 76 km (47 mi) 1959–1986 Moanda – Mbinda, Gabon – Republic of Congo.
- Longest over water:
- 1.0 km (0.62 mi) 1906 – the same century; Thio, New Caledonia. ship loading.
- 2.4 km (1.5 mi) 1941–2006 Forsby-Köping limestone cableway, Sweden. crossing of Hjälmaren strait. 42 km system.[17]
- 3.0 km (1.9 mi) 2007 Nha Trang City - Vinpearl Land, Hon Tre Island, Vietnam. Total length 3.3 km.[18]
- Longest currently operational:
- 13.2 km (8.2 mi) Norsjö aerial tramway Mensträsk-Bjurfors in Norsjö, Sweden. Passenger tramway, a section of the former 96-km Kristineberg-Boliden industrial ropeway.
- 5.7 km (3.5 mi) Wings of Tatev, Armenia, the world's longest reversible cable car line of one section.[19]
- 4.94 km (3.07 mi) Medeu-Shimbulak tramway near Almaty, Kazakhstan.
- 4.35 km (2.70 mi) Sandia Peak Tramway, reversible tramway in Albuquerque, New Mexico.
- Highest lift: 3,374 m (11,070 ft) from 1,074 to 4,448 m (3,524 to 14,593 ft) at Chilecito – Mina La Mejicana, Argentina (drops back to 4,404 m or 14,449 ft at upper terminal).
- Highest station:
- Greater than 5,874 m (19,272 ft) 1935-19?? Aucanquilcha, Chile.
- Lowest station:
- 257 m (843 ft) below sea level Masada cableway, Israel.
- Tallest support tower:
- 113.6 m (372.7 ft) Gletscherbahn Kaprun, Austria.
- As mass transit:
- The Roosevelt Island Tramway in New York City was the first aerial tramway in North America used by commuters as a mode of mass transit (See Transportation in New York City). Passengers pay with the same farecard used for the New York City Subway.
- The Portland Aerial Tram in Portland, Oregon was opened in January 2007 and became the second public transportation aerial tramway in North America.
- In Medellin, Colombia, both the Metro and the recent Metrocable aerial tramway addition can be used while paying a single fare.
- Largest rotating cars:
List of accidents
Despite the introduction of various safety measures (back-up power generators, evacuation plans, etc.) there have been several serious incidents on aerial tramways, some of which were fatal.
- August 29, 1961: A military plane split the hauling cable of the Vallee Blanche Aerial Tramway on the Aiguille du Midi in the Mont Blanc massif: six people killed.
- March 9, 1976: In the Italian Dolomites at Cavalese, a cab fell after a rope break, killing 43. (See Cavalese cable car disaster (1976))
- April 15, 1978: In a storm, two carrying ropes of the Squaw Valley Aerial Tramway in California fell from the aerial tramway support tower. One of the ropes partly destroyed the cabin. 4 killed, 32 injured.
- June 1, 1990: Tbilisi, Georgia. After the hauling rope broke, the lower car rolled back and slammed on the wall of the lower station injuring people. The upper car subsequently rolled down, generating higher speed due to a failure of the brakes; on reaching the lower cable car support mast, it collided with the broken hauling rope which tore the cabin apart and caused people to fall from a height of 20 meters onto rooftops and ground. 20 killed[20] and many injured after jumping from accelerating cabin. Most of them were children celebrating "Children's day". Year before, the cable car went under major reconstruction also standard Soviet gondolas were changed to bigger ones brought from Finland without any precautions. (See 1990 Tbilisi aerial tramway accident)
- February 3, 1998: U.S. military aircraft severed the cable of an aerial ropeway in Cavalese, Italy, killing 20 people. (See Cavalese cable car disaster (1998))
- July 1, 1999: Saint-Étienne-en-Dévoluy, France. An aerial tramway car detached from the cable it was traveling on and fell 80 metres (260 ft) to the valley floor, killing all 20 occupants. The majority were employees and contractors of an international astronomical observatory run by the Institut de Radioastronomie Millémétrique. (See Saint-Étienne-en-Dévoluy cable car disaster)
- October 19, 2003: Four were killed and 11 injured when three cars slipped off the cable of the Darjeeling Ropeway.
- October 9, 2004: Crash of a cabin of the Grünberg aerial tramway in Gmunden, Austria. Many hurt.
- April 18, 2006: New York's Roosevelt Island Tramway experienced a power failure, leaving 69 passengers in two trams stranded over the East River for approximately seven hours, just eight months after a similar incident in which trams were stranded for 90 minutes. No injuries or fatalities occurred in either incident.
- December 31, 2012: The Alyeska Resort Aerial Tramway was blown sideways while operating in high winds and was impaled on the tower guide, severely damaging the contacting cabin. Only minor injuries were incurred.
Gallery
|
Cableways in fiction
- Blind Fury
- Where Eagles Dare
- On Her Majesty's Secret Service (film)
- Moonraker (film)
- Night Train to Munich
- "Ascension"
- Hoodwinked!
- Get Carter – coal spoil conveyor Blackhall Beach near Blackhall Colliery
- Kongfrontation
See also
References
- ↑ "Aerial Technologies, Lesson 5: Aerial Trams « The Gondola Project". Gondolaproject.com. Retrieved 2016-01-02.
- ↑ Edward S. Neumann. "Cable Propelled Systems in Urban Environments" (PDF). Adr.coalliance.org. Retrieved 2015-01-02.
- 1 2 "Adam Wijbe-Galeria Wielkich Zapomnianych-Wydział Postaciologii". Rzygacz.webd.pl. Retrieved 2016-01-02.
- ↑ "Cable lift pioneer from Harlingen built Gdansk bastion and dikes » The Windmill news articles". goDutch. Retrieved 2016-01-02.
- ↑ "File:Gibraltar Aerial Railway equipped by Bullivant in Going to the Isle of Dogs Tracts vol 9 p255.jpg - Wikimedia Commons". Commons.wikimedia.org. Retrieved 2016-01-02.
- ↑ Archived December 13, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Un transbordador pionero 1907.". Diariovasco.com. 1997-12-01.
- ↑ "Ulia (Donostia-San Sebastian)". Ingeba.org.
- ↑ "Blog Archive » Ferrocarril del Monte Ulia – San Sebastián". Spanish Railway.
- ↑ "Teleférico - Casiopea". Wiki.ead.pucv.cl (in Spanish). 2011-06-03.
- ↑ Archived July 2, 2015, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Basic Lesson 3: Aerial Trams & Funiculars « The Gondola Project". Gondolaproject.com. Retrieved 2016-01-02.
- 1 2 Lusted, A., 1985: The Electric Telpherage Railway. Glynde Archivist 2:16–28.
- ↑ "Switzerland launches the world's first Cabrio aerial cableway". Swisstravelsystem.com. Retrieved 2016-01-02.
- ↑ "La Teleferica Massaua-Asmara". Trainweb.org. Retrieved 2016-01-02.
- ↑ Widén, E. G. A. (1943). The ropeway Kristineberg-Boliden : A record ropeway construction. Stockholm: Nordströms linbanor.
- ↑ "Linbanan Forsby - Köping". Privat.bahnhof.se. Retrieved 2016-01-02.
- ↑ Archived March 30, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "World's longest cable car line opens to Armenia". Physorg.com. Retrieved 2016-01-02.
- ↑ "CNN - Major worldwide cable car accidents since 1976 - July 1, 1999". Edition.cnn.com. Retrieved 2016-01-02.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aerial tramway. |
- Aerial Tramways (worldwide) Lift-Database
- Information Center for Ropeway Studies at Colorado School of Mines
- Tatever ropeway - is the aerial ropeway to the natural and historic treasures of Syunik.