Algiers Metro
 | |
|
Tafourah - Grande Poste station | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Native name |
مترو الجزائر العاصمة Métro d'Alger |
| Locale | Algiers, Algeria |
| Transit type | Rapid transit |
| Number of lines |
1[1] (2 planned)[2] |
| Number of stations | 14[1] |
| Annual ridership | 16,000,000 (2014)[3] |
| Website |
www |
| Operation | |
| Began operation | 1 November 2011[2] |
| Operator(s) | RATP El-Djazaïr (FR) |
| Technical | |
| System length | 13.5 km (8.4 mi)[4] |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge |
| Electrification | N/A |
The Algiers Metro (Arabic: مترو الجزائر العاصمة, French: Métro d'Alger), serving Algiers, the capital of Algeria, is a transport project dating from the 1970s that was designed to address the need for mass transport caused by the city's growth. Formally launched in the 1980s, the project slowed down due to financial difficulties and security issues in the 1990s. The project recommenced in 2003. Algerian President Abdelaziz Bouteflika attended the Metro's 31 October ribbon-cutting opening ceremony.[1][2] The Algiers Metro then opened to passengers on the following day, 1 November 2011,[2] making Algiers only the second capital city in Africa (after Cairo) to have a metro system.[5]
The first phase of Line 1, "Haï el Badr"–"Tafourah-Central Post Office", which spanned 9.2 kilometres (5.7 mi) and 10 stations, opened for public service on 1 November 2011.[1] A 4-kilometre (2.5 mi) extension from "Haï el Badr" to "El Harrach Centre" opened for commercial service on 4 July 2015 after test runs in June.[6][7]
History
During the 1970s, the promoters of the Algiers rapid transit subway project envisioned a 64 km (40 mi) network. The project was officially inaugurated in 1982, with technical studies completed in 1985. Authorities retained a German company and a Japanese specialist for building the network. The collapse of oil prices in the 1980s considerably affected the Algerian state's ability to continue funding the project. Authorities discussed the possibility of folding the subway development programme into other mass-transit projects but eventually decided to continue with the original Metro program, albeit slowly.
In 1988, Algeria awarded construction contracts to two national companies COSIDER and GENISIDER. Neither was experienced in running large urban transit development projects. Construction encountered financial and political difficulties, with only four stations constructed in 15 years. Moreover, the Algiers soil is difficult to dig in, and the city's topography is irregular. Work did not advance significantly for many years.
In 1994, a first 450 m long section, called Emir-Abdelkader, was completed. Another 650 m section, connecting the Central Post Office to Khélifa-Boukhalfa, was completed soon after. In 1999, the Metro of Algiers Company (EMA) invited international companies to participate in a tender offering, resulting in two new contractors being added to the project: French Systra-Sgte for project management, and Agéro-German GAAMA for construction and completion, within 38 months, of the civil engineering tasks and earthworks.
In 2003, benefiting from the return of economic stability and improved security, the government increased funding and introduced a new organizational and operational structure.
In January 2006, further changes were introduced to the project, with integral system development handed to Siemens Transportation Systems. This included the installation of gixed material, signals and electrification. Vinci was responsible for civil engineering, and the Spanish company Construcciones y Auxiliar de Ferrocarriles (CAF) was to deliver a new set of rolling stock, including 14 trains of 6 cars each. The network would use the Trainguard MT CBTC technology, which had already been implemented on line 1 and 14 of the Paris Métro.
System
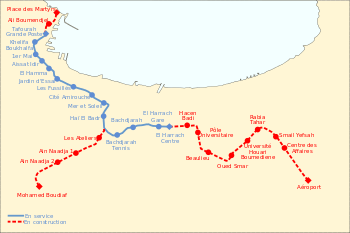
With a length of 9.2 kilometres (5.7 mi), the first section of Line 1 to open included ten stations, connecting Tafourah–Grande Poste to Haï El Badr.[1] Nine of the ten stations are underground with two central tracks flanked by two 115 metres (377 ft) long side platforms. Only the Haï El Badr terminus station is on the surface and it has three tracks and two island platforms.
- The El Hamma - Haï El Badr section, with its 4 stations and 17 other works for ventilation and cables was carried out within 38 months. Civil engineering work and rail laying were officially completed on 30 June 2007.
- The installation and the welding of 23 kilometres (14 mi) of tracks was started in April 2007 by the French company South-western Travaux France (TSO) with the first metro car to be delivered to Algiers by December 2007.
In July 2015, this was supplemented by the opening of the 4-kilometre (2.5 mi), four-station expansion from "Haï el Badr" to "El Harrach Centre". The system now serves 14 stations, over a total route length of approximately 13.5 kilometres (8.4 mi).
Stations
| Name | Community | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Place des Martyrs | Kasbah | Under construction |
| Ali Boumendjel | Alger Centre | Under construction |
| Tafourah - Grande Poste | Alger Centre | |
| Khelifa Boukhalfa | Alger Centre | |
| 1er Mai | Sidi M'Hamed | |
| Aïssat Idir | Sidi M'Hamed | |
| Hamma | Belouizdad | |
| Jardin d'essai | Belouizdad | |
| Les Fusillés | Hussein Dey | |
| Cité Amirouche | Hussein Dey | |
| Cité Mer et Soleil | Hussein Dey | |
| Haï El Badr | El Magharia | |
| Bachdjarah - Tennis | Bachdjerrah | |
| Bachdjarah | Bachdjerrah / Bourouba | |
| El Harrach Gare | Bourouba | |
| El Harrach Centre | El Harrach |
Operations

The total cost of the first phase of line 1 rose to 77 billion DZD (900 million euros), consisting of DZD 30 billion for civil engineering and DZD 47 billion for the equipment.
- 14 six-car trains are being used. Each car is 108m in length with 208 seats and can transport 1,216 people.
- The metro line can move 41,000 passengers per hour, the equivalent of 150 million passengers per year, with a headway of under 2 minutes. Trains can travel at speeds of up to 70 km/h, and the line is open from 5 a.m. to 11 p.m.
- The metro's daily operation is the responsibility of the RATP, which was awarded the contract in August 2007.
Extensions
Invitations to tender were launched for the construction of a 4 km section between Bachdjarrah and El Harrach composed of 4 stations and one viaduct of 250 m above the access road to the Ouchaïah Wadi motorway. It is opened for public service on 4 July 2015.[6][7]
- The Gaama group which carried out the first section quoted 250 million euros including the construction of a multimodal station (subway/train/taxis) at the El Harrach railway station.
Two other extensions to Line 1 are now under construction, with an planned public opening in 2017:[7]
- a branch line from Haï El Badr to Aïn Naâdja".
- a extension north from Tafourah Grande Poste to Place des Martyrs
Construction of Line 2 has also begun.
See also
- Template:Suburban railways in Africa
- Algiers Tram
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Alger metro inaugurated". Railway Gazette International. 31 October 2011. Retrieved 2013-09-14.
- 1 2 3 4 "Maghreb's first metro system opens in Algeria". Radio France International. 31 October 2011. Retrieved 2013-09-14.
- ↑ http://www.ratp.fr/fr/upload/docs/application/pdf/2015-07/cp_groupe_ratp_prolongement_metro_alger.pdf
- ↑ Robert Schwandl. "Algiers . Al Jaza'Ir". UrbanRail.net. Retrieved 2015-08-06.
- ↑ "Metro systems: Going Underground". The Economist. 5 January 2013. Retrieved 2013-09-14.
- 1 2 "Algiers Metro: New line Hai El Badr-El Harrach operational in July". Algeria Press Service. 14 June 2015. Retrieved 2015-08-06.
- 1 2 3 "Alger metro extends". Railway Gazette International. 6 July 2015. Retrieved 2015-08-07.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Metro Algiers. |
- Interactive Algiers Metro Map
- Algiers Metro
- L'Etablissement de Transport Urbain et Suburbain d’Alger (ETUSA)
- Siemens Transportation Systems - Algiers Metro
- Subways.net Algiers Metro