Ammonium aluminium sulfate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Aluminium ammonium bis(sulfate) | |
| Other names
Ammonium alum Tschermigite | |
| Identifiers | |
| 7784-25-0 7784-26-1 (dodecahydrate) | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 2297489 56419 (dodecahydrate) |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.141 |
| EC Number | 232-055-3 |
| E number | E523 (acidity regulators, ...) |
| RTECS number | WS5640010 |
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
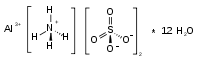
| (NH4)Al(SO4)2 | |
| Molar mass | 237.15 g/mol (anhydrous) 453.33 g/mol (dodecahydrate) |
| Appearance | white crystals |
| Density | 2.45 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 1.64 g/cm3 (dodecahydrate) |
| Melting point | 93.5 °C (200.3 °F; 366.6 K) (dodecahydrate) |
| Boiling point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) dehydr. (dodecahydrate) |
| 15 g/100 ml (20 °C, dodecahydrate) | |
| Structure[1] | |
| Hexagonal (anhydrous) Cubic (dodecahydrate) | |
| Octahedral (Al3+) | |
| Hazards[2] | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | WARNING |
| H315, H319 | |
| P264, P280, P302+352, P305+351+338, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362 | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Ammonium aluminium sulfate, also known as ammonium alum or just alum, is a white crystalline double sulfate usually encountered as the dodecahydrate, formula (NH4)Al(SO4)2·12H2O. It is used in small amounts in a variety of niche applications. The dodecahydrate occurs naturally as the rare mineral tschermigite.[1]
Production and basic properties
Ammonium alum is made from aluminium hydroxide, sulfuric acid and ammonium sulfate. It forms a solid solution with potassium alum. Pyrolysis leaves alumina. Such alumina is used in the production of grinding powders and as precursors to synthetic gems.[3]
Uses
Ammonium alum is not a major industrial chemical or a particularly useful laboratory reagent, but it is inexpensive and nontoxic, which invites many niche applications. It is used in water purification, in vegetable glues, in porcelain cements, in deodorants and in tanning, dyeing and in fireproofing textiles.[4] The pH of the solution resulting from the topical application of ammonium alum with perspiration is typically in the slightly acid range, from 4 to 5.[5]
Ammonium alum is a common ingredient in animal repellant sprays.[6][7][8]
Toxicology
Aluminium sulfate, closely related to ammonium alum, is nontoxic with an LD50 of 6207 mg/kg. No human or ecological (for reduced concentrations) toxicity registered.[9]
References
- 1 2 3 Weast, Robert C., ed. (1981). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (62nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. pp. B–74, B–75. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8..
- ↑ HSNO Chemical Classification Information Database, New Zealand Environmental Risk Management Authority, retrieved 2009-11-23.
- ↑ Otto Helmboldt, L. Keith Hudson, Chanakya Misra, Karl Wefers, Wolfgang Heck, Hans Stark, Max Danner, Norbert Rösch "Aluminum Compounds, Inorganic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2007, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_527.pub2
- ↑ "Alum", The Columbia Encyclopedia (6th ed.), Ithaca, NY: Columbia University Press, 2004, retrieved 2009-11-23.
- ↑ Aluminum Ammonium Sulfate Material Safety Data Sheet, J. T. Baker, March 2009, retrieved 2009-11-23.
- ↑ D-TER Animal and Bird Repellent, Bruce Harris Project Management Pty Ltd, 2004-09-04, retrieved 2010-03-03.
- ↑ Multicrop Scat Bird and Animal Repellent Data Sheet (PDF), Multicrop (Aust.) Pty. Ltd., 2003-03-04, retrieved 2010-03-03.
- ↑ Pest Control: Foxes, Tandridge District Council (UK), February 2006, retrieved 2010-03-03.
- ↑ "Ammonium alum", PAN Pesticide Database, Pesticides Action Network, retrieved 2009-11-23.