Ammonium formate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ammonium formate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 540-69-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 10442 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.959 |
| PubChem | 2723923 |
| RTECS number | BQ6650000 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH5NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 63.06 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White monoclinic crystals, deliquescent |
| Odor | Slightly ammoniac |
| Density | 1.26 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 116 °C (241 °F; 389 K) |
| Boiling point | 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) decomposes[2] |
| (grams per 100g of water)102g(0 °C) 142.7 g (20 °C) 202.4 g (40 °C) 516 g (80 °C)[2] | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in liquid ammonia, alcohol, diethyl ether[2] |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−556.18 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | JT Baker MSDS |
| GHS pictograms |  [1] [1] |
| GHS signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335[1] | |
| P261, P305+351+338[1] | |
| EU classification (DSD) |
|
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26, S36 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
410 mg/kg (mice, intravenous)[2] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Ammonium formate, NH4HCO2, is the ammonium salt of formic acid. It is a colorless, hygroscopic, crystalline solid.
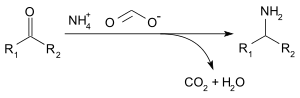
Reductive amination
Acetone can be transformed into isopropylamine as follows:
CH3C(O)CH3 + 2HC(O)O− +NH4 --> (CH3)2CHNHCH(O) + 2H2O + NH3 + CO2
(CH3)2CHNHCH(O) + H2O --> (CH3)CHNH2 + HC(O)OH
Uses
Pure ammonium formate decomposes into formamide and water when heated, and this is its primary use in industry. Formic acid can also be obtained by reacting ammonium formate with a dilute acid, and since ammonium formate is also produced from formic acid, it can serve as a way of storing formic acid.
Ammonium formate can also be used in palladium on carbon (Pd/C) reduction of functional groups. In the presence of Pd/C, ammonium formate decomposes to hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and ammonia. This hydrogen gas is adsorbed onto the surface of the palladium metal, where it can react with various functional groups. For example, alkenes can be reduced to alkanes, or formaldehyde to methanol. Activated single bonds to heteroatoms can also be replaced by hydrogens (hydrogenolysis).
Ammonium formate can be used for reductive amination of aldehydes and ketones (Leuckart reaction), by the following reaction:[3]
Ammonium formate can be used as a buffer in high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and is suitable for use with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC/MS). The pKa values of formic acid and the ammonium ion are 3.8 and 9.2, respectively.
Reactions
When heated, ammonium formate eliminates water, forming formamide. Upon further heating, it forms hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and water. A side reaction of this is the decomposition of formamide to carbon monoxide (CO) and ammonia.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ammonium formate. Retrieved on 2014-06-10.
- 1 2 3 4 http://chemister.ru/Database/properties-en.php?dbid=1&id=1071
- ↑ Alexander, Elliot; Ruth Bowman Wildman (1948). "Studies on the Mechanism of the Leuckart Reaction". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 70: 1187–1189. doi:10.1021/ja01183a091.
External links
![]() Media related to Ammonium formate at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ammonium formate at Wikimedia Commons