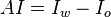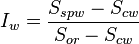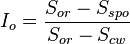Amott test
The Amott test is one of the most widely used empirical wettability measurements for reservoir cores in petroleum engineering. The method combines two spontaneous imbibition measurements and two forced displacement measurements. This test defines two different indices: the Amott water index (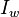 ) and the Amott oil index (
) and the Amott oil index (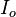 ).
).
Amott–Harvey index
The two Amott indices are often combined to give the Amott–Harvey index. It is a number between -1 and 1 describing wettability of a rock in drainage processes. It is defined as:

These two indices are obtained from special core analysis (SCAL) experiments (porous plate or centrifuge) by plotting the capillary pressure curve as a function of the water saturation as shown on figure 1:
with 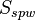 is the water saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the imbibition process,
is the water saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the imbibition process, 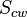 is the irreducible water saturation and
is the irreducible water saturation and 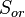 is the residual oil saturation after imbibition.
is the residual oil saturation after imbibition.
with 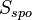 is the oil saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the secondary drainage process,
is the oil saturation for a zero capillary pressure during the secondary drainage process, 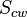 is the irreducible water saturation and
is the irreducible water saturation and 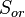 is the residual non-wetting phase saturation after imbibition.
is the residual non-wetting phase saturation after imbibition.
A rock is defined as:
- Water wet when the Amott–Harvey index is between 0.3 and 1,
- Weakly water wet when the Amott–Harvey index is between 0 and 0.3,
- Weakly oil wet when the Amott–Harvey index is between -0.3 and 0,
- Oil wet when the Amott–Harvey index is between -1 and -0.3.
See also
- USBM index - an alternative wettability index
- Rise In Core - An alternate Reservoir Wettability Characterization Method
- Relative permeability
- Multiphase flow
- Capillary pressure
- Leverett J-function
- Imbibition
External links
- http://www.jgmaas.com/scores/facts.html
- https://www.slb.com/~/media/Files/resources/oilfield_review/ors07/sum07/p44_61.pdf
- http://perminc.com/resources/fundamentals-of-fluid-flow-in-porous-media/chapter-2-the-porous-medium/multi-phase-saturated-rock-properties/wettability/laboratory-determination-wettability/
References
- Dake, L.P., "Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering", Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam, 1977.
- Amott, E., "Observations relating to the wettability of porous rock", Trans. AIME 219, pp. 156–162, 1959.