Angina bullosa haemorrhagica
| Angina bullosa haemorrhagica | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
| DiseasesDB | 32589 |
| eMedicine | article/1078960 |
Angina bullosa haemorrhagica (ABH) is a condition of the mucous membranes characterized by the sudden appearance of one or more blood blisters within the oral cavity.[1]:808 The lesions, which may be caused by mild trauma to the mouth tissues such as hot foods, typically rupture quickly and heal without scarring or further discomfort.[2] The condition is not serious except in rare cases where a large bulla that does not rupture spontaneously may cause airway obstruction.
The blisters usually affect the palate or oropharynx and are often long lived to the extent that patients burst them for symptomatic relief.[3]
.jpg)
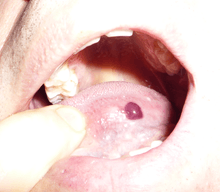
Diagnosis
The condition is diagnosed on the basis of exclusion of other conditions and the typical presentation, particularly the constant presence of blood as the blister fluid. Angina bullosa haemorrhagica does not cause desquamative gingivitis[3]