Aortic sinus
| Aortic sinus | |
|---|---|
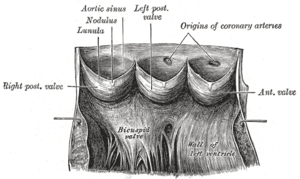 Aorta laid open to show the semilunar valves. (N.B. captions don't align with current terminology) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sinus aortae |
| TA | A12.2.03.002 |
| FMA | 3745 |
An aortic sinus is one of the anatomic dilations of the ascending aorta, which occurs just above the aortic valve. These widenings are between the wall of the aorta and each of the three cusps of the aortic valve.[1]
There are generally three aortic sinuses: the left, the right and the posterior sinuses:
- The left aortic sinus gives rise to the left coronary artery.
- The right aortic sinus gives rise to the right coronary artery.
- Usually, no vessels arise from the posterior aortic sinus, which is therefore known as the non-coronary sinus.
Each aortic sinus can also be referred to as the sinus of Valsalva, the sinus of Morgagni, the sinus of Mehta, the sinus of Otto, or Petit's sinus.
See also
References
External links
- Anatomy photo:20:29-0108 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Heart: The Aortic Valve and Aortic Sinuses"
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/6/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.