Instituto Antártico Argentino
 IAA emblem | |
| Abbreviation | IAA |
|---|---|
| Formation | 1962 |
| Legal status | Government Organisation |
Region served |
|
| Website |
www |
The Instituto Antártico Argentino (IAA; English: Argentine Antarctic Institute ) is the Argentine federal agency in charge of orientating, controlling, addressing and performing scientific and technical research and studies in the Antarctic.[1]
Known as Argentine Antarctica (Spanish: Antártida Argentina) the country claimed a sector as part of its national territory consisting of the Antarctic Peninsula and a triangular section extending to the South Pole, is delimited by the 25° West and 74° West meridians and the 60° South parallel.[2] Administratively, Argentine Antarctica is a department of the province of Tierra del Fuego, Antarctica, and South Atlantic Islands.
This sector overlaps with Chilean and British claims but, under the Antarctic Treaty System, there are no attempts by Argentina or any other country to actually enforce territorial claims in Antarctica.
Mission
According to the principles of its creation, the Instituto Antártico Argentino participates with its scientific, technical and administrative staff, in a wide range of national and international programmes for a better understanding of the Antarctic. Scientists are trained and deployed on Argentine bases for researching on different fields of science, including Atmosphere, Biology, Oceanography, Weather, Chemistry, Ozone Layer, Global warming and CO2.
History
First years


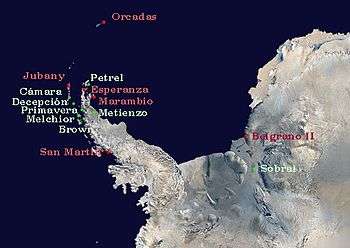
José María Sobral, who is considered in Argentina the father of the Argentine Antarctica and a national hero, began exploration at the end of 1901. In 1903, the Argentine Navy corvette ARA Uruguay commanded by Captain de Corbeta (Lieutenant commander) Julián Irízar successfully rescued the Swedish expedition team of Otto Nordenskjöld. In 1904 the Argentine permanent presence in Antarctica began with the opening of Orcadas Base on Laurie Island. Argentina was the only nation to have an Antarctic base for 40 years until the British built a base on the same islands.
Expansion
On April 1, 1940, the first radio communication by radio hams was made between Orcadas Base (LSX) and Buenos Aires (LU 7 ET).
On February 7, 1942, an amphibious Stearman aircraft embarked on the ARA 1 de Mayo cargo ship made the first Argentine flight over Antarctica.
On December 13, 1947 an Argentine Naval Aviation Douglas DC-4 piloted by Comodoro Gregorio Portillo flew over the Antarctic Circle in a 15 hours and 30 minutes flight.
On 17 April 1951 the Instituto Antartico Argentino is created by Decree Nº 7338
In 1953 the San Martín Base started operations, and Jubany base opened two years later.
In 1958 the United States handed over the Ellsworth Station located in the Weddell Sea.
In 1965 the Argentine military conducted a land military manoeuvre known as Operación 90 in order to reach the South Pole.
In the winter of 1968 at the request by the British embassy in Buenos Aires, an Argentine Navy Douglas DC-4 successfully delivered medical supplies to the British base EFE where one of its members, James K. Portwirie, was through a medical emergency. However, after a few days, Portwirie's situation worsened, making a rescue necessary. An Argentine Air Force aircraft attempted to reach the base but crashed without casualties. On August 9, in the middle of the Antarctic winter, the Argentine Navy icebreaker ARA General San Martín was sent to rescue Portwirie. The operation was successful, gaining the thanks of the British Antarctic Survey: ‘‘an internal campaign like this was never attempted before in Antarctic History‘‘.[3]
Marambio Base was founded in 1969, currently the most important Argentine base on the Antarctica. In 1975 the Esperanza Base was built, and in 1979 the General Belgrano II. In 1978, the first Antarctic baby, Emilio Palma, was born in the Fortín Sargento Cabral at the Esperanza Base.
Modern years

In 2002, the Argentine Navy mounted an internal operation sending Icebreaker ARA Almirante Irizar to rescue the trapped supply vessel Magdalena Oldendorff. Even though Irízar failed to break the Oldendorff free, she managed to move it to a safe position and re-supply the ship with food, medicines and medical personnel until the ice melted and the ship could return to open sea.
In 2003, under the Decree Nº 207/2003 issued by the Executive Power of Argentina, the Instituto Antártico Argentino became a part of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs
On the 2009 summer campaign, the Argentine Air Force operated the Teniente Matienzo Base only with women for three months [4][5] although there was an emergency link available with the Bell 212s helicopters stationed at Marambio Base
On 2010 a Wind generator designed and built by Argentine government company CITEDEF was installed on Marambio Base [6]
On 2011, three heavy lift helicopters were deployed in the Base Marambio: two Mil Mi 17 helicopters (bought in the same year), and the remaining Chinook from the Argentine Air Force.
References
- ↑ official site
- ↑ Beck, Peter J. (1986). The international politics of Antarctica. Routledge. p. 119. ISBN 0709932391.
- ↑ . Sir Vivian Fuchs, el vencedor del Polo Sur, dijo: "Ruego acepte nuestras sinceras gracias por el rescate del enfermo de nuestra estación en islas argentinas. Una campaña invernal de esta naturaleza resulta sin paralelo en la historia marítima Antártica'. (Despacho R.T de Director del British Antarctic Survey)
- ↑ Una base antártica exclusiva para mujeres
- ↑ Mujeres en la Antártida
- ↑ DEFENSA INSTALÓ UN GENERADOR DE ENERGÍA EÓLICA EN LA ANTÁRTIDA
- (Spanish) Argentine Antarctica History
- (Spanish) ARA San Martin Icebreaker
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Antártida Argentina. |
- (English) official site
- (Spanish) official site