Armstrong Siddeley Python
| Python | |
|---|---|
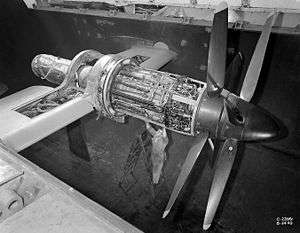 | |
| An Armstrong Siddeley Python during NACA wind tunnel testing in 1949 | |
| Type | Gas turbine turboprop |
| National origin | United Kingdom |
| Manufacturer | Armstrong Siddeley |
| First run | April 1945 |
| Major applications | Westland Wyvern |
| Developed from | Armstrong Siddeley ASX |
The Armstrong Siddeley Python was an early British turboprop engine designed and built by the Armstrong Siddeley company in the mid-1940s. Its main use was in the Westland Wyvern carrier-based heavy fighter. The prototypes had used the Rolls-Royce Eagle piston engine, but Pythons were used in production aircraft. In this application, the Python was rated at 4,110 eshp (equivalent shaft horsepower).
Design and development
The design started as an experimental pure-turbojet known as the ASX, which commenced testing in 1943. By this point other engine designs were already entering pre-production, and it seemed there was little need for the ASX in its existing form. The design was then modified by the addition of a reduction gearbox to drive a propeller. The turboprop thus formed was named ASP.[1]
Flight testing
Early flight-testing of the Python was carried out using the Lancaster B.1 (FE) TW911 and the Lincoln B.2 RE339/G: in each aircraft Pythons replaced the two outboard Rolls-Royce Merlins.
Lincoln B.2 RF403 had two Pythons similarly installed and was used for high-altitude bombing trials at Woomera, South Australia. These trials were principally of the ballistic casings for the Blue Danube atomic weapon: the Lincoln was the only available aircraft that could accommodate the large weapon casing, measuring 62 inches diameter x 24 feet (7.3 m) in length. The Pythons were fitted to increase the height from which tests could be carried out. Maximum release height and speed for the first eleven tests was 275 mph and 34,783 ft (10,602 m) with a bombing error of 61 ft.[2]
Applications
- Avro Lancaster - (test only)
- Avro Lincoln - (test only)
- Westland Wyvern
Specifications (ASP.3)
Data from Flight[3]
General characteristics
- Type: Turboprop
- Length: 123.2 in (3129 mm)
- Diameter: 54 in (1372 mm)
- Dry weight: 3,450 lb (1565 kg)
Components
- Compressor: axial flow; 14 stages
- Combustors: 11 combustion chambers
- Turbine: axial flow; two stages
Performance
- Maximum power output: 4,110 eshp (3,065 kW) at sea level at 8,000 rpm, including 1,180 lbf (535 kgf) exhaust thrust
- Overall pressure ratio: 5.35:1
- Air mass flow: 52.5 lb/sec (23.8 kg/s)
- Specific fuel consumption: 0.805 lb/hr/eshp
- Power-to-weight ratio: 1.2:1
See also
- Related development
- Related lists
References
Notes
- ↑ Gunston 1998, p.19.
- ↑ The National Archives, London, file ES 1/44 E4C Appendix 3 page 1.
- ↑ Flight Global Archive - 1954 www.flightglobal.com. Retrieved: 3 November 2008
Bibliography
- Gunston, Bill (1998). World encyclopaedia of aero engines : all major aircraft power plants, from the Wright brothers to the present day (4th ed.). Sparkford, Nr Yeovil, Somerset, [England]: P. Stephens. ISBN 978-1852605971.
- Gunston, Bill (1989). World Encyclopaedia of Aero Engines (2nd ed.). Cambridge, England: Patrick Stephens Limited. ISBN 978-1-85260-163-8.
- Bridgman, Leonard, ed. (1947). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1947. London: Sampson Low, Marston & Co. pp. 4d–5d.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Armstrong Siddeley Python. |
- Image of the Python-engined Lancaster B.Mk.I (FE) TW911
- "Python" a 1949 Flight article on the Python