Blood type distribution by country
ABO and distribution by country
| Country | Population[1] | O+ | A+ | B+ | AB+ | O− | A− | B− | AB− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
21,262,641 | 40.0% | 31.0% | 8.0% | 2.0% | 9.0% | 7.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% |
| |
8,210,281 | 30.0% | 33.0% | 12.0% | 6.0% | 7.0% | 8.0% | 3.0% | 1.0% |
| |
10,414,336 | 38.0% | 34.0% | 8.5% | 4.1% | 7.0% | 6.0% | 1.5% | 0.8% |
| |
198,739,269 | 36.0% | 34.0% | 8.0% | 2.5% | 9.0% | 8.0% | 2.0% | 0.5% |
| |
33,487,208 | 39.0% | 36.0% | 7.6% | 2.5% | 7.0% | 6.0% | 1.4% | 0.5% |
| |
1,339,724,852 | 47.7% | 27.8% | 18.9% | 5.0% | 0.3% | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.03% |
| |
10,532,770 | 27.0% | 36.0% | 15.0% | 7.0% | 5.0% | 6.0% | 3.0% | 1.0% |
| |
5,500,510 | 35.0% | 37.0% | 8.0% | 4.0% | 6.0% | 7.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% |
| |
1,315,819 | 29.5% | 30.8% | 20.7% | 6.3% | 4.3% | 4.5% | 3.0% | 0.9% |
| |
5,250,275 | 27.0% | 38.0% | 15.0% | 7.0% | 4.0% | 6.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% |
| |
66,821,000 | 36.0% | 37.0% | 9.0% | 3.0% | 6.0% | 7.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% |
| |
82,329,758 | 35.0% | 37.0% | 9.0% | 4.0% | 6.0% | 6.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% |
| |
306,694 | 47.6% | 26.4% | 9.3% | 1.6% | 8.4% | 4.6% | 1.7% | 0.4% |
| |
1,236,344,631 | 27.8% | 19.1% | 39.1% | 8.4% | 1.4% | 0.5% | 1.7% | 0.4% |
| |
4,203,200 | 47.0% | 26.0% | 9.0% | 2.0% | 8.0% | 5.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% |
| |
8,585,500 | 32.0% | 34.0% | 17.0% | 7.0% | 3.0% | 4.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% |
| |
127,368,088 | 29.9% | 39.8% | 19.9% | 9.9% | 0.15% | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.05% |
| |
73,000,000 | 36.6% | 32.8% | 21.0% | 9.0% | 0.4% | 0.2% | 0.09% | 0.03% |
| |
16,715,999 | 39.5% | 35.0% | 6.7% | 2.5% | 7.5% | 7.0% | 1.3% | 0.5% |
| |
4,213,418 | 38.0% | 32.0% | 9.0% | 3.0% | 9.0% | 6.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% |
| |
4,660,539 | 34.0% | 40.8% | 6.8% | 3.4% | 6.0% | 7.2% | 1.2% | 0.6% |
| |
99,863,000 | 44-46% | 22-23% | 24-25% | 4-6% | <1% | <1% | <1% | <1% |
| |
38,482,919 | 31.0% | 32.0% | 15.0% | 7.0% | 6.0% | 6.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% |
| |
10,707,924 | 36.2% | 39.8% | 6.6% | 2.9% | 6.0% | 6.6% | 1.1% | 0.5% |
| |
28,686,633 | 48.0% | 24.0% | 17.0% | 4.0% | 4.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% | 0.3% |
| |
49,320,000 | 39.0% | 32.0% | 12.0% | 3.0% | 7.0% | 5.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% |
| |
47,125,002 | 36.0% | 34.0% | 8.0% | 2.5% | 9.0% | 8.0% | 2.0% | 0.5% |
| |
9,059,651 | 32.0% | 37.0% | 10.0% | 5.0% | 6.0% | 7.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% |
| |
76,805,524 | 29.8% | 37.8% | 14.2% | 7.2% | 3.9% | 4.7% | 1.6% | 0.8% |
| |
61,113,205 | 37.0% | 35.0% | 8.0% | 3.0% | 7.0% | 7.0% | 2.0% | 1.0% |
| |
307,212,123 | 37.4% | 35.7% | 8.5% | 3.4% | 6.6% | 6.3% | 1.5% | 0.6% |
| Weighted mean | 2,744,996,114 | 41.9% | 31.2% | 15.4% | 4.8% | 2.9% | 2.7% | 0.8% | 0.3% |
50.0% and above 40.0–49.9% 30.0–39.9% 20.0–29.9% 10.0–19.9% 5.0–9.9%
| Ethnic distribution of ABO (without Rh) blood types[31] (This table has more entries than the table above but does not distinguish between Rh types.) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| People group | O (%) | A (%) | B (%) | AB (%) |
| Aboriginal people | 61 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| Abyssinians | 43 | 27 | 25 | 5 |
| Ainu (Japan) | 17 | 32 | 32 | 18 |
| Albanians | 38 | 43 | 13 | 6 |
| Grand Andamanese | 9 | 60 | 23 | 9 |
| Arabs | 34 | 31 | 29 | 6 |
| Armenians | 31 | 50 | 13 | 6 |
| Asian Americans | 40 | 28 | 27 | 5 |
| Austrians | 36 | 44 | 13 | 6 |
| Bantus | 46 | 30 | 19 | 5 |
| Basques | 51 | 44 | 4 | 1 |
| Belgians | 47 | 42 | 8 | 3 |
| Bororo (Brazil) | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Brazilians | 47 | 41 | 9 | 3 |
| Bulgarians | 32 | 44 | 15 | 8 |
| Burmese | 36 | 24 | 33 | 7 |
| Buryats (Siberia) | 33 | 21 | 38 | 8 |
| Bushmen | 56 | 34 | 9 | 2 |
| Chinese-Canton | 46 | 23 | 25 | 6 |
| Chinese-Peking | 29 | 27 | 32 | 13 |
| Chuvash | 30 | 29 | 33 | 7 |
| Croats | 42 | 34 | 17 | 7 |
| Czechs | 30 | 44 | 18 | 9 |
| Danes | 41 | 44 | 11 | 4 |
| Dutch | 45 | 43 | 9 | 3 |
| Egyptians | 33 | 36 | 24 | 8 |
| English | 47 | 42 | 9 | 3 |
| Inuit (Alaska) | 38 | 44 | 13 | 5 |
| Inuit (Greenland) | 54 | 36 | 23 | 8 |
| Estonians | 34 | 36 | 23 | 8 |
| Fijians | 44 | 34 | 17 | 6 |
| Finns | 34 | 41 | 18 | 7 |
| French | 43 | 47 | 7 | 3 |
| Georgians | 46 | 37 | 12 | 4 |
| Germans | 41 | 43 | 11 | 5 |
| Greeks | 40 | 42 | 14 | 5 |
| Romani people (Hungary) | 29 | 27 | 35 | 10 |
| Hawaiians | 37 | 61 | 2 | 1 |
| Hindus (Bombay) | 29 | 25 | 35 | 11 |
| Hungarians | 36 | 43 | 16 | 5 |
| Icelanders | 56 | 32 | 10 | 3 |
| Indians (India) | 29 | 21 | 40 | 9 |
| Native Americans | 79 | 16 | 4 | 1 |
| Irish | 52 | 35 | 10 | 3 |
| Italians (Milan) | 46 | 41 | 11 | 3 |
| Japanese | 30 | 38 | 22 | 10 |
| Jews (Germany) | 42 | 41 | 12 | 5 |
| Jews (Poland) | 33 | 41 | 18 | 8 |
| Kalmuks | 26 | 23 | 41 | 11 |
| Kikuyu (Kenya) | 60 | 19 | 20 | 1 |
| Koreans | 28 | 32 | 31 | 10 |
| Sami people | 29 | 63 | 4 | 4 |
| Latvians | 32 | 37 | 24 | 7 |
| Lithuanians | 40 | 34 | 20 | 6 |
| Malays | 62 | 18 | 20 | 0 |
| Māori | 46 | 54 | 1 | 0 |
| Mayans | 98 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Moros | 64 | 16 | 20 | 0 |
| Navajo Indians | 73 | 27 | 0 | 0 |
| Nicobarese | 74 | 9 | 15 | 1 |
| Norwegians | 39 | 50 | 8 | 4 |
| Papuans (New Guinea) | 41 | 27 | 23 | 9 |
| Persians | 38 | 33 | 22 | 7 |
| Peruvian Indians | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Filipinos | 45 | 22 | 27 | 6 |
| Poles | 33 | 39 | 20 | 9 |
| Portuguese | 35 | 53 | 8 | 4 |
| Romanians | 34 | 41 | 19 | 6 |
| Russians | 33 | 36 | 23 | 8 |
| Sardinians | 50 | 26 | 19 | 5 |
| Scots | 51 | 34 | 12 | 3 |
| Serbians | 38 | 42 | 16 | 5 |
| Shompen Nicobarese | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Slovaks | 42 | 37 | 16 | 5 |
| South Africans | 45 | 40 | 11 | 4 |
| Spanish | 38 | 47 | 10 | 5 |
| Sudanese | 62 | 16 | 21 | 0 |
| Swedish | 38 | 47 | 10 | 5 |
| Swiss | 40 | 50 | 7 | 3 |
| Tatars | 28 | 30 | 29 | 13 |
| Thais | 37 | 22 | 33 | 8 |
| Turks | 43 | 34 | 18 | 6 |
| Ukrainians | 37 | 40 | 18 | 6 |
| Black Americans | 49 | 27 | 20 | 4 |
| White Americans | 45 | 40 | 11 | 4 |
| Vietnamese | 42 | 22 | 30 | 5 |
| Mean | 43.91 | 34.80 | 16.55 | 5.14 |
| Standard deviation | 16.87 | 13.80 | 9.97 | 3.41 |
Blood group B has its highest frequency in Northern Asia and neighboring Central Asia, and its incidence diminishes both towards the west and the east, falling to single digit percentages in Spain.[32][33] It is believed to have been entirely absent from Native American and Australian Aboriginal populations prior to the arrival of Europeans in those areas.[33][34]
Blood group A is associated with high frequencies in Europe, especially in Scandinavia and Central Europe, although its highest frequencies occur in some Australian Aboriginal populations and the Blackfoot Indians of Montana, the US.[35][36]
Maps of allele ABO among native populations
-
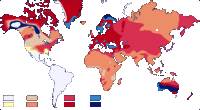
Map of allele A
among native populations -
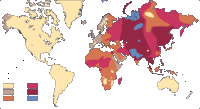
Map of allele B
among native populations -
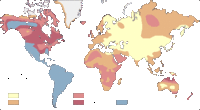
Map of allele O
among native populations
References
- ↑ CIA World Factbook
- ↑ Blood Types - What Are They?, Australian Red Cross
- ↑ "Austrian Red Cross - Blood Donor Information". Old.roteskreuz.at. 2006-03-21. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "Rode Kruis Wielsbeke - Blood Donor information material". Rodekruiswielsbeke.be. Archived from the original on 2010-11-26. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ Tipos Sanguíneos
- ↑ Canadian Blood Services - Société canadienne du sang. "Types & Rh System, Canadian Blood Services". Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- 1 2 http://bloodtypes.jigsy.com/East_Asia-bloodtypes
- ↑ Czech Red Cross. "Podíl krevních skupin v populaci České republiky". Archived from the original on 2009-06-24. Retrieved 2011-03-18.
- ↑ Frequency of major blood groups in the Danish population.
- ↑ http://www.verekeskus.ee/?op=body&id=27
- ↑ "Suomalaisten veriryhmäjakauma" (in Finnish). 2009-08-21. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "Les groupes sanguins (système ABO)". Centre Hospitalier Princesse GRACE - Monaco (in French). C.H.P.G. MONACO. 2005. Retrieved 2008-07-15.
- ↑ "Blóðflokkar" (in Icelandic). .landspitali.is. Archived from the original on 2011-07-19. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ http://www.rhesusnegative.net/themission/bloodtypefrequencies/. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ "Irish Blood Transfusion Service - Irish Blood Group Type Frequency Distribution". Irish Blood Transfusion Service. Retrieved 2009-11-07.
- ↑ "The national rescue service in Israel" (in Hebrew). Mdais.org. Archived from the original on 26 November 2010. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "血液の知識". Japanese Red Cross Society. Archived from the original on 2012-07-29. Retrieved 2012-08-07.
- ↑ "Voorraad Erytrocytenconcentraten Bij Sanquin" (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 2009-06-26. Retrieved 2009-03-27.
- ↑ "What are Blood Groups?". NZ Blood. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "Hva er en blodtype?" [What is a blood type?] (in Norwegian). Retrieved 2014-09-23.
- ↑ "Philippine Red Cross". Retrieved 2014-07-15.
- ↑ "Regionalne Centrum Krwiodawstwa i Krwiolecznictwa we Wroclawiu" (in Polish). Rckik.wroclaw.pl. 2010-09-02. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "Portuguese Blood Institute" (in Portuguese). (assuming Rh and AB antigens are independent)
- ↑ "Frequency of ABO blood groups in the eastern region of Saudi Arabia". Cat.inist.fr. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "South African National Blood Service - What's Your Type?". Sanbs.org.za. Archived from the original on 2010-02-06. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "Federación Nacional de Donantes de Sangre/La sangre/Grupos". Donantesdesangre.net. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "Frequency of major blood groups in the Swedish population". Geblod.nu. 2007-10-02. Archived from the original on 2010-11-24. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "Turkey Blood Group Site". Kangrubu.com. Archived from the original on 2010-05-29. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ↑ "Blood Group Basics". Blood.co.uk. Retrieved 2014-05-03.
- ↑ "Blood Types in the U.S". Archived from the original on 2011-07-19. Retrieved 2011-07-19.
- ↑ "Racial and ethnic distribution of ABO blood types". Bloodbook.com. Retrieved 2010-08-01.
- ↑ Blood Transfusion Division, United States Army Medical Research Laboratory (1971). Selected contributions to the literature of blood groups and immunology. 1971 v. 4. United States Army Medical Research Laboratory, Fort Knox, Kentucky.
... In northern India, in Southern and Central China and in the neighboring Central Asiatic areas, we find the highest known frequencies of B. If we leave this center, the frequency of the B gene decreases almost everywhere ...
- 1 2 Encyclopaedia Britannica (2002). The New Encyclopaedia Britannica. Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. ISBN 0-85229-787-4.
... The maximum frequency of the B gene occurs in Central Asia and northern India. The B gene was probably absent from Native Americans and Australian Aboriginal people before racial admixture occurred with the coming of the white man ...
- ↑ Carol R. Ember, Melvin Ember (1973). Anthropology. Appleton-Century-Crofts.
... Blood type B is completely absent in most North and South American Indians ...
- ↑ Dean 2005, 2.1.4: Blood Type A: Central and Eastern Europe Type A is common in Central and Eastern Europe. In countries such as Austria, Denmark, Norway, and Switzerland, about 45–50% of the population have this blood type, whereas about 40% of Poles and Ukrainians do so. The highest frequencies are found in small, unrelated populations. For example, about 80% of the Blackfoot Indians of Montana have blood type A ...
- ↑ Technical Monograph No. 2: The ABO Blood Group System and ABO Subgroups (PDF). Biotec. March 2005.
... The frequency of blood group A is quite high (25–55%) in Europe, especially in Scandinavia and parts of central Europe. High group A frequency is also found in the Aboriginal people of South Australia (up to 45%) and in certain American Indian tribes where the frequency reaches 35% ...