C8orf46
| Chromosome 8 open reading frame 46 | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbols | C8orf46 |
| Species | Human |
| HPRD | 14565 |
| Ensembl | ENSG00000169085 |
| UniProt | Q8TAG6 |
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_152765.3 |
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_689978.2 |
| Location | 8q13.1 |
Chromosome 8 open reading frame 46 (C8orf46) is a protein coding gene, which in humans is located along the forward strand of chromosome 8.[1] The gene is approximately 58,522 base pairs long, and encodes for 207 amino acids. C8orf46 is found to be highly expressed in regions of the brain and spinal cord.
Gene
Location
C8orf46 is found along the plus strand of chromosome 8 (8q13.1) with the genomic sequence beginning at 66,460,003 bp and ending at 66,518,524 bp.[2] The entire gene is 58,522 bp long.[2] C8orf46 is flanked by alcohol dehydrogenase iron containing 1 and v-myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog-like.[1]

Homology
Paralogs
No human paralogs for C8orf46 have been identified[1]
Orthologs
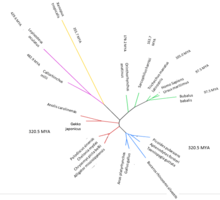
C8orf46 is found in all classes of vertebrates, including mammals, birds, fish, reptiles and amphibians.[1] While C8orf46 is found in a diverse range of mammals, birds and reptiles, only one amphibian (Xenopus tropicalis) and two fish (Callorhinchus milli and Lepisosteus oculatus) have been found to possess the C8orf46 gene.[1] The most distant ortholog of C8orf46 is in Callorhinchus milli, which diverged from the human version of the gene an estimated 482.9 million years ago.[3] The gene has not been found in any plants, fungi or single celled organisms.[1]
Homologous Domains
The N-terminus and C-terminus are highly conserved regions across both distant and close orthologs. The orthologs of C8orf46 all show conservation of the SH3 protein domain family as well as a domain of unknown function (DUF4648).
mRNA
Splice Variants
C8orf46 does not have any alternative mRNA splice variants. The mature mRNA is approximately 3741 base pairs in length and contains six exons.[2]
Protein
General Properties

The protein encoded by C8orf46 is 207 amino acids long, which equates to a molecular weight of 22.6 kdal.[2] The isoelectric point of the protein is 10.42 which indicates the pH of the protein is basic.[4] The protein of C8orf46 does contain a domain of unknown function (DUF4648) and is a part of the SH3 domain family, which is known to bind to proline-rich ligands.[1] The secondary and tertiary strcuture of this protein is not well known.
Composition
The protein derived from C8orf46 is considered rich in arginine, and poor in phenylalanine compared to the composition of the average human protein.[4] C8orf46 does contain several regions of positively charged runs, and has a high concentration of basic amino acids.[4]
Post-Translational Modifications
C8orf46 is predicted to undergo several types of post translational modifications. With a high degree of certainty, it is predicted that C8orf46 undergoes lysine glycation, O-glycosylation, serine, threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation, sumolyation and initial methionine acetylation.[5]
| Type of Modification | Amino Acid Position | Impact on Protein[6] |
|---|---|---|
| Glycation of Epsilon Amino Groups of Lysine | Lys33, Lys41, Lys124, Lys152. Lys153, Lys193 | Impairs enzymatic function of protein. |
| Initial Methionine Acetylation | Met1 | Mediates protein stability, sorting and localization. |
| O-glycosylation Sites | Ser25, Ser90, Ser97, Ser102, Ser113, Ser122, Ser126, Ser128 Ser130, Ser148, Ser194, Thr78, Thr101, Thr125, Thr134, Thr155 | Regulates transcription and translation factors. |
| Phosphorylation Sites | Ser22, Ser25, Ser26, Ser34, Ser35, Ser97, Ser122, Ser126, Ser130, Ser194, Thr78, Thr83, Thr138, Tyr50, Tyr158, Tyr196 | Regulates protein function, cell signaling and enzymatic functions of protein |
| Sumolyation Sites | Lys141, Lys195 | Plays a role in nuclear-cytosolic transport, acts as binding site. |
Subcellular Location

C8orf46 is predicted to be a nuclear protein, given the classical nuclear localization signal found at amino acids Lys191 to Lys193.[5] C8orf46 does not contain any transmembrane domains or signal peptides suggesting that it is an intracellular protein.[5]
Expression
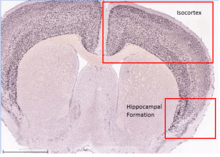
C8orf46 has shown to be ubiquitously expressed in the body. The gene is expressed in 13 different types of tissue throughout the body, with the brain, spinal cord and nerves showing elevated expression of the gene.[8] Specifically, the isocortex and hippocampal formation areas of the brain show high levels of expression. In addition to healthy tissue, C8orf46 is also found in several disease states. These disease states include chondrosarcoma, glioma, kidney tumors, liver tumors, and germ cell tumors.[8] C8orf46 is only expressed in infants and adults.[8]
Regulation of Expression
Promoter
The promoter region of C8orf46, GXP_80707, is approximately 1044 bp in length.[9] The promoter sequence begins at 66,492,708 bp and ends at 66,493,751 bp.[9] There are several important transcription factors that are predicted to bind to the promoter sequence of C8orf46. The most common transcription factors include; HMG box-containing protein 1, repressive glucocorticoid receptor, cAMP-responsive binding protein and Homeo domain factor Pbx-1.[9]
Clinical Significance
C8orf46 has been associated with breast cancer in humans. The gene has been researched in connection with estrogen receptor 1- enhancer (ESR1), whose expression determines if a breast cancer patient receives endocrine therapy.[10] It is predicted that C8orf46 has ESR1 enhancer regions that become hypermethylated and promote acquired endocrine resistance in breast cancer.[10]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "C8orf46 chromosome 8 open reading frame 46 [Homo sapiens (human)] - Gene - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2016-04-25.
- 1 2 3 4 "http://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=C8orf46". www.genecards.org. Retrieved 2016-04-25. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ "TimeTree :: The Timescale of Life". www.timetree.org. Retrieved 2016-05-09.
- 1 2 3 "SDSC Biology Workbench".
- 1 2 3 "ExPASy: SIB Bioinformatics Resource Portal - Home". www.expasy.org. Retrieved 2016-04-25.
- ↑ "Overview of Post-Translational Modification". www.thermofisher.com. Retrieved 2016-05-09.
- ↑ "ISH Data :: Allen Brain Atlas: Developing Mouse Brain" Check
|url=value (help). developingmouse.brain-map.org. Retrieved 2016-05-09. - 1 2 3 "EST Profile - Hs.268869". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2016-05-09.
- 1 2 3 "ElDorado Introduction". www.genomatix.de. Retrieved 2016-05-09.
- 1 2 Stone, Andrew; Zotenko, Elena; Locke, Warwick J.; Korbie, Darren; Millar, Ewan K. A.; Pidsley, Ruth; Stirzaker, Clare; Graham, Peter; Trau, Matt (2015-07-14). "DNA methylation of oestrogen-regulated enhancers defines endocrine sensitivity in breast cancer". Nature Communications. 6: 7758. doi:10.1038/ncomms8758. PMC 4510968
 . PMID 26169690.
. PMID 26169690.
Further reading
- PMC, Europe; et al. (2014). "Targeted CNS Delivery Using Human MiniPromoters and Demonstrated Compatibility with Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors". Molecular Therapy. Methods & Clinical Development. 1: 5.
- Stone, Andrew. "DNA Methylation of Oestrogen-Regulated Enhancers Defines Endocrine Sensitivity in Breast Cancer". Nature Communications.
- Pandey, Ashutosh K.; et al. (2014). "Functionally Enigmatic Genes: A Case Study of the Brain Ignorome". PLoS ONE. 9 (2): e88889. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0088889.