Cariñena (DO)
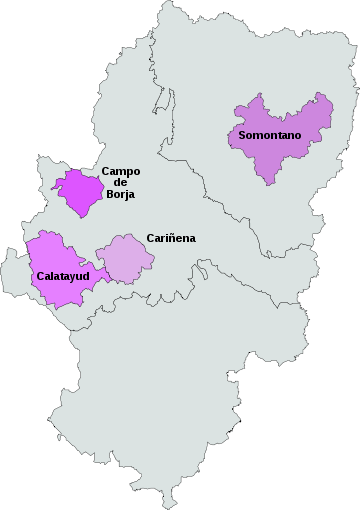

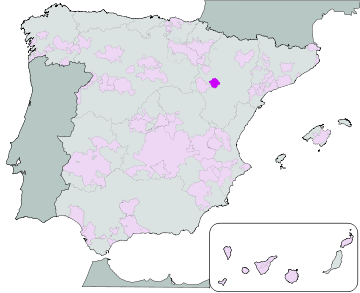
Cariñena is a Spanish Denominación de Origen (DO) for wines located in Cariñena, Aragón, Spain. It is one of the oldest protected growing areas in Europe, the DO having been created in 1932. Cariñena vineyards are located near the centre of Aragón, about 50 km southwest of Zaragoza, on a plateau known as the Campo de Cariñena. The lower vineyards lie at an altitude of 400 m, rising to 800 m as they approach the Sierra de la Virgen mountains. To the west they border on the Calatayud (DO).
The 1990s was a period of rapid development due partly to the numerous mergers of small wineries and cooperatives, and to the adaptation of the wines produced to a more modern palate. The traditional robust, high alcohol content wines are still produced for local consumption, but now fruitier, lighter and well balanced wines are also produced in response to the tastes and preferences of the average export consumer. Exports have quadrupled since 1995 and a new research centre is helping to improve production.
The region is the acknowledged source of the Carignan grape, which is also grown in Italy, California and several other New World regions. The grape is still widely grown in Cariñena, where it tends to be better-known as Mazuelo.
History
The ancient Romans founded the city of Carae in the year 50 BC in an area where the local population had been producing mead since the 3rd century BC. During the Middle Ages grape-growing and wine-making prospered under the protection of several monasteries, and by the 16th century vineyards covered 50% of the territory of the province of Zaragoza.
Climate
The climate is continental (long, hot summers, cold winters) with extremes of temperature over the course of the year: 38 °C in summer and -8 °C in winter. The “cierzo” a cold northerly wind, helps to keep the humidity low. The main problems for the grape-growers are the risk of hailstones, the strong winds and excessive summer heat, as drought can affect the harvest. However the large difference between daytime and night-time temperatures is a positive contributory factor to the characteristic intensity of Cariñena wines.
Soil
The topsoil is reddish-brown limestone over a subsoil of loose rock with a high calcium carbonate content, and in some places, slate and clay.
Grape varieties

The most widely planted variety is Garnacha tinta (55%) which is used to produce reds and rosés, followed by Mazuelo and Tempranillo (15%), while Viura (20%) is common for whites. Growers are also experimenting with foreign varieties such as Chardonnay and Parellada which have opened up the range of wines produced considerably in recent years. Most vines are planted on trellises (en espaldera) in marco real layout with 3 m between rows and a planting density of between 1500 and 3000 vines/ha. The harvest generally starts in September.
Wine production
Red wines are produced ensuring that malolactic fermentation has been completed, though carbonic maceration is also used for young wines. Selection for Crianza, Reserva and Gran Reserva starts in the vineyards. Tempranillo is blended with Garnacha to make the Crianza. The whites are made with Viura and the rosés use Garnacha along with other white and red varieties. The rosés do not undergo malolactic fermentation, so as to conserve all their acidity, and are macerated for colour.
Both the fresh young whites and rosé wines produced in Cariñena are best consumed within the year of production. Reds have the characteristic style of Garnacha wines produced in hot climates and, in the case of oak-aged Crianzas, have the taste and strength provided by 5% of Cariñena (Carignan) grapes. Dry whites represent 20% of total production. Sweet Moscatels, for which the region has long been famous, are still produced in quantity from the Moscatel Romano grape.