Cascades (conservation area)
| Cascades | |
| Protected Area | |
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| State | Virginia |
| Counties | Giles County, Virginia |
| Ranger district | Eastern Divide |
| Coordinates | 37°22′5″N 80°35′43″W / 37.36806°N 80.59528°WCoordinates: 37°22′5″N 80°35′43″W / 37.36806°N 80.59528°W |
| Area | 1,833 acres (741.8 ha) |
| Owner | US Forest Service |
| IUCN category | VI - Managed Resource Protected Area |
| Headquarters | Roanoke, Virginia |
|
Location of Cascades (conservation area) in Virginia
| |
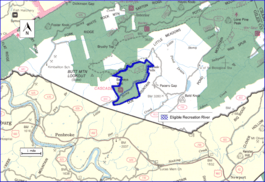
Cascades (conservation area) is an area in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia, United States, that has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction The area is named after a 60-foot waterfall on Little Stony Creek which flows out of the area into the New River. With easily accessible trails, the area has become a popular destination.[1][2]
Location and access
The Cascades Conservation Area is located in the Appalachian Mountains in Giles County near Pembroke, Va. The area is bounded on the north by Pacers Gap Road (SR 714), on the west by Butt Mountain and on the south and east by Doe Mountain.[3]
The trailhead for the hike to the Cascades waterfall is about 4 miles from Pembroke on a well maintained road. The Forest Service collects a fee for parking at the trailhead.[2] On weekends, there may be a wait required before entering the parking area. Driving directions to the trailhead are given below in the external link.
A second popular destination is Barney’s Wall, a tall cliff that gives a commanding view of the area.[1] This trailhead is about 34 miles from Pembroke. However, the last part of the route is on a dirt road that can be difficult to manage for cars with a low suspension.[3] Driving directions are given in the external link.
Roads and trails are shown on National Geographic Trail Map 788.[3]
Natural history
The habitat of the southern Appalachians is rich in its biological diversity with nearly 10,000 species, some not found anywhere else. The great diversity is related to the many ridges and valleys which form isolated communities in which species evolve separately from one another. The region lies south of the glaciers that covered North America 11,000 years go. To escape the glaciers, northern species retreated south to find refuge in the southern Appalachians. When the glaciers retreated, many of these species remained along with the southern species that were native to the area. The diversity includes trees, mosses, millipedes and salamanders.[4]
Among interesting plants in the area are the walking fern and Jeffersonian twin-leaf.[1] Walking fern (asplenium rhizophyllum) is a small fern with long, narrow tips that can touch the ground, then root to give a walking appearance. Jeffersonian twin-leaf (Jeffersonia diphylla) has showy white flowers that emerge with the spring ephemerals before the forest canopy appears and blocks sunlight to the forest floor.
Little Stony Creek is eligible for designation as a Wild and Scenic River.[5]
The area has 445 acres of potential old growth forest.[1]
Topography
The Cascades Conservation Area is in the Ridge and Valley Province of the Appalachian Mountains. The province consists of a thick layer of sedimentary rock that has undergone folding and/or faulting to create a series of ridges and valleys. During the sedimentation process fossils were formed leaving evidence of life existing millions of years ago. The fossils can be seen in rock exposures throughout the mountains.[6]
Forest Service management
The U.S. Forest Service has conducted a survey of their lands to determine their potential for wilderness designation. Wilderness designation provides a high degree of protection from development. The areas that were found suitable are referred to as inventoried roadless areas. Later a Roadless Rule was adopted that limited road construction in these areas. The rule provided some degree of protection by reducing the negative environmental impact of road construction and thus promoting the conservation of roadless areas. The Cascades Conservation Area was not included in the inventoried roadless areas, and therefore subject to possible road construction and timber sales.[1]
Nearby Wildlands
- Cascades (conservation area) is in the Mountain Lake Wilderness Cluster
- Mottesheard
- Hickory Flats
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Parsons, Shireen (1999). Virginia's Mountain Treasures (First ed.). Washington, DC: The Wilderness Society. p. 43.
- 1 2 "Cascades Day Use Area". George Washington and Jefferson National Forest. Retrieved 5 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 "National Geographic". 788 :: Covington, Alleghany Highlands [George Washington and Jefferson National Forests]. National Geographic. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ↑ "Biodiversity of Southern Appalachians". Highlands Biological Station. Retrieved 6 December 2015.
- ↑ Land and Resource Management Plan, Jefferson National Forest, Management Bulletin R8-MB 115A, January 2004, page 2-44
- ↑ Dietrich, Richard V. (1970). Geology and Virginia. University Press of Virginia.