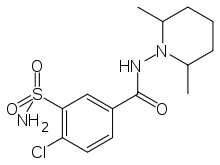
Clopamide
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | C03BA03 (WHO) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
636-54-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 2804 |
| ChemSpider |
2702 |
| UNII |
17S83WON0I |
| KEGG |
D02460 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1361347 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.238 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H20ClN3O3S |
| Molar mass | 345.846 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Clopamide (trade name Brinaldix) is a piperidine diuretic.[1]
Mechanism of action
Clopamide is categorised as a thiazide-like diuretic and works in similar way as the thiazide diuretics do. It acts in the kidneys, at the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) of the nephron where it inhibits the sodium-chloride symporter. Clopamide selectively binds at the chloride binding site of the sodium-chloride symporter in the PCT cells on the luminal (interior) side and thus interferes with the reabsorption of sodium chloride, causing an equiosmolar excretion of water along with sodium chloride.
References
- ↑ McNeil, J. J.; Conway, E. L.; Drummer, O. H.; Howes, L. G.; Christophidis, N.; Louis, W. J. (1987). "Clopamide: Plasma concentrations and diuretic effect in humans". Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 42 (3): 299–304. doi:10.1038/clpt.1987.151. PMID 3621784.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.