Commonwealth of Nations membership criteria
.png)
Commonwealth of Nations membership criteria are the corpus of requirements that members and prospective members must meet to be allowed to participate in the Commonwealth of Nations. The criteria have been altered by a series of documents issued over the past eighty-two years.
The most important of these documents were the Statute of Westminster (1931), the London Declaration (1949), the Singapore Declaration (1971), the Harare Declaration (1991), the Millbrook Commonwealth Action Programme (1995), the Edinburgh Declaration (1997), and the Kampala Communiqué (2007). New members of the Commonwealth must abide by certain criteria that arose from these documents, the most important of which are the Harare principles and the Edinburgh criteria.
The Harare principles require all members of the Commonwealth, old and new, to abide by certain political principles, including democracy and respect for human rights. These can be enforced upon current members, who may be suspended or expelled for failure to abide by them. To date, Fiji, Nigeria, Pakistan, and Zimbabwe have been suspended on these grounds; Zimbabwe later withdrew.
The foremost of the Edinburgh criteria requires new members to have either constitutional or administrative ties to at least one current member of the Commonwealth of Nations. Traditionally, new Commonwealth members had ties to the United Kingdom. The Edinburgh criteria arose from the 1995 accession of Mozambique, at the time the only member that was never part of the British Empire (in whole or part). The Edinburgh criteria have been reviewed, and were revised at the 2007 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting (CHOGM), allowing the admission of Rwanda at the 2009 CHOGM.[1]
History
Founding documents

The formation of the Commonwealth of Nations is dated back to the Statute of Westminster, an Act of the British Parliament passed on 11 December 1931. The Statute established the independence of the Dominions, creating a group of equal members where, previously, there was one (the United Kingdom) paramount. The solitary condition of membership of the embryonic Commonwealth was that a state be a Dominion. Thus, the independence of Pakistan (1947), India (1947), and Sri Lanka (1948) saw the three countries join the Commonwealth as independent monarchies. On the other hand, Burma (1948) and Israel (1948) did not join the Commonwealth, as they chose to become republics. The membership of Ireland lapsed when it unambiguously became a republic in 1949.[2]
With India on the verge of promulgating a republican constitution, the 1949 Commonwealth Prime Ministers Conference was dominated by the impending departure of over half of the Commonwealth's population. To avoid such a fate, Canadian Prime Minister Louis St. Laurent proposed that republics be allowed to remain in the Commonwealth, provided that they recognise King George VI as 'Head of the Commonwealth'. Known as the London Declaration, this agreement thus established the only formalised rule as being that members must recognise the Head of the Commonwealth. The arrangement prompted suggestions that other countries, such as France,[3] Israel, and Norway,[4] join. However, until Western Samoa joined in 1970, only recently independent countries would accede.
Singapore Declaration
The first statement of the political values of the Commonwealth of Nations was issued at the 1961 conference, at which the members declared that racial equality would be one of the cornerstones of the new Commonwealth, at a time when the organisation's ranks were being swelled by new African and Caribbean members. The immediate result of this was the withdrawal of South Africa's re-application, which it was required to lodge before becoming a republic, as its government's apartheid policies clearly contradicted the principle.
Further political values and principles of the Commonwealth were affirmed in Singapore on 22 January 1971, at the first Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting (CHOGM). The fourteen points clarified the political freedom of its members, and dictated the core principles of the Commonwealth: world peace, liberty, human rights, equality, and free trade.[5] However, neither the terms nor the spirit of the Declaration were binding, and several openly flouted it; despite little conformity, only Fiji was ever expelled for breaching these tenets (on 15 October 1987, following the second coup of that year).[6]
Harare Declaration
The Harare Declaration, issued on 20 October 1991 in Harare, Zimbabwe, reaffirmed the principles laid out in Singapore, particularly in the light of the ongoing dismantling of apartheid in South Africa. The Declaration put emphasis on human rights and democracy by detailing these principles once more:
| “ |
|
” |
Millbrook Programme
The Millbrook Commonwealth Action Programme, issued on 12 November 1995 at the Millbrook Resort, near Queenstown, New Zealand, clarified the Commonwealth's position on the Harare Declaration. The document introduced compulsion upon its members, with strict guidelines to be followed in the event of breaching its rules. These included but were not limited to expulsion from the Commonwealth. Adjudication was left to the newly created Commonwealth Ministerial Action Group (CMAG).[8]
At the same CHOGM, the Programme was enforced for the first time, as Nigeria was suspended. On 19 December 1995, the CMAG found that the suspension was in line with the Programme, and also declared its intent on enforcing the Programme in other cases (particularly Sierra Leone and The Gambia).[9] On 29 May 1999, the day after the inauguration of Nigeria's first democratically elected President since the end of military rule, Olusẹgun Ọbasanjọ, the country's suspension was lifted, on the advice of the CMAG.[10]
Edinburgh criteria
In 1995, Mozambique joined the Commonwealth, becoming the first member to have never had a constitutional link with the United Kingdom or another Commonwealth member. Concerns that this would allow open-ended expansion of the Commonwealth and dilute its historic ties prompted the 1995 CHOGM to launch the Inter-Governmental Group on Criteria for Commonwealth Membership, to report at the 1997 CHOGM, to be held in Edinburgh, Scotland. The group decided that, in future, new members would be limited to those with constitutional association with an existing Commonwealth member.[11]
In addition to this new rule, the former rules were consolidated into a single document. They had been prepared for the High Level Appraisal Group set up at the 1989 CHOGM, but not publicly announced until 1997.[12] These requirements, which remain the same today, are that members must:
- accept and comply with the Harare principles.
- be fully sovereign states.
- recognise Queen Elizabeth II as the Head of the Commonwealth.[13]
- accept the English language as the means of Commonwealth communication.
- respect the wishes of the general population vis-à-vis Commonwealth membership.[14]
Kampala review
On the advice of Secretary-General Don McKinnon, the 2005 CHOGM, held in Valletta, Malta, decided to re-examine the Edinburgh criteria. The Committee on Commonwealth Membership reported at the 2007 CHOGM, held in Kampala, Uganda.[15] According to Don McKinnon, the members of the Commonwealth decided in principle to expand the membership of the organisation to include countries without linkages to the Commonwealth, but Eduardo del Buey stated that it would still take some time until the criteria are reformed. Outstanding applications as of the 2007 meeting included former Belgian colony Rwanda (application submitted in 2003 and approved in 2009), the former French colonies of Algeria and Madagascar, and the former British colony of Yemen and condominium of Sudan.[16]
The revised requirements stated that:[17]
- (a) an applicant country should, as a general rule, have had a historic constitutional association with an existing Commonwealth member, save in exceptional circumstances;
- (b) in exceptional circumstances, applications should be considered on a case-by-case basis;
- (c) an applicant country should accept and comply with Commonwealth fundamental values, principles, and priorities as set out in the 1971 Declaration of Commonwealth Principles and contained in other subsequent Declarations;
- (d) an applicant country must demonstrate commitment to: democracy and democratic processes, including free and fair elections and representative legislatures; the rule of law and independence of the judiciary; good governance, including a well-trained public service and transparent public accounts; and protection of human rights, freedom of expression, and equality of opportunity;
- (e) an applicant country should accept Commonwealth norms and conventions, such as the use of the English language as the medium of inter-Commonwealth relations, and acknowledge Queen Elizabeth II as the Head of the Commonwealth; and
- (f) new members should be encouraged to join the Commonwealth Foundation, and to promote vigorous civil society and business organisations within their countries, and to foster participatory democracy through regular civil society consultations
Rwanda became the 54th nation to join the Commonwealth at the 2009 CHOGM. It became the second country (after Mozambique) not to have any historical ties with the United Kingdom. Rwanda had been a colony of Germany in the 19th century and of Belgium for the first half of the 20th century.[18] Later ties with France were severed during the 1994 Rwandan Genocide. President Paul Kagame also accused it of supporting the killings and expelled a number of French organisations from the country.[19] In recent years, English has replaced French as the official language in parts of Rwanda.[20] Prime Minister of Malaysia Najib Tun Razak stated that Rwanda's application "was boosted by its commitment towards democracy as well as the values espoused by the Commonwealth".[21] Consideration for its admission was also seen as an "exceptional circumstance" by the Commonwealth Secretariat.[22]
Prospective members
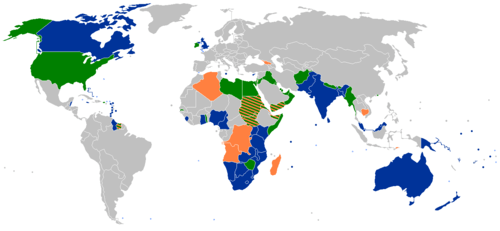
Eligible states
The following states would be eligible under the Edinburgh criteria (but not necessarily under the Harare criteria). The first list is former colonies, protectorates, mandates and dominions of the British Empire and do have some constitutional link where some or all of this nations territory at one point was under British control.
 Bahrain:[14] British protectorate until 1971.
Bahrain:[14] British protectorate until 1971. Egypt:[14] British protectorate from 1882 until 1922 but British troops still defended Egypt in the Second World War and helped train and controlled the Egyptian Army. British troops controlled the Suez Canal until 1956; English commonly used as a language of instruction and administration and the currency today still is the 'Egyptian pound".
Egypt:[14] British protectorate from 1882 until 1922 but British troops still defended Egypt in the Second World War and helped train and controlled the Egyptian Army. British troops controlled the Suez Canal until 1956; English commonly used as a language of instruction and administration and the currency today still is the 'Egyptian pound". Eritrea:[14] administered by Britain under a UN Mandate until 1951.
Eritrea:[14] administered by Britain under a UN Mandate until 1951. The Gambia: member of the Commonwealth until its withdrawal in 2013. However, newly-elected President Adama Barrow has pledged to return The Gambia to the Commonwealth.[23]
The Gambia: member of the Commonwealth until its withdrawal in 2013. However, newly-elected President Adama Barrow has pledged to return The Gambia to the Commonwealth.[23] Iraq:[14] British Mandate of Mesopotamia until 1932.
Iraq:[14] British Mandate of Mesopotamia until 1932. Ireland:[24] the only country ever to secede from the United Kingdom; shared a monarch with England, then Scotland and England, later Great Britain and later the United Kingdom from 1177 to 1949; parliamentary ties with the parliament of England and later Great Britain from 1494 to 1782; a part of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1922; and a British Dominion from 1922 to 1937. Ireland was formerly a member of the Commonwealth, but its membership terminated when it declared itself a republic in 1949, prior to the London Declaration, which allowed republics to remain in the Commonwealth.
Ireland:[24] the only country ever to secede from the United Kingdom; shared a monarch with England, then Scotland and England, later Great Britain and later the United Kingdom from 1177 to 1949; parliamentary ties with the parliament of England and later Great Britain from 1494 to 1782; a part of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1922; and a British Dominion from 1922 to 1937. Ireland was formerly a member of the Commonwealth, but its membership terminated when it declared itself a republic in 1949, prior to the London Declaration, which allowed republics to remain in the Commonwealth.  Israel:[19][25] part of the British Mandate of Palestine until 1948. Israel's eligibility was declared in 2006 by the Commonwealth secretary-general.[25]
Israel:[19][25] part of the British Mandate of Palestine until 1948. Israel's eligibility was declared in 2006 by the Commonwealth secretary-general.[25] Jordan:[14] part of the British Mandate of Palestine 1920–1921; protectorate of Transjordan 1921–1946.
Jordan:[14] part of the British Mandate of Palestine 1920–1921; protectorate of Transjordan 1921–1946. Kuwait:[14] British protectorate until 1961.
Kuwait:[14] British protectorate until 1961. Libya:[14] In 1943 the British administered the provinces of Tripolitania and Cyrenaica until 1951.
Libya:[14] In 1943 the British administered the provinces of Tripolitania and Cyrenaica until 1951. Maldives: member of the Commonwealth until its withdrawal in 2016.
Maldives: member of the Commonwealth until its withdrawal in 2016. Myanmar:[14] British Colony until 1948.
Myanmar:[14] British Colony until 1948. Qatar:[14] British protectorate until 1971.
Qatar:[14] British protectorate until 1971. South Sudan:[26] administered between 1899 and 1956, when it was a condominium of the United Kingdom and Egypt as part of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan. (South Sudan has applied to join the Commonwealth.)[27]
South Sudan:[26] administered between 1899 and 1956, when it was a condominium of the United Kingdom and Egypt as part of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan. (South Sudan has applied to join the Commonwealth.)[27]  Sudan:[14] Anglo-Egyptian condominium but a British colony in reality until 1956. (Sudan has applied to join the Commonwealth.)[1]
Sudan:[14] Anglo-Egyptian condominium but a British colony in reality until 1956. (Sudan has applied to join the Commonwealth.)[1] Suriname:[28] English colony of Willoughbyland from 1650 to 1667 and again controlled by the British from 1799 to 1816. In 2012 Suriname expressed plans to join the Commonwealth[29] and the British government has made it a priority to provide guidance to Suriname in applying for Commonwealth membership[30]
Suriname:[28] English colony of Willoughbyland from 1650 to 1667 and again controlled by the British from 1799 to 1816. In 2012 Suriname expressed plans to join the Commonwealth[29] and the British government has made it a priority to provide guidance to Suriname in applying for Commonwealth membership[30] United Arab Emirates:[14] seven British protectorates, known collectively as the Trucial States, until 1971.
United Arab Emirates:[14] seven British protectorates, known collectively as the Trucial States, until 1971. United States:[14]
United States:[14] Yemen:[1][14] South Yemen was a British colony (Aden) and British protectorates (Protectorate of South Arabia and the states, apart from Aden, in the Federation of South Arabia) until 1967. (Yemen has applied to join the Commonwealth.)[19]
Yemen:[1][14] South Yemen was a British colony (Aden) and British protectorates (Protectorate of South Arabia and the states, apart from Aden, in the Federation of South Arabia) until 1967. (Yemen has applied to join the Commonwealth.)[19] Zimbabwe:[12] member of the Commonwealth until 2003.
Zimbabwe:[12] member of the Commonwealth until 2003.
Secessionist movements and other territories
There are several secessionist movements and other sub-national territories that, were they to gain independence, would be eligible to join the Commonwealth. The following countries and territories would be eligible under the Edinburgh criteria (but not necessarily Harare) and have either expressed interest in joining or been considered for entry:
 Hong Kong:[14] British Colony until 1997.
Hong Kong:[14] British Colony until 1997.- Northern Ireland:[31] constituent country of the United Kingdom, a member since the Commonwealth's foundation.
 Quebec:[32] province of Canada, a member since the Commonwealth's foundation.
Quebec:[32] province of Canada, a member since the Commonwealth's foundation. Scotland:[33] constituent country of the United Kingdom, a member since the Commonwealth's foundation.
Scotland:[33] constituent country of the United Kingdom, a member since the Commonwealth's foundation. Wales:[34] constituent country of the United Kingdom, a member since the Commonwealth's foundation.
Wales:[34] constituent country of the United Kingdom, a member since the Commonwealth's foundation.- Crown dependencies – The
 Bailiwick of Jersey, the Bailiwick of Guernsey(
Bailiwick of Jersey, the Bailiwick of Guernsey( Guernsey,
Guernsey, Alderney,
Alderney, Sark) and the
Sark) and the  Isle of Man: While their constitutional status bears some resemblance to that of the Commonwealth realms, the Crown dependencies are not members of the Commonwealth of Nations. They participate in the Commonwealth of Nations by virtue of their association with the United Kingdom, and participate in various Commonwealth institutions in their own right. For example, all three participate in the Commonwealth Parliamentary Association and the Commonwealth Games. All three Crown dependencies regard the existing situation as unsatisfactory and have lobbied for change. The States of Jersey have called on the UK Foreign Secretary to request that the Commonwealth Heads of Government "consider granting associate membership to Jersey and the other Crown Dependencies as well as any other territories at a similarly advanced stage of autonomy". Jersey has proposed that it be accorded "self-representation in all Commonwealth meetings; full participation in debates and procedures, with a right to speak where relevant and the opportunity to enter into discussions with those who are full members; and no right to vote in the Ministerial or Heads of Government meetings, which is reserved for full members".[35] The States of Guernsey and the Government of the Isle of Man have made calls of a similar nature for a more integrated relationship with the Commonwealth,[36] including more direct representation and enhanced participation in Commonwealth organisations and meetings, including Commonwealth Heads of Government Meetings.[37]
Isle of Man: While their constitutional status bears some resemblance to that of the Commonwealth realms, the Crown dependencies are not members of the Commonwealth of Nations. They participate in the Commonwealth of Nations by virtue of their association with the United Kingdom, and participate in various Commonwealth institutions in their own right. For example, all three participate in the Commonwealth Parliamentary Association and the Commonwealth Games. All three Crown dependencies regard the existing situation as unsatisfactory and have lobbied for change. The States of Jersey have called on the UK Foreign Secretary to request that the Commonwealth Heads of Government "consider granting associate membership to Jersey and the other Crown Dependencies as well as any other territories at a similarly advanced stage of autonomy". Jersey has proposed that it be accorded "self-representation in all Commonwealth meetings; full participation in debates and procedures, with a right to speak where relevant and the opportunity to enter into discussions with those who are full members; and no right to vote in the Ministerial or Heads of Government meetings, which is reserved for full members".[35] The States of Guernsey and the Government of the Isle of Man have made calls of a similar nature for a more integrated relationship with the Commonwealth,[36] including more direct representation and enhanced participation in Commonwealth organisations and meetings, including Commonwealth Heads of Government Meetings.[37] - The British overseas territories of
 Anguilla,
Anguilla,  Bermuda,
Bermuda,  British Antarctic Territory,
British Antarctic Territory,  British Indian Ocean Territory,
British Indian Ocean Territory,  British Virgin Islands,
British Virgin Islands,  Cayman Islands,
Cayman Islands,  Falkland Islands,
Falkland Islands,  Gibraltar,
Gibraltar,  Montserrat,
Montserrat,  Pitcairn,
Pitcairn,  Saint Helena,
Saint Helena,  Ascension Island,
Ascension Island,  Tristan da Cunha, and
Tristan da Cunha, and  Turks and Caicos Islands, and other similar states in free association with New Zealand (
Turks and Caicos Islands, and other similar states in free association with New Zealand ( Niue,
Niue,  Tokelau,
Tokelau,  Cook Islands and
Cook Islands and  Ross Dependency) and Australia (
Ross Dependency) and Australia ( Christmas Island,
Christmas Island,  Coral Sea Islands,
Coral Sea Islands,  Heard and McDonald Islands,
Heard and McDonald Islands, _Islands.svg.png) Cocos (Keeling) Islands,
Cocos (Keeling) Islands,  Australian Antarctic Territory, and
Australian Antarctic Territory, and  Norfolk Island). Many of these territories and associated states participate in the Commonwealth of Nations by virtue of their association with the United Kingdom, Australia, or New Zealand, and participate in various Commonwealth institutions in their own right, and are frequently listed as members of the Commonwealth by virtue of their relationship with these full member states.[38]
Norfolk Island). Many of these territories and associated states participate in the Commonwealth of Nations by virtue of their association with the United Kingdom, Australia, or New Zealand, and participate in various Commonwealth institutions in their own right, and are frequently listed as members of the Commonwealth by virtue of their relationship with these full member states.[38]
Other territories
 Palestine:[1][14] the area comprising this non-member UN observer state was part of the British Mandate for Palestine until 1948. The State of Palestine has shown interest in joining the Commonwealth.[19]
Palestine:[1][14] the area comprising this non-member UN observer state was part of the British Mandate for Palestine until 1948. The State of Palestine has shown interest in joining the Commonwealth.[19]
Other states
There are a range of other states that have expressed formal or informal interest in joining the Commonwealth or have merely made enquiries about membership (expressing no view on whether they wish to become members), despite some not meeting the Edinburgh criteria as they are now. However, with the criteria being re-examined, they may be inclined to launch membership bids in the future:
 Algeria: has expressed interest.[1]
Algeria: has expressed interest.[1] Angola[14]
Angola[14] Burundi[39]
Burundi[39] Cambodia[1]
Cambodia[1] Democratic Republic of the Congo[14]
Democratic Republic of the Congo[14] East Timor[14][40]
East Timor[14][40] France: During the Suez crisis in 1956 there was a move by some politicians to closen the ties between Britain and France, in part to align their interests in the Middle East. The French Prime Minister, Guy Mollet, first proposed the creation of a Franco-British Union with common citizenship and Queen Elizabeth II as head of state. As an alternative, Mollet proposed that France join the Commonwealth with Commonwealth citizenship rights and recognising the Queen as the Head of the Commonwealth. British Prime Minister Anthony Eden rejected both proposals. [41]
France: During the Suez crisis in 1956 there was a move by some politicians to closen the ties between Britain and France, in part to align their interests in the Middle East. The French Prime Minister, Guy Mollet, first proposed the creation of a Franco-British Union with common citizenship and Queen Elizabeth II as head of state. As an alternative, Mollet proposed that France join the Commonwealth with Commonwealth citizenship rights and recognising the Queen as the Head of the Commonwealth. British Prime Minister Anthony Eden rejected both proposals. [41] Madagascar: has expressed interest.[1]
Madagascar: has expressed interest.[1]
Footnotes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Howden, Daniel (26 November 2009). "The Big Question: What is the Commonwealth's role, and is it relevant to global politics?". The Independent. London.
- ↑ Ireland's status was ill-defined between 1936 and 1949.
- ↑ "France and UK considered 1950s 'merger'". London: Guardian Unlimited. 15 January 2007. Retrieved 22 July 2007.
- ↑ "Kongebesøk i øyriket" (in Norwegian). Aftenposten. 26 October 2005. Archived from the original on 10 March 2007. Retrieved 15 December 2008.
- ↑ "Singapore Declaration of Commonwealth Principles 1971". Commonwealth Secretariat. 22 January 1971. Retrieved 16 September 2006.
- ↑ "Fiji Rejoins the Commonwealth". Commonwealth Secretariat. 30 September 1997. Retrieved 16 September 2006.
- ↑ "Harare Commonwealth Declaration, 1991". Commonwealth Secretariat. 1991-10-20. Retrieved 2006-09-16.
- ↑ "The Millbrook Commonwealth Action Programme on the Harare Declaration, 1995". Commonwealth Secretariat. 12 November 1995. Retrieved 16 September 2006.
- ↑ "First Meeting of the Commonwealth Ministerial Action Group on the Harare Declaration". Commonwealth Secretariat. 20 December 1995. Retrieved 16 September 2006.
- ↑ "Nigeria Resumes Full Commonwealth Membership". Commonwealth Secretariat. 18 May 1999. Retrieved 16 September 2006.
- ↑ "Edinburgh Communique, 1997". Commonwealth Secretariat. 27 October 1997. Retrieved 16 September 2006.
- 1 2 McIntyre, W. David (April 2008). "The Expansion of the Commonwealth and the Criteria for Membership". Round Table. 97 (395): 273–85. doi:10.1080/00358530801962089.
- ↑ Collinge, John (July 1996). "Criteria for Commonwealth Membership". Round Table. 85 (339): 279–86. doi:10.1080/00358539608454314.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 te Velde-Ashworth, Victoria (10 October 2005). "The future of the modern Commonwealth: Widening vs. deepening?". Commonwealth Policy Studies Unit. Archived from the original (doc) on 23 July 2011. Retrieved 16 September 2006.
- ↑ "2005 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting: Final Communiqué". Commonwealth Secretariat. 27 November 2005. Retrieved 16 September 2006.
- ↑ Osike, Felix (24 November 2007). "Rwanda membership delayed". New Vision. Retrieved 29 November 2009.
- ↑ 2007 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting: final communiqué
- ↑ Kron, Josh (28 November 2009). "Rwanda Joins Commonwealth". The New York Times. Retrieved 29 November 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 "Rwanda seeks to join Commonwealth". BBC News. 21 December 2006. Retrieved 29 November 2009.
- ↑ Ross, Will (27 November 2009). "What would the Commonwealth do for Rwanda?". BBC News. Retrieved 29 November 2009.
- ↑ Muin, Abdul; Majid, Abdul (29 November 2009). "Commonwealth Accepts Rwanda's Membership Bid". Bernama. Retrieved 29 November 2009.
- ↑ "Rwanda: Joining the Commonwealth". The New Times. AllAfrica. 27 November 2009. Retrieved 29 November 2009.
- ↑ "Gambia's Jammeh loses to Adama Barrow in shock election result". BBC News. 2 December 2016. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- ↑ Mole, Stuart (July 1998). "Issues of Commonwealth membership". Round Table. 87 (347): 307–12. doi:10.1080/00358539808454426.
- 1 2 Report in the Telegraph: Israel and Palestine could join the Commonwealth.
- ↑ South Sudan on Track to Join Commonwealth.
- ↑ South Sudan Launches Bid to Join Commonwealth
- ↑ Suriname plans to join the Commonwealth
- ↑ Suriname eyeing membership of Commonwealth
- ↑ Worldwide Priority: Strengthening Guyana’s participation in the Commonwealth and providing guidance to Suriname as it considers applying for membership
- ↑ 1972 Cabinet Papers: Repartition - Still a Threat - By Ciaran Mulholland, Quote:Making Northern Ireland "an independent state within the Commonwealth" was also under active consideration.
- ↑ Burns, John F. (21 February 1992). "Montreal Journal; A Sovereign Quebec, He Says, Needn't Be Separe". The New York Times. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
[Mr. Parizeau] has even suggested that a sovereign Quebec might join the Commonwealth, the group of nations that were formerly British colonies.
- ↑ YOUR SCOTLAND, YOUR VOICE - Summary of the SNP White Paper on Scottish Independence, quote:Scotland would also be able to play a role in other global groups such as...the Commonwealth
- ↑ Independent Wales would be 39% richer, claims ex-MP, quote:Plaid has a long-term ambition for an independent Wales within the EU
- ↑ "Written evidence from States of Jersey". Chief Minister of Jersey. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ↑ "The role and future of the Commonwealth". House of Commons. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ↑ "Written evidence from the States of Guernsey". Policy Council of Guernsey. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ↑ "Appendix B: The Commonwealth of Nations" Library of Congress Federal Research Division country studies: Area handbook series - Caribbean islands. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ↑ Burundi plans to become Commonwealth member
- ↑ "Alkatiri Raises Possibility of Commonwealth Membership". East Timor and Indonesia Action Network. 6 November 2001. Retrieved 5 November 2006.
- ↑ Thomson, Mike (15 January 2007). "When Britain and France nearly married". BBC. Retrieved 23 November 2016..
External links
- Velde-Ashworth, Victoria. "Commonwealth Membership and the Patterson Commission Report: In the light of the Kampala Communiqué" (doc). Commonwealth Policy Studies Unit. Retrieved 6 December 2009.