Cycasin
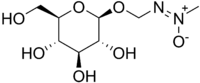 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
[(E)-Methyl-ONN-azoxy]methyl β-D-glucopyranoside[1] | |
| Other names
β-D-Glucosyloxyazoxymethane; Methylazoxymethanol β-D-glucoside; Cycas revoluta glucoside | |
| Identifiers | |
| 14901-08-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:CHEBI:17074 |
| ChemSpider | 4573631 |
| KEGG | C01418 |
| MeSH | D003492 |
| PubChem | 5459896 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H16N2O7 | |
| Molar mass | 252.22 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Cycasin is a phytotoxin found in cycads such as Cycas revoluta and Zamia pumila. Both plants are used to produce sago. The butterfly Eumaeus atala, whose larvae feed on Z. pumila, also contains the compound. The seeds of C. revoluta contain the highest level of the toxin.
It induces hepatotoxicity and Zamia staggers, a fatal nervous disease affecting cattle where they browse on the leaves or fruit of cycads.
The enzyme methyl-ONN-azoxymethanol beta-D-glucosyltransferase uses the two substrates UDP-glucose and methyl-ONN-azoxymethanol to produce UDP and cycasin.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ b-D-Glucosyloxyazoxymethane, ChemSpider
- ↑ Tadera K, Yagi F, Arima M, Kobayashi A (1985). "Formation of cycasin from methylazoxymethanol by UDP-glucosyltransferase from leaves of Japanese cycad". Agric. Biol. Chem. 49 (9): 2827–2828. doi:10.1271/bbb1961.49.2827.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.