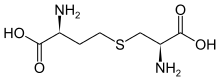
Cystathionine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
S-((R)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)-L-homocysteine | |
| Other names
L-Cystathionine; S-[(2R)-2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl]-L-homocysteine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 56-88-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17755 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL209241 |
| ChemSpider | 388392 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.269 |
| KEGG | C00542 |
| MeSH | Cystathionine |
| PubChem | 439258 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H14N2O4S | |
| Molar mass | 222.26 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Cystathionine is an intermediate in the synthesis of cysteine.
An excess in the urine is called cystathioninuria.
Biosynthetically, cystathionine is generated from homocysteine and serine by cystathionine beta synthase (upper reaction in the diagram below). It is then cleaved into cysteine and α-ketobutyrate by cystathionine gamma-lyase (lower reaction).
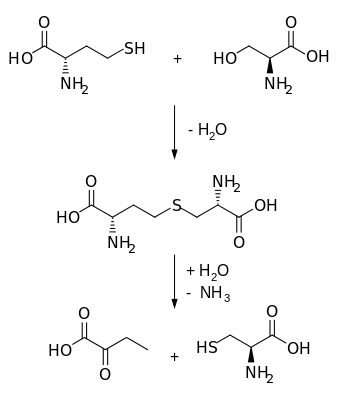
Cysteine metabolism. Cystathionine beta synthase catalyzes the upper reaction and cystathionine gamma-lyase catalyzes the lower reaction.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/18/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.