Daidzin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
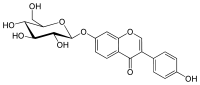
| IUPAC name
3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one | |
| Other names
Daidzoside Daidzein 7-glucoside Daidzein-7-glucoside Daidzein 7-O-glucoside daidzein 7-O-beta-D-glucoside | |
| Identifiers | |
| 552-66-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:42202 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL486422 |
| ChemSpider | 97088 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.107.506 |
| PubChem | 107971 |
| UNII | 4R2X91A5M5 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H20O9 | |
| Molar mass | 416.38 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Daidzin is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as isoflavones. Daidzin can be found in Japanese plant kudzu (Pueraria lobata, Fabaceae) and from soybean leaves.[1]
Daidzin is the 7-O-glucoside of daidzein.
Daidzin has shown the potential for the treatment of alcohol dependency (antidipsotropic) based on animal models.[2][3]
List of plants that contain the chemical
- Pueraria candollei[4]
- Pueraria lobata[5]
- Pueraria thomsonii[6]
- Pueraria thunbergiana[7]
Notes and references
- ↑ Osman, S; Fett, W (1983). "Isoflavone glucoside stress metabolites of soybean leaves". Phytochemistry. 22 (9): 1921. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(83)80013-2.
- ↑ Rezvani, A; Overstreet, David H; Perfumi, Marina; Massi, Maurizio (2003). "Plant derivatives in the treatment of alcohol dependency". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 75 (3): 593. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(03)00124-2.
- ↑ Keung WM; Vallee BL (February 1998). "Kudzu root: an ancient Chinese source of modern antidipsotropic agents". Phytochemistry. 47 (4): 499–506. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(97)00723-1. PMID 9461670.
- ↑ Pongkitwitoon B; Sakamoto S; Tanaka H; et al. (December 2009). "Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Total Isoflavonoids in Pueraria candollei Using Anti-Puerarin and Anti-Daidzin Polyclonal Antibodies". Planta Medica. 76 (8): 831–6. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1240725. PMID 20033865.
- ↑ Jin WS; Tan YY; Chen YG; Wang Y (January 2003). "[Determination of puerarin, daidzin and daidzein in root of Pueraria lobata of different origin by HPLC]". Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi (in Chinese). 28 (1): 49–51. PMID 15015267.
- ↑ Zhou HY; Wang JH; Yan FY (May 2007). "[Separation and determination of puerarin, daidzin and daidzein in stems and leaves of Pueraria thomsonii by RP-HPLC]". Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi (in Chinese). 32 (10): 937–9. PMID 17655152.
- ↑ Park EK; Shin J; Bae EA; Lee YC; Kim DH (December 2006). "Intestinal bacteria activate estrogenic effect of main constituents puerarin and daidzin of Pueraria thunbergiana". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 29 (12): 2432–5. doi:10.1248/bpb.29.2432. PMID 17142977.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/16/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.