Dihydrotanshinone
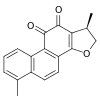 2D Structure | |
 3D Conformer | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1R)-1,6-Dimethyl-1,2-dihydronaphtho[1,2-g][1]benzofuran-10,11-dione | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,6-dimethyl-1,2-dihydrophenanthro[1,2-b]furan-10,11-dione | |
| Other names
15,16-dihydrotanshinone I, phenanthro[1,2-b]furan-10,11-dione, 1,2-dihydro-1,6-dimethyl- | |
| Identifiers | |
| 87205-99-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Abbreviations | DI |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.222.905 |
| PubChem | 11425923 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H14O3 | |
| Molar mass | 278.31 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Red powder |
| Density | 1.32 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 479.2 °C (894.6 °F; 752.3 K) |
| 12.9 mg/L (est.) | |
| Solubility in ethanol | 1 mg/mL, clear orange to red |
| log P | log Kow = 3.93 (est) |
| Vapor pressure | 3.41x10−9 mmHg |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dihydrotanshinone I (DI) is a naturally occurring compound extracted from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, also known as Chinese sage, red sage root, and the Chinese herbal Dan Shen. It belongs to a class of lipophilic abietane biterpenoids[2] and has been reported to have cytotoxicity to a variety of tumor cells.[3] Since they were first discovered, over 40 related compounds and over 50 hydrophilic compounds have been isolated from Dan Shen.[2]
References
- ↑ "Dihydrotanshinone I". PubChem. PubChem. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
- 1 2 "HSDB: DIHYDROTANSHINONE I". NIH. Retrieved 1 September 2015.
- ↑ Bian, Weipeng; et al. "Dihydrotanshinone I inhibits angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo". ABBS. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/9/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.