Dvinosauria
| Dvinosauria Temporal range: Late Carboniferous - Early Triassic | |
|---|---|
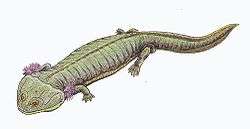 | |
| Dvinosaurus primus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | †Temnospondyli |
| Suborder: | †Dvinosauria Yates and Warren, 2000 |
| Subgroups | |
|
See text. | |
Dvinosaurs are one of several new clades of Temnospondyl amphibians named in the phylogenetic review of the group by Yates and Warren 2000. They represent a group of primitive semi-aquatic to completely aquatic amphibians, and are known from the Late Carboniferous to the Early Triassic, being most common in the Permian period. Their distinguishing characteristics are a reduction of the otic notch; the loss of a flange on the rear side of the pterygoid; and 28 or more presacral vertebrae.
Trimerorhachidae is the most basal family of dvinosaurs. Most other dvinosaurs are placed in the superfamily Dvinosauroidea. Within Dvinosauroidea are two families, Eobrachyopidae and Tupilakosauridae, as well as dvinosaurs that cannot be placed in either family, such as Dvinosaurus and Kourerpeton. A 2008 phylogenetic analysis found Eobrachyopidae to be paraphyletic, representing a grade of basal dvinosauroids. Below is a cladogram showing the phylogenetic relationships of dvinosaurs from Englehorn et al. (2008):[1]
| Dvinosauria |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
References
- ↑ Englehorn, J.; Small, B.J.; Huttenlocker, A. (2008). "A redescription of Acroplous vorax (Temnospondyli: Dvinosauria) based on new specimens from the Early Permian of Nebraska and Kansas, U.S.A.". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 28 (2): 291–305. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2008)28[291:AROAVT]2.0.CO;2.
- Laurin, M. and Steyer, J-S (2000) Phylogeny and Apomorphies of Temnospondyls, The Tree of Life Web Project
- Yates, A. M., and Warren A. A., 2000, The phylogeny of the ‘higher’ temnospondyls (Vertebrata: Choanata) and its implications for the monophly and origins of the Stereospondyli: Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, v. 128, p. 77-121.
External links
- Temnospondyli: Limnarchia at Palaeos
- Dvinosauria at Mikko's Phylogeny Archive (cladogram based on Yates and Warren 2000)
- Suborder †Dvinosauria - Scientific Hierarchy at the Taxonomicon