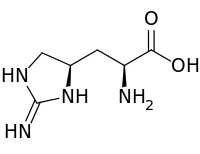
Enduracididine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-[(4R)-2-Imino-4-imidazolidinyl]-L-alanine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 24775830 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 172.19 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Enduracididine is an α-amino acid that is non-proteinogenic. It corresponds to alanine with 2-imino-4-imidazolidinyl group in place of a methyl hydrogen.
Biological roles
Enduracididine is not genetically encoded in protein sequences, but rather is generated as a posttranslational modification. For example, enduracididine is found in the antibacterial compound teixobactin.[1]
References
- ↑ Ling, LL; Schneider, T; Peoples, AJ; Spoering, AL; Engels, I; Conlon, BP; Mueller, A; Schäberle, TF; Hughes, DE; Epstein, S; Jones, M; Lazarides, L; Steadman, VA; Cohen, DR; Felix, CR; Fetterman, KA; Millett, WP; Nitti, AG; Zullo, AM; Chen, C; Lewis, K (22 January 2015). "A new antibiotic kills pathogens without detectable resistance.". Nature. 517 (7535): 455–9. doi:10.1038/nature14098. PMID 25561178.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
