Epsilon Tauri
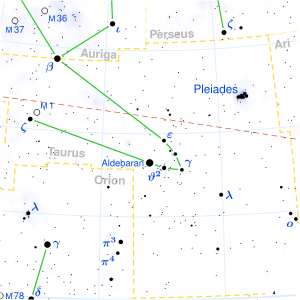 The position of ε Tauri in the Taurus constellation. | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Taurus |
| Right ascension | 04h 28m 37.00s[1] |
| Declination | +19° 10′ 50″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +3.53[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K0III[2] |
| B−V color index | 1.014[1] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 106.19 ± 0.38[1] mas/yr Dec.: -37.84 ± 0.30[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 22.24 ± 0.25[1] mas |
| Distance | 147 ± 2 ly (45.0 ± 0.5 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 2.7 ± 0.1[2] M☉ |
| Radius | 12.692 ± 0.545 [3] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 97 ± 8[4] L☉ |
| Temperature | 4901 ± 20[2] K |
| Metallicity | +0.17 ± 0.04[2] |
| Age | 625 × 106 [2] years |
| Other designations | |
Epsilon Tauri (ε Tauri, abbreviated Epsilon Tau, ε Tau), also named Ain,[5] is an orange giant star located approximately 45 parsecs (147 light-years) from the Sun in the constellation of Taurus.[2] An extrasolar planet (designated Epsilon Tauri b, later named Amateru) is believed to be orbiting the star.
It is a member of the Hyades open cluster. As such its age is well constrained at 625 million years.[4] It is claimed to be the heaviest among planet-harboring stars with reliable initial masses[4] although the star HD 13189 is potentially more massive.[6] Given its large mass, this star, though presently of spectral type K0 III, was formerly of spectral type A that has now evolved off the main sequence into the giant phase. It is regarded as a red clump giant; that is, a core-helium burning star.[4]
Since Epsilon Tauri lies near the plane of the ecliptic, it is sometimes occulted by the Moon and (very rarely) by planets.
It has an 11th magnitude companion 182 arcseconds from the primary.
Nomenclature
ε Tauri (Latinised to Epsilon Tauri) is the star's Bayer designation; it also bears the Flamsteed designation of 74 Tauri. On discovery the planet was designated Epsilon Tauri b (or Ain b).
The star bore the traditional name Ain (Arabic عين for "eye") and was given the name Oculus Boreus (Latin for "Northern eye") by John Flamsteed.[7][8] In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[9] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016[10] included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included Ain for this star.
In July 2014 the International Astronomical Union launched a process for giving proper names to certain exoplanets.[11] The process involved public nomination and voting for the new names.[12] In December 2015, the IAU announced the winning name was Amateru for this planet.[13]
The winning name was based on that submitted by the Kamagari Astronomical Observatory of Kure, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan: namely 'Amaterasu', the Shinto goddess of the Sun, born from the left eye of the god Izanagi. The IAU substituted 'Amateru' - which is a common Japanese appellation for shrines when they enshrine Amaterasu - because 'Amaterasu' is already used for an asteroid (10385 Amaterasu).[14]
Planetary system
In 2007 a massive extrasolar planet was reported orbiting the star with a period of 1.6 years in a somewhat eccentric orbit. Its discoverers claimed it was the first planet ever discovered in an open cluster.[4]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b (Amateru) | >7.6 (± 0.2) MJ | 1.93 (± 0.03) | 594.9 (± 5.3) | 0.151 (± 0.023) | — | — |
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Entry for star HIP 20889". Vizier Catalogue Service. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Notes for planet eps Tau b". The Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
- ↑ Gerard T. van Belle and Kaspar von Braun (2009). "Directly Determined Linear Radii and Effective Temperatures of Exoplanet Host Stars" (abstract). The Astrophysical Journal. 694 (2): 1085–1098. arXiv:0901.1206
 . Bibcode:2009ApJ...694.1085V. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/694/2/1085.(web Preprint)
. Bibcode:2009ApJ...694.1085V. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/694/2/1085.(web Preprint) - 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sato, Bun'ei; et al. (2007). "A Planetary Companion to the Hyades Giant ε Tauri". The Astrophysical Journal. 661 (1): 527–531. Bibcode:2007ApJ...661..527S. doi:10.1086/513503.
- ↑ "IAU Catalog of Star Names". Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ↑ "Notes for planet HD 13189 b". The Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia. Retrieved 2015-09-15.
- ↑ Flamsteed, John (1725). Historia Coelestis Britannica. H. Meere. p. 47.
- ↑ Allen, Richard Hickley (1963). Star Names – Their Lore and Meaning. Dover Books. p. 391.
- ↑ "IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)". Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ↑ "Bulletin of the IAU Working Group on Star Names, No. 1" (PDF). Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ↑ NameExoWorlds: An IAU Worldwide Contest to Name Exoplanets and their Host Stars. IAU.org. 9 July 2014
- ↑ NameExoWorlds The Process
- ↑ Final Results of NameExoWorlds Public Vote Released, International Astronomical Union, 15 December 2015.
- ↑ NameExoWorlds The Approved Names
External links
- "Star Names". Frosty Drew Observatory. Retrieved 2008-06-24.
- Epsilon Tauri at the SIMBAD Astronomical Database.
Coordinates: ![]() 04h 28m 37.0s, +19° 10′ 49″
04h 28m 37.0s, +19° 10′ 49″