Esfenvalerate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
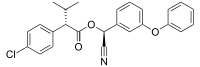
| Systematic IUPAC name
(S)-cyano (3-phenoxyphenyl) methyl-(S)-4-chloro-alpha-(1-methylethyl) benzeneacetate | |
| Other names
Asana (S)-Fenvalerate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 66230-04-4 | |
| ChemSpider | 8517510 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.118.804 |
| Properties | |
| C25H22ClNO3 | |
| Molar mass | 419.91 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.211 g/cm3 |
| Vapor pressure | 0 mmHg at 25 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Esfenvalerate is a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide marketed under the brand Asana.[2] It is the (S)-enantiomer of fenvalerate.[3]
In the United States, a limit of .05 ppm of the chemical's residue is permissible in food.[4]
References
- ↑ Kelly, Kevin. "Environmental Fate of Esfenvalerate" (PDF). California Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved January 10, 2013.
- ↑ Fishel, Frederick M. (2012). "Pesticide Toxicity Profile: Synthetic Pyrethroid Pesticides". University of Florida. Retrieved January 10, 2013.
- ↑ "Esfenvalerate". EXTONET (Extension Toxicology Network). Cooperative Extension Offices of Cornell University, Michigan State University, Oregon State University, and University of California at Davis. May 1994. Retrieved January 10, 2013.
- ↑ The Code of Federal Regulations of the United States of America. U.S. Government Printing Office. 2006. pp. 445–446.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.