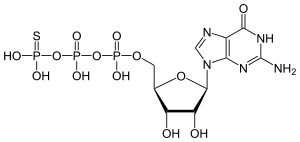
GTPgammaS
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[(2S,3R,4S,5S)-5-(2-amino-6-oxo-3H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl dihydroxyphosphinothioyl hydrogen phosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 37589-80-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| PubChem | 37792 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H16N5O13P3S | |
| Molar mass | 539.24 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
GTPgammaS (GTPγS, guanosine 5'-O-[gamma-thio]triphosphate) is a non-hydrolyzable or slowly hydrolyzable G-protein-activating analog of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). Many GTP binding proteins demonstrate activity when bound to GTP, and are inactivated via the hydrolysis of the phosphodiester bond that links the γ-phosphate to the remainder of the nucleotide, leaving a bound guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and releasing an inorganic phosphate. This usually occurs rapidly, and the GTP binding protein can then only be activated by exchanging the GDP for a new GTP molecule. The substitution of sulfur for one of the oxygens of the γ-phosphate of GTP creates a nucleotide that either cannot be hydrolyzed or is only slowly hydrolyzed. This prevents the GTP binding proteins from being inactivated, and allows the cellular processes that they carry out when active to be more easily studied. The consequences of the constitutive activation of GTP binding proteins include stimulation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis, cyclic AMP accumulation or elimination, and activation of specific proto-oncogenes. The 35S labelled radioligand of the compound, 35SGTPγS, is used in autoradiography and G-protein binding studies.