Geography of Hungary
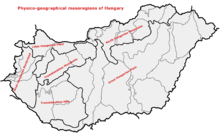
1., Great Hungarian Plain
2., North Hungarian Mountains
3., Transdanubian Mountains
4., Transdanubian Hills
5., Little Hungarian Plain
6., West-Hungarian Borderland
With a land area of 93,028 square km, Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It measures about 250 km from north to south and 524 km from east to west. It has 2,106 km of boundaries, shared with Austria to the west, Serbia, Croatia and Slovenia to the south and southwest, Romania to the southeast, Ukraine to the northeast, and Slovakia to the north.
Hungary's modern borders were first established after World War I when, by the terms of the Treaty of Trianon in 1920, it lost more than 71% of what had formerly been the Kingdom of Hungary, 58.5% of its population, and 32% of the Hungarians. The country secured some boundary revisions from 1938 to 1941: In 1938 the First Vienna Award gave back territory from Czechoslovakia, in 1939 Hungary occupied Carpatho-Ukraine. In 1940 the Second Vienna Award gave back Northern Transylvania and finally Hungary occupied the Bácska and Muraköz regions during the Invasion of Yugoslavia. However, Hungary lost these territories again with its defeat in World War II. After World War II, the Trianon boundaries were restored with a small revision that benefited Czechoslovakia.
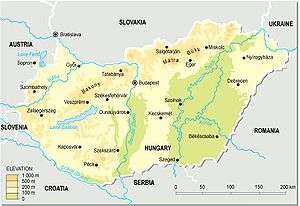
Most of the country has an elevation of fewer than 200 m. Although Hungary has several moderately high ranges of mountains, those reaching heights of 300 m or more cover less than 2% of the country. The highest point in the country is Kékes (1,014 m) in the Mátra Mountains northeast of Budapest. The lowest spot is 77.6 m above sea level, located in the south of Hungary, near Szeged.
The major rivers in the country are the Danube and Tisza. The Danube also flows through parts of Germany, Austria, Croatia, Slovakia, Serbia, and Romania.It is navigable within Hungary for 418 kilometers. The Tisza River is navigable for 444 km in the country. Less important rivers include the Drava along the Croatian border, the Rába, the Szamos, the Sió, and the Ipoly along the Slovakian border. Hungary has three major lakes. Lake Balaton, the largest, is 78 km long and from 3 to 14 km wide, with an area of 592 square km. Hungarians often refer to it as the Hungarian Sea. It is Central Europe's largest freshwater lake and an important recreation area. Its shallow waters offer good summer swimming, and in winter its frozen surface provides excellent opportunities for winter sports. Smaller bodies of water are Lake Velence (26 square km) in Fejér County and Lake Fertő (Neusiedler See—about 82 square km within Hungary), and the artificial Lake Tisza.
Hungary has three major geographic regions (which are subdivided to seven smaller ones): the Great Alföld, lying east of the Danube River; the Transdanubia, a hilly region lying west of the Danube and extending to the Austrian foothills of the Alps; and the North Hungarian Mountains, which is a mountainous and hilly country beyond the northern boundary of the Great Hungarian Plain.
The country's best natural resource is fertile land, although soil quality varies greatly. About 70% of the country's total territory is suitable for agriculture; of this portion, 72% is arable land. Hungary lacks extensive domestic sources of energy and raw materials needed for industrial development.
Rivers and lakes
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Plains and hills
- Main articles: Little Hungarian Plain, Transdanubia, Great Alföld.

The Little Alföld or Little Hungarian Plain is a plain (tectonic basin) of approximately 8,000 km2 in northwestern Hungary, southwestern Slovakia and eastern Austria, along the lower course of the Rába River, with high quality fertile soils.
The Transdanubia region lies in the western part of the country, bounded by the Danube River, the Drava River, and the remainder of the country's border with Slovenia and Croatia. It lies south and west of the course of the Danube. It contains Lake Fertő and Lake Balaton. The region consists mostly of rolling hills. Transdanubia is primarily an agricultural area, with flourishing crops, livestock, and viticulture. Mineral deposits and oil are found in Zala county close to the border of Croatia.
The Great Alföld contains the basin of the Tisza River and its branches. It encompasses more than half of the country's territory. Bordered by mountains on all sides, it has a variety of terrains, including regions of fertile soil, sandy areas, wastelands, and swampy areas. Hungarians have inhabited the Great Plain for at least a millennium. Here is found the puszta, a long, and uncultivated expanse (the most famous such area still in existence is the Hortobágy National Park), with which much Hungarian folklore is associated. In earlier centuries, the Great Plain was unsuitable for farming because of frequent flooding. Instead, it was the home of massive herds of cattle and horses. In the last half of the 19th century, the government sponsored programs to control the riverways and expedite inland drainage in the Great Plain. With the danger of recurrent flooding largely eliminated, much of the land was placed under cultivation, and herding ceased to be a major contributor to the area's economy.
Mountains
- Main articles: Alpokalja, Transdanubian Mountains, Mecsek, North Hungarian Mountains.
Although the majority of the country has an elevation lesser than 300 m, Hungary has several moderately high ranges of mountains. They can be classified to four geographic regions, from west to east: Alpokalja, Transdanubian Mountains, Mecsek and North Hungarian Mountains. Alpokalja (literally the foothills of the Alps) is located along the Austrian border; its highest point is Írott-kő with an elevation of 882 metres. The Transdanubian Mountains stretch from the west part of Lake Balaton to the Danube Bend near Budapest, where it meets the North Hungarian Mountains. Its tallest peak is the 757 m high Pilis. Mecsek is the southernmost Hungarian mountain range, located north from Pécs - Its highest point is the Zengő with 682 metres.
The North Hungarian Mountains lie north of Budapest and run in a northeasterly direction south of the border with Slovakia. The higher ridges, which are mostly forested, have rich coal and iron deposits. Minerals are a major resource of the area and have long been the basis of the industrial economies of cities in the region. Viticulture is also important, producing the famous Tokaji wine. The highest peak of it is the Kékes, located in the Mátra mountain range.
Highest peaks
| # | Name | Height | Mountain range | Geographic region |
| 1. | Kékes | 1014 m | Mátra | North Hungarian Mountains |
| 2. | Galyatető | 964 m | Mátra | North Hungarian Mountains |
| 3. | Istállós-kő | 959 m | Bükk | North Hungarian Mountains |
| 4. | Bálvány | 956 m | Bükk | North Hungarian Mountains |
| 5. | Tar-kő | 950 m | Bükk | North Hungarian Mountains |
| 6. | Csóványos | 938 m | Börzsöny | North Hungarian Mountains |
| 7. | Nagy-Milic | 894 m | Zemplén Mountains | North Hungarian Mountains |
| 8. | Írott-kő | 882 m | Kőszeg Mountains | Alpokalja |
| 9. | Nagyhideghegy | 864 m | Börzsöny | North Hungarian Mountains |
| 10. | Tót-hegyes | 814 m | Mátra | Northern Medium Mountains |
Climate

Hungary has a mainly continental climate, with cold winters and warm to hot summers. The average annual temperature is about 10 °C (50 °F), in summer 27 to 35 °C (81 to 95 °F), and in winter 0 to −15 °C (32 to 5 °F), with extremes ranging from about 42 °C (108 °F) in summer to −35 °C (−31 °F) in winter. Average yearly rainfall is about 600 mm (23.6 in). Distribution and frequency of rainfall are unpredictable. The western part of the country usually receives more rain than the eastern part, where severe droughts may occur in summertime. Weather conditions in the Great Plain can be especially harsh, with hot summers, cold winters, and scant rainfall.
By the 1980s, the countryside was beginning to show the effects of pollution, both from herbicides used in agriculture and from industrial pollutants. Most noticeable was the gradual contamination of the country's bodies of water, endangering fish and wildlife. Although concern was mounting over these disturbing threats to the environment, no major steps had yet been taken to arrest them.
Extreme points
Hungary's westernmost settlement is Felsőszölnök in Vas county, the easternmost is Garbolc in Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg county, the northernmost is Hollóháza in Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county and the southernmost is Kásád in Baranya county.
The country's highest point is Kékes (1014 m) while the lowest is River Tisza near Szeged (78 m).
Agriculture

Hungary, with its plains and hilly regions, is highly suitable for agriculture.
Arable land
Doubtless, one of Hungary's most important natural resources is arable land. It covers about 48.57% of the country, which is outstanding in the world (see the related map). The mass majority of the fertile soil has a good quality.
The most important agricultural zones are the Little Hungarian Plain (it has the highest quality fertile soil in average), Transdanubia, and the Great Hungarian Plain. The last covers more than half of the country (52,000 km2 in number), whereas soil quality varies extremely; the territory even contains a small, grassy semi-desert, the so-called puszta (steppe in English). Puszta is exploited by sheep and cattle raising.
The most important Hungarian agricultural products include corn, wheat, barley, oat, sunflower, poppy, potato, millet, sugar-beet, flax, and many other plants. There are also some newly naturalized plants too, for example amaranth. Poppy seed is part of the traditional Hungarian cuisine.

The country is well known for producing high quality peppers, which are often made into paprika. There are numerous fruits reared, including many subspecies of apple, pear, peach, grape, apricot, water melon, cantaloupe, etc.
Hungary does not grow any GMO products, thus these products are mainly imported from the United States. They cannot, however, be distributed without a mark on the wrapping.
Viticulture
Wine production has a long history in Hungary. There are two languages in Europe in which the word for "wine" does not derive from the Latin, being Greek – and Hungarian. The Hungarian word is bor.
Viticulture has been recorded in the territory of today's Hungary already in the Roman times, who were responsible for the introduction of the cultivation of wines. The arriving Hungarians took over the practice and maintained it ever since.
Today, there are numerous wine regions in Hungary, producing quality and inexpensive wines as well, comparable to Western European ones. The majority of the country's wine regions are located in the mountains or in the hills, such as Transdanubian Mountains, North Hungarian Mountains, Villány Mountains, and so on. Important ones include the regions of Eger, Hajós, Somló, Sopron, Villány, Szekszárd, and Tokaj-Hegyalja.
Forestry
19% of the country is covered by forests. These are mainly mountainous areas, such as the North Hungarian and the Transdanubian Mountains, and the Alpokalja. The composition of forests is various, with trees like fir, beech, oak, willow, acacia, plane, etc.
Statistics and notes
| Geography of Hungary | |
| Geographic coordinates: | 47°00′N 20°00′E / 47.000°N 20.000°E |
| Map references: | Europe |
| Area: | |
| total: | 93,030 km2 |
| land: | 92,340 km2 |
| water: | 690 km2 |
| Land boundaries, total: | 2,009 km |
| border countries: | Austria (366 km), Croatia (329 km), Romania (443 km), Serbia (151 km), Slovakia (679 km), Slovenia (102 km), Ukraine (103 km) |
| Coastline: | 0 km (landlocked) |
| Maritime claims: | none (landlocked) |
| Climate: | temperate; cold, cloudy, humid winters; warm summers |
| Terrain: | mostly flat to rolling plains; hills and low mountains on the Slovakian border |
| Elevation extremes: | |
| lowest point: | Tisza River 78 m |
| highest point: | Kékes 1,014 m |
| Natural resources: | bauxite, coal, natural gas, fertile soils, arable land |
| Land use: | |
| arable land: | 51% |
| permanent crops: | 3.6% |
| permanent pastures: | 12.4% |
| forests and woodland: | 19% |
| other: | 14% (1999) |
| Irrigated land: | 2,060 km2 (1993 est.) |
| Environment - current issues: | the approximation of Hungary's standards in waste management, energy efficiency, and air, soil, and water pollution with environmental requirements for EU accession will require large investments |
| Environment - international agreements: | |
| party to: | Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands |
| signed, but not ratified: | Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol |
| Geography - note: | landlocked; strategic location astride main land routes between Western Europe and Balkan Peninsula as well as between Ukraine and Mediterranean basin |
Pictures
-

A famous tourist destination: the Danube Bend
-

The mountainous part of the county: in the North Hungarian Mountains, more precisely in Mátra
-

Old wells in the Great Alföld
-

Typical countryside in Transdanubia
-

Balaton, the greatest lake of Hungary is sometimes referred as the "Hungarian sea".
-

Mecsek, Southern Hungary
-

The waterfall of Lillafüred
-

Viticulture near Villány
See also
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from the Library of Congress Country Studies website http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/.
This article incorporates public domain material from the Library of Congress Country Studies website http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/. This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html.
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Geography of Hungary. |

