Growth hormone 1
| View/Edit Human | |||
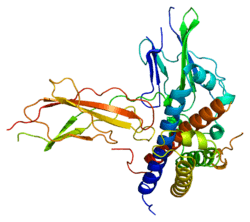
Somatotropin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GH1 gene.[2]
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin family of hormones that play an important role in growth control. The gene, along with four other related genes, is located at the growth hormone locus on chromosome 17 where they are interspersed in the same transcriptional orientation, an arrangement thought to have evolved by a series of gene duplications. The five genes share a remarkably high degree of sequence identity. Alternative splicing generates additional isoforms of each of the five growth hormones, leading to further diversity and potential for specialization. This particular family member is expressed in the pituitary but not in placental tissue as is the case for the other four genes in the growth hormone locus. Mutations in or deletions of the gene lead to growth hormone deficiency and short stature.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Barsh GS, Seeburg PH, Gelinas RE (Aug 1983). "The human growth hormone gene family: structure and evolution of the chromosomal locus". Nucleic Acids Res. 11 (12): 3939–58. doi:10.1093/nar/11.12.3939. PMC 326017
 . PMID 6306568.
. PMID 6306568. - ↑ "Entrez Gene: GH1 growth hormone 1".
Further reading
- Binder G (2003). "Isolated growth hormone deficiency and the GH-1 gene: update 2002.". Horm. Res. 58 Suppl 3: 2–6. doi:10.1159/000066476. PMID 12435888.
- Waxman DJ, O'Connor C (2007). "Growth hormone regulation of sex-dependent liver gene expression.". Mol. Endocrinol. 20 (11): 2613–29. doi:10.1210/me.2006-0007. PMID 16543404.
- Cattini PA, Yang X, Jin Y, Detillieux KA (2006). "Regulation of the human growth hormone gene family: possible role for Pit-1 in early stages of pituitary-specific expression and repression.". Neuroendocrinology. 83 (3–4): 145–53. doi:10.1159/000095522. PMID 17047377.
- Wagner K, Hemminki K, Försti A (2007). "The GH1/IGF-1 axis polymorphisms and their impact on breast cancer development". Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 104 (3): 233–48. doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9411-9. PMID 17082888.