Hyaline
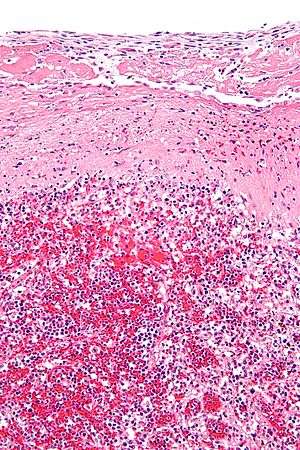
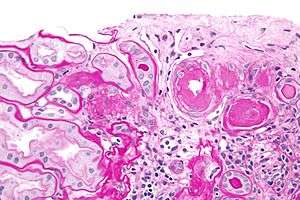
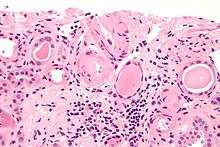
A hyaline substance is one with a glassy appearance. The word is derived from Greek: ὑάλινος transparent and Greek: ὕαλος crystal, glass.
Histopathology
In histopathological medical usage, a hyaline substance appears glassy and pink after being stained with haematoxylin and eosin — usually it is an acellular, proteinaceous material. An example is hyaline cartilage, a transparent, glossy articular joint cartilage.
Some mistakenly refer to all hyaline as hyaline cartilage; however, hyaline is a descriptive term that applies to other material besides the cartilage itself.
Arterial hyaline is seen in aging, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus and in association with some drugs (e.g. calcineurin inhibitors). It is bright pink with PAS staining.
Ichthyology and entomology
In ichthyology and entomology, the hyaline term usage denotes a type of colorless, transparent substance.
See also
- Infant respiratory distress syndrome, previously known as hyaline membrane disease.
- Hyaloserositis
- Hyaline arteriolosclerosis
References
- IMA Mycological Glossary: Hyaline.
- Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary, 19th Edition. Donald Venes ed. 1997 F.A. Davis. Page 1008.