Intel 5 Series
Intel 5 Series is a computing architecture introduced in 2008 that improves the efficiency and balances the use of communication channels in the motherboard. The architecture consists primarily of a central processing unit (CPU) (connected to the graphics card and memory) and a single chipset (connected to motherboard components). All motherboard communications and activities circle around these two devices.
The architecture is a product of adjustments made to the Intel 4 Series to deliver higher performance motherboards while maintaining efficiency and low power. The changes revolve around chipset and processor design, in conjunction with a rearrangement of functions and controllers. The result is the first major change in many years of computing.
Design concept
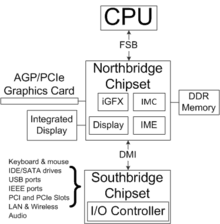
The concept of the architecture was to improve motherboard mechanics to keep pace with the CPU as it gained more speed and multiplied in number of cores. In the previous architecture, the CPU was communicating heavily with the motherboard's central component, the Northbridge chipset, as it was the intermediary between the CPU, memory, and, in most cases, graphics card. The CPU would communicate with the Northbridge chipset when it needed data from the memory or when it needed to output graphics to the display. This arrangement caused the communication channel known as the front-side bus (FSB) to be heavily used. It was not long till either the FSB would reach full capacity or operate inefficiently with more cores. With the memory controller and/or graphics core moved into the processor, the reliance of separate motherboard chipsets for these functions are reduced.
Ibex Peak[1][2]
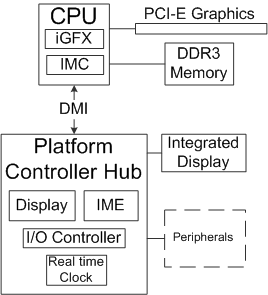
The Ibex Peak chipset includes only Platform Controller Hub (PCH) per model, which provides peripheral connections, and display controllers for CPU with integrated graphics via Flexible Display Interface (excluding P-models). Additionally, the PCH is connected to the CPU via Direct Media Interface (DMI).
Taking advantage of Intel Nehalem CPUs with integrated graphics and PCI Express ports, the Intel management engine (ME) and a display controller for integrated graphics, once housed in north bridge, are moved into the Platform Controller Hub (PCH). The I/O Controller Hub (ICH) function is integrated into the PCH, removing the need for separate north bridge and south bridge.
| Model | Top marking |
|---|---|
| P55 Express | BD82P55 |
| H55 Express | BD82H55 |
| H57 Express | BD82H57 |
| Q57 Express | BD82Q57 |
| B55 Express | ? |
| Model | Top marking |
|---|---|
| PM55 Express | BD82PM55 |
| QM57 Express | BD82QM57 |
| HM55 Express | BD82HM55 |
| HM57 Express | BD82HM57 |
| QS57 Express | BD82QS57 |
| Model | Top marking |
|---|---|
| 3400 | BD3400 |
| 3420 | BD3420 |
| 3450 | BD3450 |
Tylersburg
Unlike the Ibex Peak chipsets, The Tylersburg family of chipsets do not include PCH, and the I/O Hub mainly provides extra PCI Express 2.0 ports. Peripheral connections are provided by I/O Controller Hub (ICH) connected to DMI interface. Intel 5 series IOH support ICH10, while Intel 5500 Series IOH support ICH9 or ICH10.
| Model | Top marking |
|---|---|
| X58[3] | AC82X58 SLGBT (B2), AC82X58 SLGMX 901076 (B3), AC82X58 SLH3M 904727 (C2) |
| Model | Top marking |
|---|---|
| 5520 | AC5520 SLGMU 901037 (B-3), AC5520 SLH3P 904729 (C-2) |
| 5500 | AC5500 SLGMT 901036 (B-3), AC5500 SLH3N 904728 (C-2) |
See also
References
External links
Ibex Peak
- Intel 5 series: H55, H57, P55, Q57
- Mobile Intel 5 series: HM55, HM57, PM55, QM57, QS57
- Intel 3400 and 3420 Chipsets Overview
- Intel 5 Series Chipset and Intel 3400 Series Chipset
- Support for the Intel 5 Series Chipset
- Intel's "Ibex Peak"
Tylersburg
- Intel X58 Express Chipset
- Intel 5500 series: 5500, 5520
- Intel 5500 and 5520 Chipset