Islamic interlace patterns
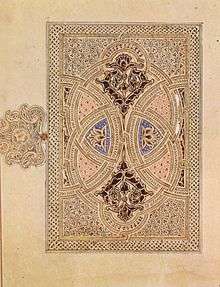
Interlacing patterns dominate Islamic ornament. They can be broadly divided into arabesque, using curving plant-based elements, and girih using mostly geometrical forms with straight lines or regular curves. Both of these forms of Islamic art developed from the rich interlacing patterns of the Byzantine Empire, and Coptic art.
Overview
Islamic art makes use of two broad categories of interlacing patterns, namely arabesque, using curving plant-based elements, and girih using mostly geometrical forms. Eva Baer, in her book Islamic Ornament (1998), describes the art:
....the intricate interlacings common in later medieval Islamic art, are already prefigured in Umayyad architecture revetments: in floor mosaics, window grilles, stone and stucco carvings and wall paintings(Khirbat al-Mafjar, Qusayr'Amra, Qasr al-Hayr al-Gharbi etc.), and in the decoration of a whole group of early east Iranian, eighth- to tenth-century metal objects.[1]
One of the first Western studies of the subject was E. H. Hankin's "The Drawing of Geometric Patterns in Saracenic Art", published in Memoirs of the Archaeological Societry of India in 1925.[2] In this essay, Hankin takes the view that the artists who created these designs used a method based on the use of the compass and the straight edge.[3] This view is supported by the majority of contemporary authorities on the subject, such as Keith Critchlow in his book, Islamic Patterns: An Analytical and Cosmological Approach.[4] This explains how ornamented objects as varied in size as a book or a mosque, were treated by artists using the same geometric methods adapted to the size and nature of the object being ornamented.[5]
On the other hand, Owen Jones describes a method whereby interlace ornament is designed on a foundation of geometric grids, with the same grids re-drawn to the size of the object.[6] In his catalog for the Crystal Palace exhibition, Jones wrote about the decorative art found in the Alhambra, where much of the decoration consists of interwoven designs, that:
The grace and refinement of Greek ornament is here surpassed. Possessing, equally with the Greeks, an appreciation of pure form, the Moors exceeded them in variety and imagination.[7]
Arabesque
The Islamic arabesque is a form of artistic decoration consisting of "surface decorations based on rhythmic linear patterns of scrolling and interlacing foliage, tendrils" or plain lines,[8] often combined with other elements. It usually consists of a single design which can be 'tiled' or seamlessly repeated as many times as desired.[9]
Girih
Girih (Persian: گره, "knot"), also girih sāzī (گره سازی, "knot making") or girih chīnī (گره چینی), is an Islamic decorative art form used in architecture and handicrafts (book covers, tapestry, small metal objects), consisting of geometric lines that form an interlaced strapwork. In Iranian architecture, gereh sazi patterns were seen in banna'i brickwork, stucco, and mosaic faience work.[10] Girih has been defined as "geometric (often star-and-polygon) designs composed upon or generated from arrays of points from which construction lines radiate and at which they intersect.[11]
Examples
-

Interlaced Islamic geometric patterns with 8-point star design in glazed ceramic
-
Alhambra Courtyard of the Lions
-

Decorative grating at the Mosque of Cordoba
-

Wallpaper group p4. From The Grammar of Ornament (1856), by Owen Jones
-

A Quran with geometric medallion of six overlapping circles and 6-point star design
-
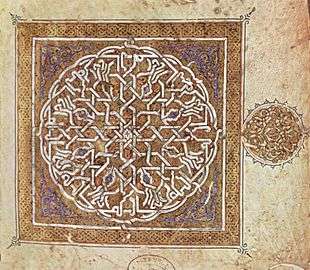
Geometrical ornament with interlaced knotwork border in a Quran, c. 1180
-

Hafez tomb
See also
- Khachkars – Armenian knotwork
- Knots and graphs – mathematical way of describing ornamental knots
References
- ↑ Eva Baer Islamic Ornament p. 41. New York University Press, 1998 ISBN 0-8147-1329-7
- ↑ "The Drawing of Geometric Patterns in Saracenic Art", "Preface"
- ↑ E. H Hankin, The Drawing of Geometric Patterns in Saracenic Art, p.2
- ↑ Keith Critchlow, Islamic Patterns: An Analytical and Cosmological Approach, p.9
- ↑ Daud Sutton, Islamic Design: A Genius for Geometry, Walker Publishing Company, 2007. p. 1. (ISBN 0-8027-1635-0)
- ↑ Owen Jones, The Grammar of Ornament, p. 72-73
- ↑ Iain Zaczek quoting Owen Jones, in his annotation of Owen Jones' The Grammar of Ornament, p.206
- ↑ Fleming, John; Honour, Hugh (1977). Dictionary of the Decorative Arts. Penguin. ISBN 978-0-670-82047-4.
- ↑ Robinson, Francis (1996). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the Islamic World. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-66993-1.
- ↑ "Gereh Sazi". Encyclopaedia Iranica Online. Retrieved 15 December 2015.
- ↑ Allen, Terry (2004). "Islamic Art and the Argument from Academic Geometry". Retrieved 15 December 2015.
Further reading
- Critchlow, Keith, Islamic Patterns : an analytical and cosmological approach, London : Thames and Hudson, 1976. ISBN 0500270716
- Yahya Abdullahi; Mohamed Rashid Bin Embi (2013). Evolution of Islamic geometric patterns. Elsevier.
External links
- Craig S. Kaplan Taprats a website devoted to Islamic design, with an applet to draw such star-like figures.


