Jean-Baptiste Olive
| Jean-Baptiste Olive | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born |
Jean Baptiste Joseph Olive July 31, 1848 Marseille |
| Died |
1936 Marseille |
| Nationality | French |
| Education | École des beaux-arts de Marseille |
| Notable work | Paris-Gare de Lyon train station, golden room of Le Train Bleu (restaurant) |
Jean-Baptiste Olive (July 31, 1848[1]- 1936) was a French painter.
Biography
Olive, the son of a wine merchant, was born in Marseille's Saint-Martin neighbourhood. Étienne Cornellier, a decorator, encouraged him to register at École des beaux-arts de Marseille where he studied under the guidance of Joanny Rave. There he received several awards including, in 1871, the live model class's first prize. While training as a decorator, he painted many scenes of Marseille, its Vieux-Port, its islands, and its seashore. In 1874 he travelled to Italy, mainly to Genoa and Venice. He occasionally participated in some of Provence's exhibitions at the time.
In 1882 he relocated to Paris. He contributed to the decoration of Cirque d’Hiver, Basilica of the Sacré Cœur and Exposition universelle de 1889 (he was awarded a silver medal for the latter). From 1874 onward he exhibited repeatedly at Salon de Paris and was awarded several prizes there. In 1881 he became a member of Société des Artistes Français.
In 1900 he won an order by the company Chemins de fer de Paris à Lyon et à la Méditerranée for two paintings created to as decoration for the Golden Room at Le Train Bleu (restaurant) designed by architect Marius Toudoire in the Paris-Gare de Lyon train station (both paintings can still be seen there).
In 1930, aged 82, he was awarded the Léon Bonnat prize.
In addition to Étienne Cornellier, his friends were painters Gustave Marius Jullien (1825-1881), Antoine Vollon, Robert Mols, Raymond Allègre and Théophile Décanis.
He was supported by several patrons, among them General Malesherbes and Marie-Louis Gassier, the owner of company Berger, a producer of pastis. In 1948, twelve years after his death, Marseille's Musée Cantini dedicated an exhibition to his centenary, displaying eighty-two of his paintings.
Artwork
Although relatively little-known outside France - unlike his Marseillais fellow citizen Adolphe Monticelli -, Olive is one of Provence's most iconic painters and an emblematic figure of the French marine art movement.
While proud of his Marseille origins, he long remained doubtful of his own painting talent. His introverted - decidedly un-Mediterranean - character was in sheer contrast with his artwork's dazzling luminosity.
His favourite themes are the sea, seashores and ports. His views of le Vieux-Port, in which the rendering of light compares to that of Félix Ziem's paintings, are especially well-known, together with his calanques (a local term for cliff-edged inlets along the coast between Marseille and La Ciotat).
Quite intriguingly, his views of le Vieux-Port depict it as seen from offshore, not from the ground.
His still lifes, the early ones frugal, the later ones more opulent and varied, generally focus on Provence fruits and ornamental tableware.
"The light's "timing", its penetration on the firm ground, its diffusion and fugitive nature are his artwork's constitutive elements." [2]
Public collections
- Paris-Gare de Lyon train station, golden room of Le Train Bleu (restaurant) :
- Le Vieux port de Marseille, 1900, oil on canvas
- Saint-Honorat, 1901, oil on canvas
- Marseille, musée Cantini :
- Carry-le-Rouet, prior to 1917, oil on canvas
- L'Épave de la Navarre, près de Carry, prior to 1917, oil on canvas
- Tempête, avant 1917, oil on canvas
- Marseille, musée Grobet-Labadié : Une Vague, oil on canvas
- Musée des beaux-arts de Marseille :
- La Corniche à Marseille, oil on canvas
- La Salute à Venise, oil on canvas
- Marine, oil on canvas
- Musée des beaux-arts de Béziers : Nature morte aux fruits, 1872, oil on canvas
- Musée d'art de Toulon :
- Port de Toulon, 1878, oil on canvas
- Calanque d'en Vau
- Le Havre, Museum of modern art André Malraux - MuMa : La Falaise, oil on canvas
- Colmar, Haut-Rhin prefecture : Le Soir, rade de Villefranche, 1893, India ink scratchboard. Study for a painting exhibited at the 1893 Salon de Paris
- São Paulo Museum of Art : Marine aux rochers
Gallery
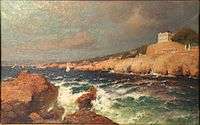 La Réserve à Marseille, Cannes, fr:Musée de la Castre.
La Réserve à Marseille, Cannes, fr:Musée de la Castre.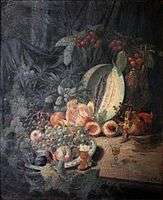 Nature morte aux fruits (1872), fr:musée des beaux-arts de Béziers.
Nature morte aux fruits (1872), fr:musée des beaux-arts de Béziers. Marine aux rochers, São Paulo Museum of Art.
Marine aux rochers, São Paulo Museum of Art. Vue du port de Marseille, private collection.
Vue du port de Marseille, private collection. The city of Marseille on Paris–Marseille railway, golden room of restaurant Le Train Bleu in Paris-Gare de Lyon train station.
The city of Marseille on Paris–Marseille railway, golden room of restaurant Le Train Bleu in Paris-Gare de Lyon train station. Nature morte à la grenade, à l'orange, aux cerises et aux figues, private collection.
Nature morte à la grenade, à l'orange, aux cerises et aux figues, private collection. Calanque d'En-Vau, private collection.
Calanque d'En-Vau, private collection.
Exhibitions
- 1882 : Plage du Prado par un temps de mistral, mention honourable
- 1885 : 3rd class medal
- 1893 : Le soir, rade de Villefranche
- 1913 : Le Matin, Côte d'Azur
- 1914 : Rochers, Côte d'Azur, La Mer, Provence
- Paris, Exposition universelle de 1889 (silver medal)
- 1948, Marseille's Musée Cantini, Jean-Baptiste Olive centenary exhibition, 82 works displayed
- 2008, Geneva, Switzerland - Marc Stammegna gallery invited by Bartha and Senarclens gallery from June 6 to July 31, 2008, « Painters of Provence », a collective exhibition featuring 22 painters including Jean-Baptiste Olive, Frédéric Montenard, Louis Valtat and Félix Ziem
- September 26, 2008 to January 25, 2009, Palais des Arts (Marseille), « Jean-Baptiste Olive - Prisme de lumière »,[3] organized by Regards de Provence foundation
Bibliography
- Benezit Dictionary of Artists. Oxford University Press. 2010. ISBN 978-0199773787. (14 volumes)
- Jean-Claude and Gérard Gamet, Jean-Baptiste Olive, sa vie, son œuvre, ed. Frebert, 1977.
- Magali Raynaud and Franck Baille, Jean-Baptiste Olive: Prisme de lumière, ed. CRES 2008, ISBN 2914374178.
- Collective work, Le Train Bleu, ed. Presse Lois Unis Service, Paris 1990, ISBN 2908557010.
References
- ↑ Archives des Bouches-du-Rhône, commune de Marseille, registre 4, acte de naissance numéro 558, année 1880 (looked upon December 13, 2014)
- ↑ Translated excerpt from museeregardsdeprovence.com
- ↑ museeregardsdeprovence.com