Kamakhya Temple
| Kamakhya Temple | |
|---|---|
| কামাখ্যা মন্দিৰ | |
|
Kamakhaya Temple | |
| Name | |
| Other names | Kamrup-Kamakhya |
| Proper name | Kamakhya Temple |
| Geography | |
| Coordinates | 26°09′59″N 91°42′20″E / 26.166426°N 91.705509°ECoordinates: 26°09′59″N 91°42′20″E / 26.166426°N 91.705509°E |
| Country | India |
| State | Assam |
| Location | Nilachal Hill, Guwahati |
| Culture | |
| Primary deity | Kamakhya |
| Important festivals | Ambubachi Mela |
| Architecture | |
| Architectural styles | Nilachal type |
| Number of temples | 6 |
| Number of monuments | 6 |
| History and governance | |
| Date built | 8th-17th century[1] |
| Creator | Various |
The Kamakhya Temple (Assamese: kāmākhyā mandir); also Kamrup-Kamakhya[2] is a Hindu temple dedicated to the mother goddess Kamakhya.[3] It is one of the oldest of the 51 Shakti Pithas.[4] Situated on the Nilachal Hill in western part of Guwahati city in Assam, India, it is the main temple in a complex of individual temples dedicated to the ten Mahavidyas: Kali, Tara, Sodashi, Bhuvaneshwari, Bhairavi, Chhinnamasta, Dhumavati, Bagalamukhi, Matangi and Kamala.[5] Among these, Tripurasundari, Matangi and Kamala reside inside the main temple whereas the other seven reside in individual temples.[6] It is an important pilgrimage destination for general Hindu and especially for Tantric worshipers.
In July 2015, the Supreme Court of India transferred the administration of the Temple from the Kamakhya Debutter Board to the Bordewri Samaj.[7]
Description
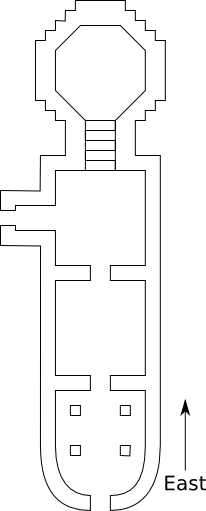
The current structural temple, built and renovated many times in the period 8th-17th century, gave rise to a hybrid indigenous style that is sometimes called the Nilachal type: a temple with a hemispherical dome on a cruciform base.[8] The temple consists of four chambers: garbhagriha and three mandapas locally called calanta, pancharatna and natamandira aligned from east to west.
Garbhagriha
The garbhagriha has a pancharatha plan[9] that rests on plinth moldings that are similar to the Surya Temple at Tezpur. On top of the plinths are dados from a later period which are of the Khajuraho or the Central Indian type, consisting of sunken panels alternating with pilasters.[10] The panels have delightful sculptured Ganesha and other Hindu gods and goddesses.[11] Though the lower portion is of stone, the shikhara in the shape of a polygonal beehive-like dome is made of brick, which is characteristic of temples in Kamrup.[12] The shikhara is circled by a number of minaret inspired angashikharas[13] of Bengal type charchala. The Shikhara, angashikharas and other chambers were built in the 16th century and after.
The inner sanctum, the garbhagriha, is below ground level and consists of no image but a rock fissure in the shape of a yoni:
The garbhagriha is small, dark and reached by narrow steep stone steps. Inside the cave there is a sheet of stone that slopes downwards from both sides meeting in a yoni-like depression some 10 inches deep. This hollow is constantly filled with water from an underground perennial spring. It is the vulva-shaped depression that is worshiped as the goddess Kamakhya herself and considered as most important pitha (abode) of the Devi.[14]
The garbhaghrihas of the other temples in the Kamakhya complex follow the same structure—a yoni-shaped stone, filled with water and below ground level.

Calanta, Pancharatna, and Natamandir
The temple consists of three additional chambers. The first to the west is the calanta, a square chamber of type atchala (similar to the 1659 Radha-Vinod Temple of Bishnupur[15]). The entrance to the temple is generally via its northern door, that is of Ahom type dochala. It houses a small movable idol of the Goddess, a later addition, which explains the name.[16] The walls of this chamber contain sculpted images of Naranarayana, related inscriptions and other gods.[17] It leads into the garbhagriha via descending steps.
The pancharatna to the west of calanta is large and rectangular with a flat roof and five smaller shikharas of the same style as the main skhikara. The middle shikhara is slightly bigger than the other four.
The natamandira extends to the west of the pancharatna with an apsidal end and ridged roof of the Ranghar type Ahom style. Its inside walls bear inscriptions from Rajeswar Singha (1759) and Gaurinath Singha (1782), which indicate the period this structure was built.[18]
History
Ancient
The earliest historical dynasty of Kamarupa, the Varmans (350-650), as well as Xuanzang, a 7th-century Chinese traveler ignore the Kamakhya; and it is assumed that the worship at least till that period was Kirata-based beyond the brahminical ambit.[19] The first epigraphic notice of Kamakhya is found in the 9th-century Tezpur plates of Vanamalavarmadeva of the Mlechchha dynasty.[20] Since the archaeological evidence too points to a massive 8th-9th century temple, [21] it can be safely assumed that the earliest temple was constructed during the Mlechchha dynasty.
The later Palas of Kamarupa kings, from Indra Pala to Dharma Pala, were followers of the Tantrik tenet and about that period Kamakhya had become an important seat of Tantrikism. The Kalika Purana (10th century) was composed and Kamakhya soon became a renowned centre of Tantrik sacrifices, mysticism and sorcery. Mystic Buddhism, known as Vajrayana and popularly called the "Sahajia cult", too rose in prominence Kamarupa in the tenth century. It is found from Tibetan records that some of the eminent Buddhist professors in Tibet, of the tenth and the eleventh centuries, hailed from Kamarupa. The Kalika Purana gives the Sanskritized names of most of the rivers and hills of Brahmaputra valley. It gives a full account of the Naraka legend, the physical description of the land and the old city of Pragjyotishpura as well as the special merit and sanctity of the Kamakhya Temple.[22]
Medieval
There is a tradition that the temple was destroyed by Kalapahar, a general of Sulaiman Karrani (1566–1572). Since the date of reconstruction (1565) precedes the possible date of destruction, and since Kalapahar is not known to have ventured so far to the east, it is now believed that the temple was destroyed not by Kalapahar but during Hussein Shah's invasion of the Kamata kingdom (1498).[23] The ruins of the temple was said to have been discovered by Vishwasingha (1515–1540), the founder of the Koch dynasty, who revived worship at the site; but it was during the reign of his son, Naranarayan (1540–1587), that the temple reconstruction was completed in 1565. The reconstruction used material from the original temples that was lying scattered about, some of which still exists today. Banerji (1925) records that this structure was further built over by the rulers of the Ahom kingdom.
According to historical records and epigraphic evidence, the main temple was rebuilt by Chilarai using the available stone ruins,[24] with the brick dome being an innovation. The current final structure has been rebuilt during the Ahom times,[25] with remnants of the earlier Koch temple carefully preserved.[26][27][28]
According to a legend the Koch Bihar royal family was banned by Devi herself from offering puja at the temple. In fear of this curse, to this day no descendants of that family dares to even look upward towards the Kamakhya hill while passing by.
Without the support of the Koch royal family the temple faced lot of hardship. By the end of 1658, the Ahoms under king Jayadhvaj Singha had conquered the Kamrup and their interests in the temple grew. In the decades that followed the Ahom kings, all who were either devout Shaivite or Shakta continued to support the temple by rebuilding and renovating it.[29]

Rudra Singha (reign 1696 to 1714) was a devout Hindu and as he grew older he decided to formally embrace the religion and become an orthodox Hindu by being initiated or taking sharan of a Guru, who would teach him the mantras and become his spiritual guide. But, he could not bear the thought of humbling himself in front of a Brahmin who is his subject. He therefore sent envoys to Bengal and summoned Krishnaram Bhattacharyya, a famous mahant of Shakta sect who lived in Malipota, near Santipur in Nadia district. The mahant was unwilling to come, but consented on being promised to be given the care of the Kamakhya temple to him. Though the king did not take sharan, he satisfied the mahant by ordering his sons and the Brahmins in his entourage to accept him as their spiritual guru.
When Rudra Singha died, his eldest son Siba Singha (reign 1714 to 1744), who became the king, gave the management of the Kamakhya temple and along with it large areas of land (Debottar land) to Mahant Krishnaram Bhattacharyya. The Mahant and his successors came to be known as Parbatiya Gosains, as they resided on top of the Nilachal hill. Many Kamakhya priests and modern Saktas of Assam are either disciples or descendants of the Parbatiya Gosains, or of the Nati and Na Gosains.[30]
Worship

It is likely that this is an ancient Khasi sacrificial site, and worshiping here still includes sacrifices. Devotees come every morning with goats to offer to Shakti.[31]
The Kalika Purana, an ancient work in Sanskrit describes Kamakhya as the yielder of all desires, the young bride of Shiva, and the giver of salvation.Shakti is known as Kamakhya.
The worship of all female deity in Assam symbolizes the "fusion of faiths and practices" of Aryan and non-Aryan elements in Assam.[32] The different names associated with the goddess are names of local Aryan and non-Aryan goddesses.[33] The Yogini Tantra mentions that the religion of the Yogini Pitha is of Kirata origin.[34] According to Banikanta Kakati, there existed a tradition among the priests established by Naranarayana that the Garos, a matrilineal people, offered worship at the earlier Kamakhya site by sacrificing pigs.[35]
The goddess is worshiped according to both the Vamachara (Left-Hand Path) as well as the Dakshinachara (Right-Hand Path) modes of worship.[36] Offerings to the goddess are usually flowers, but might include animal sacrifices. In general female animals are exempt from sacrifice, a rule that is relaxed during mass sacrifices.[37]
Legends
According to the Kalika Purana, Kamakhya Temple denotes the spot where Sati used to retire in secret to satisfy her amour with Shiva, and it was also the place where her yoni fell after Shiva danced with the corpse of Sati.[38] It mentions Kamakhya as one of four primary shakti peethas: the others being the Vimala Temple within the Jagannath Temple complex in Puri, Odisha; Tara Tarini) Sthana Khanda (Breasts), near Brahmapur, Odisha, and Dakhina Kalika in Kolkata, West Bengal originated from the limbs of the Corpse of Mata Sati. This is not corroborated in the Devi Bhagavata, which lists 108 places associated with Sati's body, though Kamakhya finds a mention in a supplementary list.[39]
The Yogini Tantra, a latter work, ignores the origin of Kamakhya given in Kalika Purana and associates Kamakhya with the goddess Kali and emphasizes the creative symbolism of the yoni.[40]
Vatsyayana, a Vedic Sage in Varanasi during the later first Century was approached by the King in the Himalayan region (now Nepal) to find a solution to convert the tribals and their rituals of human sacrifice to a more socially accepted worship.
The Sage suggested the worship of a tantric goddess Tara that spread towards the eastern Himalayan belt till the Garo Hills where the tribals worshipped a fertility 'yoni' goddess 'Kameke'. It was much later in the later Brahaminical period Kalika Purana that most tantric goddess were related to the legend of 'Shakti' and began to be erroneously worshiped as a 'devi' by the Hindus.
Festivals

Being the centre for Tantra worship this temple attracts thousands of tantra devotees in an annual festival known as the Ambubachi Mela. Another annual celebration is the Manasha Puja. Durga Puja is also celebrated annually at Kamakhya during Navaratri in the autumn. This five-day festival attracts several thousand visitors.[41]
See also
Notes
- ↑ "it is certain that in the pit at the back of the main shrine of the temple of Kamakhya we can see the remains of at least three different periods of construction, ranging in dates from the eighth to the seventeenth century A.D." (Banerji 1925, p. 101)
- ↑ Suresh Kant Sharma, Usha Sharma,Discovery of North-East India,2005
- ↑ "About Kamakhya Temple". Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ↑ (Urban 2008, p. 500)
- ↑ "About Kamakhya Temple".
- ↑ (Shin 2010, p. 4)
- ↑ Kashyap, Samudra Gupta, As SC directs the return of old order at Kamakhya, looking back, and ahead
- ↑ (Sarma 1988:124)
- ↑ (Sarma 1983, p. 47)
- ↑ (Banerji 1925, p. 101)
- ↑ "Kamakhya temple". Archived from the original on 2006-03-18. Retrieved 2006-09-12.
- ↑ (Banerji & 1925 100)
- ↑ (sarma 1988, p. 124)
- ↑ (Shin 2010, p. 5)
- ↑ http://www.asikolkata.in/bankura.aspx#RadhaVinod
- ↑ "There is a mobile (calanta) image of Kamakhya at the outskirt of the cave", (Goswami 1998:14)
- ↑ "Kamakhya". Retrieved 2006-09-12.
- ↑ (Neog 1980:315ff)
- ↑ "The cult of goddess Kamakhya seems to have remained beyond the brahmanical ambit till the end of the seventh century. The ruling family of Kamarupa during the Bhauma-Varmans dynasty did not pay any attention to her." (Shin 2010, p. 7)
- ↑ "The first epigraphic references to the goddess Kamakhya are found in the Tezpur plates and the Parbatiya plates of Vanamaladeva in the mid-ninth century." (Shin 2010, p. 7)
- ↑ "The steps which lead from the landing stage on the river to the top of Nilachala hill at Kamakhya are composed of immense blocks of stone some of which were evidently taken from a temple of great antiquity. The carvings on these slabs indicate that they must belong to the seventh or eighth century A.D., being slightly later than the carving on the stone door-frame at Dah Parbatiya. Some of the capitals of pillars are of such immense size that they indicate that the structure to which they belonged must have been as gigantic as the temple of the Sun god at Tezpur." (Banerji 1925, p. 100)
- ↑ Barua, Kanak Lal (1933), Early History of Kamarupa
- ↑ Karrani's expedition against the Koch kingdom under the command of Kalapahar took place in 1568, after Chilarai had the temple rebuilt in 1565. Kalapahar was in seize of the Koch capital when he was recalled to put down a rebellion in Orissa—and there is no evidence that he ventured further east to the Guwahati region. Therefore, Kalapahar, Karrani's general, was not the person who destroyed the Kamakhya temple. (Nath 1989, pp. 68–71)
- ↑ Sarkar 1992 p16. It is said that Viswa Simha revived worship at Kamakhya. According to an inscription in the temple, his son Chilarai built the temple during the reign of Naranarayana, the king of Koch Bihar and the son of Viswa Simha, in the year 1565.
- ↑ The temple of the goddess Kali or Kamakhya on the top of the hill was built during the domination of the Ahoms." (Banerji 1925, p. 100)
- ↑ "This temple was built on the ruins of another structure erected by king Sukladhvaja or Naranarayana, the first king and founder of the Koch dynasty of Cooch Bihar, whose inscription is still carefully preserved inside the mandapa. (Banerji 1925, p. 100)
- ↑ Encyclopaedia Indica - Volume 2 - 1981 -Page 562 Statues of King Nara Narayan and his brother, general Chilarai were also enshrined on an inside wall of the temple.
- ↑ Tattvālokaḥ - Volume 29 - 2006 - Page 18 It was rebuilt by the Koch king, Nara Narayan. Statues of the king and his brother Sukladev and an inscription about them are found in the temple
- ↑ (Sarma 1983, p. 39)
- ↑ Gait,Edward A History of Assam, 1905, pp172-173
- ↑ "Kamakhya temple". Retrieved 2006-09-12.
- ↑ Satish Bhattacharyya in the Publishers' Note, Kakati 1989.
- ↑ Kakati suspects that Kama of Kamakhya is of extra-Aryan origin, and cites correspondence with Austric formations: Kamoi, Kamoit, Komin, Kamet etc. (Kakati 1989, p. 38)
- ↑ Kakati 1989, p9: Yogini Tantra (2/9/13) siddhesi yogini pithe dharmah kairatajah matah.
- ↑ (Kakati 1989, p. 37)
- ↑ (Kakati 1989, p. 45)
- ↑ Kakati mentions that the list of animals that are fit for sacrifice as given in the Kalika Purana and the Yogini Tantra are made up of animals that are sacrificed by different tribal groups in the region.(Kakati 1989, p. 65)
- ↑ Kakati 1989, p34
- ↑ Kakati, 1989, p42
- ↑ Kakati, 1989 p35
- ↑ "Kamakhya Temple". Retrieved 2006-09-12.
References
- Banerji, R D (1925), "Kamakhya", Annual Report 1924-25, Archaeological Survey of India, pp. 100–101, retrieved March 2, 2013
- Choudhury, Nishipad Dev (1997), "Ahom Patronage on the Development of Art and Architecture in Lower Assam", Journal of the Assam Research Society, 33 (2): 59–67
- Das Gupta, Rajatananda (1960), An Architectural Survey of the Kamakhya Temple, Guwahati: Nilima Das Gupta
- Kakati, Banikanta (1989) The Mother Goddess Kamakhya, Publication Board, Guwahati
- Gait, Edward (1905) A History of Assam
- Goswami, Kali Prasad (1998). Kamakhya Temple. Guwahati: Kāmākhyā Mandira.
- Neog, Maheshwar (1980). Early History of the Vaishnava Faith and Movement in Assam. Delhi: Motilal Banarasidass.
- Sarkar, J. N. (1992) Chapter I: The Sources in The Comprehensive History of Assam, (ed H K Barpujari) Publication Board, Assam.
- Sarma, P (1983). "A Study of Temple Architecture under Ahoms". Journal of Assam Research Society.
- Sarma, P C (1988). Architecture of Assam. Delhi: Agam Kala Prakashan.
- Shin, Jae-Eun (2010). "Yoni, Yoginis and Mahavidyas : Feminine Divinities from Early Medieval Kamarupa to Medieval Koch Behar". Studies in History. 26 (1): 1–29. doi:10.1177/025764301002600101.
- Urban, Hugh B. (2008). "Matrix of Power: Tantra, Kingship, and Sacrifice in the Worship of Mother Goddess Kāmākhyā". The Journal of South Asian Studies. Routledge. 31 (3): 500–534. doi:10.1080/00856400802441946.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kamakhya Temple. |
- Kamakhya Temple Website
- Kamakhya Temple - Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts
- Kamakhya Temple - Guwahati
- Sri Kamakhya Mahavidya Mandir
- Sri Sri Kamakhya Temple: A Socio-Religious Perspective
- Kamakhya - in Assam
- Kamakhya Temple, Guwahati, Assam
- Tantra Temples
- Story of Kamakhya
