Kanowna Belle Gold Mine
| Location | |
|---|---|
 Kanowna Belle Gold Mine Location in Australia | |
| Location | Kalgoorlie |
| State | Western Australia |
| Country | Australia |
| Coordinates | 30°59′S 121°58′E / 30.983°S 121.967°ECoordinates: 30°59′S 121°58′E / 30.983°S 121.967°E |
| Production | |
| Production | 284,000 |
| Financial year | 2009 |
| History | |
| Opened | 1993 |
| Owner | |
| Company | Northern Star Resources Limited |
| Website | http://www.nsrltd.com/ NSRL website] |
| Year of acquisition | 2014 |
The Kanowna Belle Gold Mine is a gold mine located 19 km north east of Kalgoorlie, Western Australia, near the ghost town of Kanowna.
It is operated by Northern Star Resources[1] Kanowna Belle has one viewing platform and an interpretive centre.[2][3]
History
The gold deposit was discovered in 1989 by Delta Gold NL and Geopeko Gold and construction begun in 1992, with mining in open pit operation starting in 1993.[4] The mine was officially opened by Western Australian Premier Richard Court on 19 November 1993.[5]
The project was solely owned by Delta Gold Ltd from 1999, when it purchased the remaining 50% for A$90 million. Delta later merged with fellow Australian company Goldfields Ltd to form Auriongold Ltd in February 2002.[4] Aurion was taken over by Placer Dome Inc in 2003, who already, at this stage, held a 60% interest in the mine,[6] and Placer Dome in turn by Barrick Gold in March 2006 for US$10.4 billion.[4][7]
The mine, as of 2008, consists of three underground operations, Kanowna Belle, Raleigh and Bullant.[1]
In August 2009, Daniel Williams, a truck driver working 900 metres underground, fell to death at the mine.[8][9] It was the fourth fatal accident in Australian mining in 2009 and the eighth in 14 months.[10]
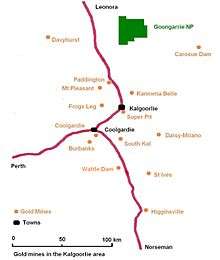
Technology
The Kanowna site is underground a trial of Caterpillar’s Minegem autonomous loader technology.[11]
Production
Production figures for the mine:
| Year | Gold production |
Grade | Cost per ounce |
| 2000[12] | 314,363 ounces | 5.68 g/t | A$245 |
| 2001[12] | 270,552 ounces | 4.87 g/t | A$306 |
| 2002 1[12] | 178,582 ounces | 4.63 g/t | A$320 |
| 2003 | |||
| 2004[4] | 237,291 ounces | US$ 316 | |
| 2005[4] | 490,000 ounces | ||
| 2006[13] | 506,000 ounces | 0.102 oz/t | US$477 |
| 2007[14] | 362,000 ounces | 0.102 oz/t | US$659 |
| 2008[14] | 267,000 ounces | 0.160 oz/t | US$734 |
| 2009 | 284,000 ounces | US$532 |
- 1 Figures for January to September 2002.
Sources
- The Australian Mines Handbook: 2003-2004 Edition, Louthean Media Pty Ltd, Editor: Ross Louthean
- Western Australian Mineral and Petroleum Statistics Digest 2008 Page 34: Principal Mineral and Petroleum Producers - Gold
References
- 1 2 Kanowna Belle Gold Mine, Northern Star Website , accessed: 30 August 2015
- ↑ Kanowna Belle Gold Mines australia.shopsafe.com.au, accessed: 4 January 2010
- ↑ Kanowna Belle Gold Mines traveldownunder.com.au, accessed: 4 January 2010
- 1 2 3 4 5 Kanowna Belle Gold Mine, Kalgoorlie, Australia mining-technology.com, accessed: 4 January 2010
- ↑ Kanowna Belle. (Kanowna gold mine in Kalgoorlie, Western Australia) Mining Magazine, published: 1 December 1993, accessed: 4 January 2010
- ↑ Placer Dome Seeks to Buy 2 Mining Concerns for $600 Million The New York Times, published: 29 November 1996, accessed: 2 January 2010
- ↑ MINEDEX website - Granny Smith search result, accessed: 2 January 2010
- ↑ New Zealand man killed in Kalgoorlie mine accident perthnow.com.au, published: 8 August 2009, accessed: 4 January 2010
- ↑ "Kiwi killed in Australian gold mine". Television New Zealand. NZPA. 12 August 2009. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ↑ "NZ man dies in gold mine fall". The New Zealand Herald. NZPA. 12 August 2009. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ↑ Proceedings 11th AusIMM Underground Operators' Conference - Case Study Comparison of Teleremote and Autonomous Assist Underground Loader Technology at the Kanowna Belle Mine
- 1 2 3 The Australian Mines Handbook: 2003-2004 Edition, page 98
- ↑ Fourth Quarter & Year-End Mine Statistics 2007 accessed: 1 January 2010
- 1 2 Fourth Quarter & Year-End Mine Statistics 2008 accessed: 1 January 2010