Kinetic tournament
A Kinetic Tournament is a kinetic data structure that functions as a priority queue for elements whose priorities change as a continuous function of time. It is implemented analogously to a "tournament" between elements to determine the "winner" (maximum or minimum element), with the certificates enforcing the winner of each "match" in the tournament. It supports the usual priority queue operations - insert, delete and find-max. They are often used as components of other kinetic data structures, such as kinetic closest pair.
Implementation
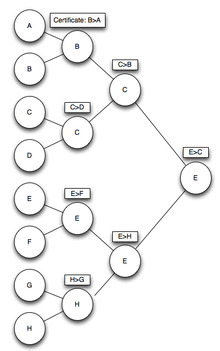
A kinetic tournament is organized in a binary tree-like structure, where the leaves contain the elements, and each internal node contains the larger (or smaller) of the elements in its child nodes. Thus, the root of the tree contains the maximum (or minimum) element at a given time. The validity of the structure is enforced by creating a certificate at each node, which asserts that the element in the node is the larger of the two children. When this certificate fails, the element at the node is changed (to be the element in the other child), and a new certificate representing the new invariant is created. If the element this node was a winner at its parent node, then the element and certificates at the parent must be recursively updated too.
Analysis
This is a O(n) space, responsive, local, compact and efficient data-structure.
- Responsiveness: A certificate failure will cause the creation of a new certificate to replace the old one, which must be put into the event queue. It may also trigger changes to the O(logn) certificates at its parent nodes. Each certificate change requires a delete and insert operation in the priority queue of events. Each of these takes O(log n) time, so the responsiveness, the total time required to process an certificate failure, is . While this is considered responsive in general, it is less responsive than other kinetic priority queues such as kinetic heaps which respond to certificate failures with O(1) certificate changes.
- Locality: Each element is involved in O(logn) certificates (for example, the maximal element is involved in a certificate at each of its parents all the way up to the root node). Again, while this is considered local, a kinetic heap is much more local.
- Compactness: This is a very compact structure, containing O(n) certificates - exactly one for every edge in the tree.
- Efficiency: Kinetic heaps are very efficient, with the number of internal events (certificate changes) being only a factor of O(log n) more than the number of external events. Specifically, for a collection of space-time trajectories where each pair intersects at most s times, the kinetic tournament processes O(λs+2log n) events in O(λs+2log2n) time, where λs+2 is a Davenport-Schinzel sequence. Additionally, insertions and deletions cause O(logn) certificate changes each. Each certificate change takes O(logn) time, which is determined by the time required to execute the event queue update.
References
Basch, J. 1999. Kinetic data structures. Ph.D. thesis, Dept. Computer Science, Stanford University.