Kvant-2

Kvant-2 (Russian: Квант-2; English: Quantum-II/2) (77KSD, TsM-D, 11F77D) was the third module and second major addition to the Mir space station. Its primary purpose was to deliver new science experiments, better life support systems, and an airlock to Mir. It was launched on November 26, 1989 on a Proton rocket. It docked to Mir on December 6. Its control system has been designed by the NPO "Electropribor"[1] (Kharkiv, Ukraine).
Specifications
- Length: 12.2 m
- Diameter: 4.35 m
- Mass: 19,640 kg
- Habitable volume: 61.9 m3
- Wingspan: 24 m
- Configuration: 77K (TKS) based module
Description
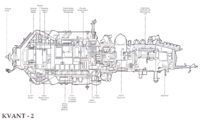
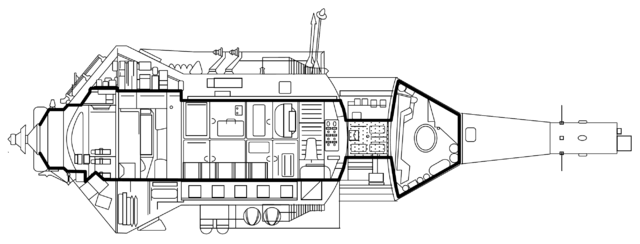
Kvant-2 was the first Mir module based on the TKS spacecraft. Kvant-2 was divided into three compartments. They were the EVA airlock, the instrument/cargo compartment, and the instrument/experiment compartment. The instrument/cargo compartment could be sealed off and act as an extension or a back-up to the airlock. Before Kvant-2 docked to the station, EVAs had to be carried by depressurizing the docking node on the Core Module. Kvant-2 also carried the Soviet version of the Manned Maneuvering Unit for the Orlan space suit. It delivered the Salyut 5B computer which was an improvement over the Argon 16B computer already on the station. Kvant-2 had a system for regenerating water from urine and a shower for personal hygiene. It carried six gyrodynes to augment those already located in Kvant-1. Unlike Kvant-1, Kvant-2's gyrodynes were only accessible from the exterior which turned out to make replacement of failed ones more difficult.
Scientific equipment on Kvant-2 included a high-resolution camera, spectrometers, X-ray sensors, the Volna 2 fluid flow experiment, and the Inkubator-2 unit which was used for hatching and raising quail. A list of experiments and equipment follows:
- ARIZ X-ray spectrometer
- ASPG-M scan platform carrying ITS-7D IR spectrometer (using the Czech sensor platform first used on Vega spacecraft).
- Cosmic dust detectors
- Gamma 2 spectrometer package
- Ikar EVA unit
- Inkubator 2 - bird egg incubator
- KAP-350 topographic camera
- MKF-6MA Earth resources film camera - 6 spectral bands. Provided by East Germany.
- MKS-M2 optical spectrometer
- Phaza AFM-2 spectrometer
- Spektr-256 spectrometer
- Sprut 5 charged particle spectrometer (installed 1991).
- TV cameras
- Volna 2 propellant tank demonstration (250 kg)
Gallery
 Airlock section on Kvant-2. Notice the SPK unit moored on the left.
Airlock section on Kvant-2. Notice the SPK unit moored on the left. Close-up of the SPK unit outside the airlock. The SPK was analogous to the American manned maneuvering unit. After being tested in 1990, it was stowed in Kvant-2 until 1996. It was then moved outside the airlock to save room in Kvant-2.
Close-up of the SPK unit outside the airlock. The SPK was analogous to the American manned maneuvering unit. After being tested in 1990, it was stowed in Kvant-2 until 1996. It was then moved outside the airlock to save room in Kvant-2.
References
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kvant-2. |
- Russian Space Web
- Encyclopedia Astronautica
- Gunter's Space Page - information on Kvant-2