La Chaux-de-Fonds
| La Chaux-de-Fonds | ||
|---|---|---|
|
La Chaux de Fonds in September 2005 | ||
| ||
 La Chaux-de-Fonds | ||
|
Location of La Chaux-de-Fonds  | ||
| Coordinates: 47°6.08′N 6°49.5′E / 47.10133°N 6.8250°ECoordinates: 47°6.08′N 6°49.5′E / 47.10133°N 6.8250°E | ||
| Country | Switzerland | |
| Canton | Neuchâtel | |
| District | La Chaux-de-Fonds | |
| Government | ||
| • Executive |
Conseil communal with 5 members | |
| • Mayor |
Président du Conseil communal (list) Théo Huguenin-Elie | |
| • Parliament |
Conseil général with 41 members | |
| Area[1] | ||
| • Total | 55.66 km2 (21.49 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 992 m (3,255 ft) | |
| Population (Dec 2015[2]) | ||
| • Total | 38,957 | |
| • Density | 700/km2 (1,800/sq mi) | |
| Postal code | 2300 | |
| SFOS number | 6421 | |
| Surrounded by | Fontaines, Fournet-Blancheroche (FR-25), Grand'Combe-des-Bois (FR-25), La Ferrière (BE), La Sagne, Le Locle, Les Bois (JU), Les Fontenelles (FR-25), Les Hauts-Geneveys, Les Planchettes, Renan (BE) | |
| Twin towns | Winterthur (Switzerland), Frameries (Belgium) | |
| Website |
www SFSO statistics | |
| La Chaux-de-Fonds / Le Locle, watchmaking town planning | |
|---|---|
| Name as inscribed on the World Heritage List | |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | iv |
| Reference | 1302 |
| UNESCO region | Europe and North America |
| Inscription history | |
| Inscription | 2009 (33rd Session) |
La Chaux-de-Fonds (French pronunciation: [laʃodəfɔ̃]) is a Swiss city of the district of La Chaux-de-Fonds in the canton of Neuchâtel. It is located in the Jura mountains at an altitude of 1000 m, a few kilometres south of the French border. After Geneva and Lausanne, it is the third largest city located completely in the Romandie, the French-speaking part of the country, with a population (as of December 2015) of 38,957.[3]
The city was founded in 1656. Its growth and prosperity is mainly bound up with the watch making industry. It is the most important centre of the watch making industry in the area known as the Watch Valley. Completely destroyed by a fire in 1794 La Chaux-de-Fonds was rebuilt following a grid street plan, which was and is still original among Swiss cities. Karl Marx said about the very special urban design of the city that it was a "city-factory". The famous architect Le Corbusier, the writer Blaise Cendrars and the car maker Louis Chevrolet were born there. La Chaux-de-Fonds is a renowned centre of Art nouveau.
In 2009, La Chaux-de-Fonds and Le Locle, its sister city, have jointly been awarded UNESCO World Heritage status for their exceptional universal value.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites
The watch making cities of La Chaux-de-Fonds and Le Locle have jointly received recognition from UNESCO for their exceptional universal value.
The Site's planning consists of two small cities located close to each other in the mountainous environment of the Swiss Jura. Due to the altitude (1,000 m [3,300 ft]) and the lack of water (porous sandstone underground) the land is ill suited to farming. Planning and buildings reflect the watch-making artisans need of rational organization. Rebuilt in the early 19th Century, after extensive fires, both towns owe their survival to the manufacturing and exports of watches, to which, in the 20th Century, was added the minute micromechanical industry.
Along an open-ended scheme of parallel strips on which residential housing and workshops intermingle, the town's planned lay-out reflects the needs of the local watch-making culture that dates back to the 17th century, and which is still alive today. Both agglomerations present outstanding examples of mono-industrial manufacturing-towns, which are still well-preserved and active. The urban planning has accommodated the transition from the artisans’ production of a cottage industry to the more concentrated factory production of the late 19th and 20th centuries. In 1867 Karl Marx was already describing La Chaux-de-Fonds as a “huge factory-town” in Das Kapital, where he analyzed the division of labour in the watch making industry of the Jura.[4]
It is the tenth Swiss Site to be awarded World Heritage status, joining others such as the Old City of Bern, the Rhaetian Railway and the Abbey and Convent of St. Gallen.
History

The region was first inhabited around 10,000 years ago (Epipaleolithic). A skull and other traces have been found in caves nearby.[5]
In the middle of the 14th century, the region was colonized from the southern Val-de-Ruz. La Chaux-de-Fonds is first mentioned in 1350 as la Chaz de Fonz. In 1378 it was mentioned as Chault de Font.[5]
The region was under the authority of the lords of Valangin. In the 15th and 16th centuries, a second wave of colonization came from the so-called Clos de la Franchise (the valleys of Le Locle and La Sagne). Agriculture was the main activity but the village remained small. In 1531 there were only about 35 people living there. The first church was built in 1528. By 1530, La Chaux-de-Fonds, like the rest of the Valangin lands, converted to the new Reformed faith. The Lord of Valanginian, René de Challant, fixed the boundaries of the parish in 1550. The church and parish provided a political structure and a small community of Valanginian citizens, free farmers and peasants grew up around the church. By 1615 there were 355 people living in the village. In 1616, the low and middle jurisdiction over La Chaux-de-Fonds moved to Le Locle and La Sagne, while the high court remained in Valanginian. The agriculture, supplemented by mills on the banks of the Doubs, continued to dominate. However, at the end of the 16th century, the city became an important crossroad between Neuchâtel, Franche-Comté and the Bishopric of Basel.[5]
The community grew during the Thirty Years' War, mainly because of its strategic position for trade. Economic activity accelerated in the 18th century with the development of the city's lace and watchmaking industries. Pierre Jacquet-Droz, best known for his automata, was a particularly prominent watchmaker of this era.
In 1794, the city was devastated by fire. Charles-Henri Junod created the new city's plan in 1835, and the city is now known for its "modern," grid-like plan, in comparison with most European cities' meandering streets.[6][7] The central avenue is named the Avenue Léopold Robert.
Geography

La Chaux-de-Fonds has an area, as of 2009, of 55.7 square kilometers (21.5 sq mi). Of this area, 30.46 km2 (11.76 sq mi) or 54.7% is used for agricultural purposes, while 15.52 km2 (5.99 sq mi) or 27.9% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 9.28 km2 (3.58 sq mi) or 16.7% is settled (buildings or roads), 0.3 km2 (0.12 sq mi) or 0.5% is either rivers or lakes and 0.11 km2 (27 acres) or 0.2% is unproductive land.[8]
Of the built up area, industrial buildings made up 1.6% of the total area while housing and buildings made up 8.4% and transportation infrastructure made up 4.6%. while parks, green belts and sports fields made up 1.1%. Out of the forested land, 24.2% of the total land area is heavily forested and 3.7% is covered with orchards or small clusters of trees. Of the agricultural land, 0.4% is used for growing crops and 40.0% is pastures and 14.2% is used for alpine pastures. All the water in the municipality is flowing water.[8]
The municipality is the capital of the district of the same name. It is located in the Jura Mountains near the French border at an elevation of about 1,000 m (3,300 ft).
Coat of arms
The blazon of the municipal coat of arms is Tierced per fess, Azure three Mullets of Five Argent in fess, Argent a Hive Or surrounded by seven Bees of the same, and chequy [of 7x3] Argent and Azure.[9]
Demographics

La Chaux-de-Fonds has a population (as of December 2015) of 38,957.[10] As of 2008, 29.1% of the population are resident foreign nationals.[11] Over the last 10 years (2000–2010 ) the population has changed at a rate of 1.3%. It has changed at a rate of 1.4% due to migration and at a rate of -0.2% due to births and deaths.[12]
Most of the population (as of 2000) speaks French (31,653 or 85.5%) as their first language, Italian is the second most common (1,335 or 3.6%) and Portuguese is the third (1,173 or 3.2%). There are 900 people who speak German and 32 people who speak Romansh.[13]
As of 2008, the population was 48.0% male and 52.0% female. The population was made up of 12,444 Swiss men (33.2% of the population) and 5,578 (14.9%) non-Swiss men. There were 14,513 Swiss women (38.7%) and 4,988 (13.3%) non-Swiss women.[14] Of the population in the municipality, 15,164 or about 41.0% were born in La Chaux-de-Fonds and lived there in 2000. There were 3,778 or 10.2% who were born in the same canton, while 6,962 or 18.8% were born somewhere else in Switzerland, and 9,651 or 26.1% were born outside of Switzerland.[13]
As of 2000, children and teenagers (0–19 years old) make up 22.5% of the population, while adults (20–64 years old) make up 58.9% and seniors (over 64 years old) make up 18.6%.[12]
As of 2000, there were 14,380 people who were single and never married in the municipality. There were 17,285 married individuals, 2,573 widows or widowers and 2,778 individuals who are divorced.[13]
As of 2000, there were 17,207 private households in the municipality, and an average of 2.1 persons per household.[12] There were 7,087 households that consist of only one person and 747 households with five or more people. In 2000, a total of 16,833 apartments (88.8% of the total) were permanently occupied, while 1,376 apartments (7.3%) were seasonally occupied and 756 apartments (4.0%) were empty.[15] As of 2009, the construction rate of new housing units was 1 new units per 1000 residents.[12] The vacancy rate for the municipality, in 2010, was 2.05%.[12]
Historic Population
The historical population is given in the following chart:[5]
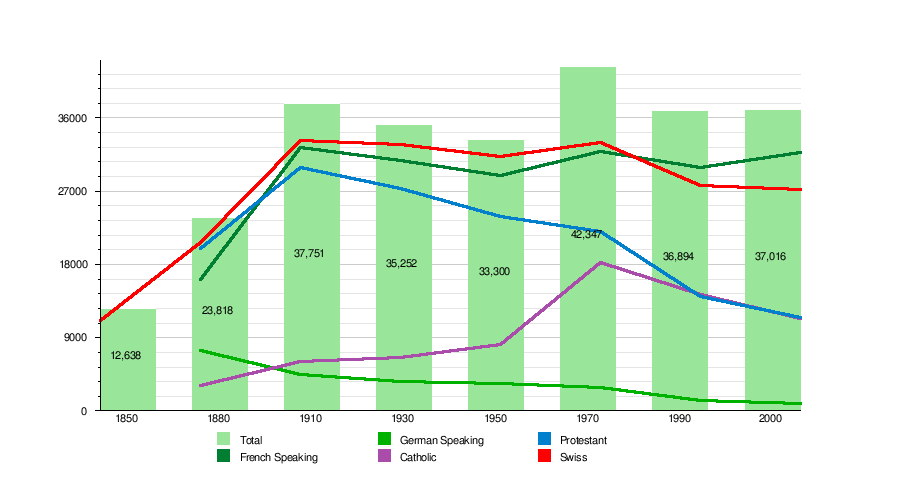
| Historic Population Data [5] | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Total Population | French Speaking | German Speaking | Catholic | Protestant | Other | Swiss | Non-Swiss | |||
| 1850 | 12,638 | 11,084 | 1,554 | ||||||||
| 1880 | 23,818 | 16,089 | 7,421 | 3,160 | 20,006 | 45 | 20,681 | 3,137 | |||
| 1910 | 37,751 | 32,363 | 4,383 | 6,077 | 29,914 | 94 | 33,218 | 4,533 | |||
| 1930 | 35,252 | 30,761 | 3,559 | 6,519 | 27,306 | 131 | 32,644 | 2,608 | |||
| 1950 | 33,300 | 28,818 | 3,305 | 8,100 | 23,877 | 127 | 31,265 | 2,035 | |||
| 1970 | 42,347 | 31,762 | 2,903 | 18,142 | 21,979 | 2,002 | 32,922 | 9,425 | |||
| 1990 | 36,894 | 29,873 | 1,191 | 14,379 | 13,963 | 3,829 | 27,689 | 9,205 | |||
| 2000 | 37,016 | 31,653 | 900 | 11,320 | 11,425 | 3,128 | 27,106 | 9,910 | |||
Heritage sites of national significance
La Chaux-de-Fonds is home to 23 Swiss heritage sites of national significance along with the UNESCO World Heritage Site of La Chaux-de-Fonds / Le Locle.
Library/museum/theater: Bibliothèque de la Ville de la Chaux-de-Fonds et Département audiovisuel (DAV), Musée des Beaux-Arts, Musée d‘histoire naturelle, the Musée international d’horlogerie «l’homme et le temps» and the Théâtre et Salle de musique on Avenue Léopold-Robert 27–29 Religious: Synagogue on Rue du Parc 63 Farms: Ferme des Brandt at Les Petites-Corsettes 6, Ferme Haute Fie and Maison Carrée at Le Valanvron 9 and Ferme les Crêtets on Rue des Crêtets 148 Companies: Spillmann SA on Rue du Doubs 32 and Usine électrique at Rue Numa-Droz 174 Houses: Villa Anatole Schwob on Rue du Doubs 167, Villa Fallet on Chemin de Pouillerel 1, Villa Gallet on Rue David-Pierre-Bourquin 55, Villa Jaquemet on Chemin de Pouillerel 8, Villa Stotzer on Chemin de Pouillerel 6 and Maison Blanche at Chemin de Pouillerel 12 Other buildings: the slaughterhouse (Abattoirs) on Rue du Commerce 120–126, the Ancien Manège (collective house from 1968), the crematorium on Rue de la Charrière, the Domaine des Arbres, the Grande Fontaine on Avenue Léopold-Robert and the Loge l‘Amitié. After the hoorid mudslide that occurred which destroyed the city of La Chaux [16]
 Usine électrique
Usine électrique Spillmann SA
Spillmann SA Ancien Manège
Ancien Manège Crematorium
Crematorium Domaine des Arbres
Domaine des Arbres Farm House les Crêtets
Farm House les Crêtets Museum des Beaux-Arts
Museum des Beaux-Arts Maison Blanche
Maison Blanche Théâtre and Salle de musique
Théâtre and Salle de musique- Synagogue
 Library of the City of Chaux-de-Fonds
Library of the City of Chaux-de-Fonds Abattoirs
Abattoirs Farm House des Brandt
Farm House des Brandt Farm House Haute Fie
Farm House Haute Fie Grand Fountain
Grand Fountain Loge l‘Amitié
Loge l‘Amitié Museum international d’horlogerie
Museum international d’horlogerie Villa Anatole Schwob
Villa Anatole Schwob Villa Fallet
Villa Fallet- Villa Gallet
 Villa Jaquemet
Villa Jaquemet
Politics
In the 2007 federal election the most popular party was the SP which received 28.18% of the vote. The next three most popular parties were the SVP (25.73%), the PdA Party (14.2%) and the Green Party (12.03%). In the federal election, a total of 10,293 votes were cast, and the voter turnout was 47.1%.[17]
Economy

As of 2010, La Chaux-de-Fonds had an unemployment rate of 8.2%. As of 2008, there were 260 people employed in the primary economic sector and about 95 businesses involved in this sector. 10,594 people were employed in the secondary sector and there were 550 businesses in this sector. 11,813 people were employed in the tertiary sector, with 1,290 businesses in this sector.[12] There were 17,870 residents of the municipality who were employed in some capacity, of which females made up 46.1% of the workforce.
In 2008 the total number of full-time equivalent jobs was 19,692. The number of jobs in the primary sector was 208, of which 198 were in agriculture and 10 were in forestry or lumber production. The number of jobs in the secondary sector was 10,153 of which 9,063 or (89.3%) were in manufacturing and 903 (8.9%) were in construction. The number of jobs in the tertiary sector was 9,331. In the tertiary sector; 2,287 or 24.5% were in wholesale or retail sales or the repair of motor vehicles, 680 or 7.3% were in the movement and storage of goods, 571 or 6.1% were in a hotel or restaurant, 150 or 1.6% were in the information industry, 372 or 4.0% were the insurance or financial industry, 573 or 6.1% were technical professionals or scientists, 816 or 8.7% were in education and 2,078 or 22.3% were in health care.[18]
In 2000, there were 8,916 workers who commuted into the municipality and 3,481 workers who commuted away. The municipality is a net importer of workers, with about 2.6 workers entering the municipality for every one leaving. About 19.3% of the workforce coming into La Chaux-de-Fonds are coming from outside Switzerland, while 0.1% of the locals commute out of Switzerland for work.[19] Of the working population, 21.4% used public transportation to get to work, and 52.8% used a private car.[12]
Religion
Religion in La Chaux-de-Fonds, 31.12.2014[20]

From the 2000 census, 11,320 or 30.6% were Roman Catholic, while 10,258 or 27.7% belonged to the Swiss Reformed Church. Of the rest of the population, there were 205 members of an Orthodox church (or about 0.55% of the population), there were 300 individuals (or about 0.81% of the population) who belonged to the Christian Catholic Church, and there were 2,365 individuals (or about 6.39% of the population) who belonged to another Christian church. There were 129 individuals (or about 0.35% of the population) who were Jewish, and 1,369 (or about 3.70% of the population) who were Islamic. There were 90 individuals who were Buddhist, 83 individuals who were Hindu and 45 individuals who belonged to another church. 10,059 (or about 27.17% of the population) belonged to no church, are agnostic or atheist, and 1,960 individuals (or about 5.30% of the population) did not answer the question.[13]
Education
In La Chaux-de-Fonds about 12,347 or (33.4%) of the population have completed non-mandatory upper secondary education, and 3,943 or (10.7%) have completed additional higher education (either university or a Fachhochschule). Of the 3,943 who completed tertiary schooling, 51.7% were Swiss men, 28.5% were Swiss women, 12.0% were non-Swiss men and 7.7% were non-Swiss women.[13]
In the canton of Neuchâtel most municipalities provide two years of non-mandatory kindergarten, followed by five years of mandatory primary education. The next four years of mandatory secondary education is provided at thirteen larger secondary schools, which many students travel out of their home municipality to attend.[21] The primary school in La Chaux-de-Fonds is combined with Les Planchettes. During the 2010-11 school year, there were 38 kindergarten classes with a total of 728 students in La Chaux-de-Fonds. In the same year, there were 113 primary classes with a total of 2,042 students.[22]
As of 2000, there were 754 students in La Chaux-de-Fonds who came from another municipality, while 644 residents attended schools outside the municipality.[19]
La Chaux-de-Fonds is home to 2 libraries. These libraries include; the Bibliothèque de la Ville and the Haute école Arc - Arts appliqué. There was a combined total (as of 2008) of 670,267 books or other media in the libraries, and in the same year a total of 342,720 items were loaned out.[23]
Culture

La Chaux-de-Fonds is the home of the Musée International d'Horlogerie (International Museum of Watch Making), originally constructed with funds donated by the Gallet watchmaking family in 1899.[24] The Museum is considered as an important showcase for the history of the timekeeping arts.
Art Nouveau had a great influence on architecture and culture in the city during the late 19th century.
The daily newspaper L'Impartial has been published in La Chaux-de-Fonds since 1880.
The Wakker Prize was granted to La-Chaux-de-Fonds in 1994.
Sports
HC La Chaux-de-Fonds is a Swiss professional ice hockey team that competes in the National League B. La Chaux-de-Fonds also has a football team FC La Chaux-de-Fonds.
Economy
The city's economy is based on industry and watch manufacturers.
Transport
The city is served by La Chaux-de-Fonds railway station, Les Eplatures Airport, and the La Chaux-de-Fonds trolleybus system.
Climate
| Climate data for La Chaux-de-Fonds (1981-2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.9) |
3.3 (37.9) |
6.2 (43.2) |
9.9 (49.8) |
14.6 (58.3) |
18.1 (64.6) |
20.7 (69.3) |
20.2 (68.4) |
16.4 (61.5) |
12.8 (55) |
6.7 (44.1) |
3.5 (38.3) |
11.3 (52.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.6 (29.1) |
−1.1 (30) |
1.8 (35.2) |
5.2 (41.4) |
9.7 (49.5) |
12.9 (55.2) |
15.3 (59.5) |
14.8 (58.6) |
11.3 (52.3) |
7.9 (46.2) |
2.5 (36.5) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
6.5 (43.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −6.0 (21.2) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−2.8 (27) |
0.6 (33.1) |
4.7 (40.5) |
7.6 (45.7) |
9.8 (49.6) |
9.4 (48.9) |
6.5 (43.7) |
3.3 (37.9) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
1.8 (35.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 107 (4.21) |
99 (3.9) |
111 (4.37) |
99 (3.9) |
141 (5.55) |
124 (4.88) |
126 (4.96) |
136 (5.35) |
128 (5.04) |
123 (4.84) |
120 (4.72) |
128 (5.04) |
1,441 (56.73) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 68 (26.8) |
64.6 (25.43) |
49 (19.3) |
17.5 (6.89) |
3.2 (1.26) |
0.1 (0.04) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
2.8 (1.1) |
27.7 (10.91) |
54.5 (21.46) |
287.4 (113.15) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 12.4 | 11.3 | 12.3 | 12.5 | 15.1 | 13.1 | 12.2 | 12.2 | 10.6 | 12.4 | 12.0 | 13.4 | 149.5 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 1.0 cm) | 9.3 | 9.2 | 7.6 | 3.7 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 5.1 | 9 | 45.3 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 82.6 | 80.8 | 79.8 | 77.4 | 76.6 | 76.6 | 74.6 | 76.7 | 78.3 | 78.6 | 81.4 | 81.6 | 78.7 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 100 | 106 | 134 | 150 | 159 | 180 | 212 | 200 | 158 | 131 | 97 | 82 | 1,710 |
| Source: MeteoSwiss [25] | |||||||||||||
Notable people
Its most famous native sons are the architect Le Corbusier, born here as Charles-Edouard Jeanneret in 1887 (his first independent project as an architect, the Villa Jeanneret-Perret, is open to the public), and Blaise Cendrars, novelist and poet, born as Frédéric Louis Sauser in 1887.
Other notable people born in La Chaux-de-Fonds include Armand Borel, a mathematician, Louis Léopold Robert, a painter, born in 1794, Paul Ditisheim, born in 1868, a famous watchmaker and inventor.
More notable people


- Charles Antenen, (1929-2000), footballer
- Georges Antenen, (1903-1979), cyclist
- Pierre Aubert, (1927-2016), lawyer, politician and Bundesrat
- Blaise Cendrars, (1887-1961), poet and novelist
- Louis Chevrolet, (1878-1941), automobile manufacturer
- Theophil Christen, (1873-1920), mathematician, physician and economist, worked here as a doctor
- Le Corbusier, (1887-1965), architect, architectural theorist, city guide, painter, draftsman, sculptor and furniture designer
- Jean-Pierre Droz, (1746-1823), medalist and Minter
- Numa Droz, (1844-1899), politician and Bundesrat (FDP)
- Pierre Graber, (1908-2003), politician and Bundesrat (SP)
- Jules Humbert-Droz, (1891-1971), politician, Communist International, KPS, SP
- Pierre Jaquet-Droz, (1721-1790), mathematician, watchmaker and machine designer
- Lenin (1870-1924), lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds during his Swiss exile.
- Nicole Petignat, (born 1966), Swiss footballer
- Georges Piroué, (1920–2005), writer
- Louis Léopold Robert, (1794-1835), painter
- Adrienne von Speyr, (1802-1967), doctor, mystic and spiritual writer
- Georges Schneider, (1925-1963), ski racer and world champion
Watch companies
Many watch companies started in La Chaux de Fonds:
- Bouchet-Lassale SA, in 1978
- Corum
- Cyma Watches, 1862 - Schwob Frères and Co. 1892 - Cyma Watch Company
- Ebel, by Eugene Blum and Alice Levy, in 1911
- Eberhard & Co., by George-Emile Eberhard, in 1887
- Gallet & Co., by Julien Gallet, in 1826
- Girard-Perregaux, by Constantin Girard and Marie Perregaux, in 1856
- Heuer Leonidas, now TAG Heuer, by Edouard Heuer, in 1860
- Invicta Watch Group, by Raphael Picard, in 1837
- Marathon Watch Co. in 1904 - Originally founded as Weinsturm Watch
- Movado, by Achilles Ditesheim, in 1881
- Omega SA, in 1848
- Rolex trademark, registered by Hans Wilsdorf, in 1908. His company, Wilsdorf and Davis, London, was later renamed Rolex Watch Company, Geneva and Biel/Bienne
- Rotary, by Moise Dreyfuss, in 1895
- Solvil et Titus, by Paul Ditisheim, in 1892
- Venus by Paul Arthur Schwarz and Olga Etienne, in 1902
- Vulcain by Maurice Ditisheim, in 1858
Twin Town
La Chaux-de-Fonds is twinned with the town of Frameries, Belgium.[26]
Notes and references
- La Chaux-de-Fonds in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- ↑ Arealstatistik Standard - Gemeindedaten nach 4 Hauptbereichen
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB, online database – Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit (German) accessed 30 August 2016
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB, online database – Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit (German) accessed 30 August 2016
- ↑ UNESCO world heritage site
- 1 2 3 4 5 La Chaux-de-Fonds in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- ↑ The Le Corbusier Guide, Google Books
- ↑ La Chaux-de-Fonds et le Locle, Swiss Tourism Site
- 1 2 Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data (German) accessed 25 March 2010
- ↑ Flags of the World.com accessed 20-October-2011
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB, online database – Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit (German) accessed 30 August 2016
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Superweb database - Gemeinde Statistics 1981-2008 (German) accessed 19 June 2010
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Swiss Federal Statistical Office accessed 20-October-2011
- 1 2 3 4 5 STAT-TAB Datenwürfel für Thema 40.3 - 2000 (German) accessed 2 February 2011
- ↑ Canton of Neuchatel Statistics, République et canton de Neuchâtel - Recensement annuel de la population (German) accessed 13 October 2011
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB - Datenwürfel für Thema 09.2 - Gebäude und Wohnungen (German) accessed 28 January 2011
- ↑ "Kantonsliste A-Objekte". KGS Inventar (in German). Federal Office of Civil Protection. 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2011.
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office, Nationalratswahlen 2007: Stärke der Parteien und Wahlbeteiligung, nach Gemeinden/Bezirk/Canton (German) accessed 28 May 2010
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB Betriebszählung: Arbeitsstätten nach Gemeinde und NOGA 2008 (Abschnitte), Sektoren 1-3 (German) accessed 28 January 2011
- 1 2 Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Statweb (German) accessed 24 June 2010
- ↑ La Chaux-de-Fonds - Contrôle des habitants (French) accessed 7 February 2016
- ↑ EDK/CDIP/IDES (2010). Kantonale Schulstrukturen in der Schweiz und im Fürstentum Liechtenstein / Structures Scolaires Cantonales en Suisse et Dans la Principauté du Liechtenstein (PDF) (Report). Retrieved 24 June 2010.
- ↑ Statistical Department of the Canton of Neuchâtel Mémento de l'année scolaire 2010/2011 (French) accessed 17 October 2011
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office, list of libraries (German) accessed 14 May 2010
- ↑ Catherine Cardinal, Jean-Michael Piquet, Catalogue of Selected Pieces, Institut l'homme et le temps, pg. 5
- ↑ "Climate Norm Value Tables". Climate diagrams and normals from Swiss measuring stations. Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology (MeteoSwiss). Retrieved 4 February 2013. The weather station elevation is 1,018 meters above sea level.
- ↑ Conseil des Communes et Regions d'Europe (French) accessed 27 April 2011
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to La Chaux-de-Fonds. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Chaux de Fonds, La. |
- Watchmaking Heritage Day: Saturday 7 November 2009
- Official website of the City of La Chaux-de-Fonds
- La Chaux-de-Fonds / Le Locle: Pictures Gallery
- La Chaux-de-Fonds in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- International watchmaking museum website
- The Art Nouveau season of events in the city


