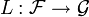List of operators
In mathematics, an operator or transform is a function from one space of functions to another. Operators occur commonly in engineering, physics and mathematics. Many are integral operators and differential operators.
In the following L is an operator
which takes a function 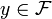 to another function
to another function ![L[y]\in\mathcal{G}](../I/m/473d3117019fb22ec48d6aae16430fcc.png) . Here,
. Here,  and
and 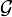 are some unspecified function spaces, such as Hardy space, Lp space, Sobolev space, or, more vaguely, the space of holomorphic functions.
are some unspecified function spaces, such as Hardy space, Lp space, Sobolev space, or, more vaguely, the space of holomorphic functions.
| Expression | Curve definition |
Variables | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear transformations | |||
![L[y]=y^{(n)} \](../I/m/49a0365dd20f66fcf0794f6fb55c3972.png) | Derivative of nth order | ||
![L[y]=\int_a^t y \,dt](../I/m/97d376fb55fecbeffbfca3446df29553.png) | Cartesian |  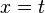 | Integral, area |
![L[y]=y\circ f](../I/m/bbb519bb3a09bf3d583e1780724dee9b.png) | Composition operator | ||
![L[y]=\frac{y\circ t+y\circ -t}{2}](../I/m/552dcd34a9489a9e3fa08329250e52c8.png) | Even component | ||
![L[y]=\frac{y\circ t-y\circ -t}{2}](../I/m/f4830acc2d8f21a36c6b1a8b8f502039.png) | Odd component | ||
![L[y]=y\circ (t+1) - y\circ t = \Delta y](../I/m/3ac8eca762f9e845d4d474539c9134eb.png) | Difference operator | ||
![L[y]=y\circ (t) - y\circ (t-1) = \nabla y](../I/m/ec80c476ef241cb4a8954fc65f1b0a49.png) | Backward difference (Nabla operator) | ||
![L[y]=\sum y=\Delta^{-1}y](../I/m/60da1f0aa0cee23191983a85b8a27a1d.png) | Indefinite sum operator (inverse operator of difference) | ||
![L[y] =-(py')'+qy \,](../I/m/d8eb95bb0644e5fbd410af126da452f8.png) | Sturm–Liouville operator | ||
| Non-linear transformations | |||
![F[y]=y^{[-1]} \](../I/m/ffe0e2136036166e8d582eb291bb2a78.png) | Inverse function | ||
![F[y]=t\,y'^{[-1]} - y\circ y'^{[-1]}](../I/m/59d5e7b0b1e30bd6a6004466c7dde91d.png) | Legendre transformation | ||
![F[y]=f\circ y](../I/m/0cb0f7a63ff9aca39bdaeb1c4a31813b.png) | Left composition | ||
![F[y]=\prod y](../I/m/29afbc9975444371e8c48fb436cb0830.png) | Indefinite product | ||
![F[y]=\frac{y'}{y}](../I/m/a4c904350b714a063b4095662b3a3767.png) | Logarithmic derivative | ||
![F[y]={\frac{ty'}{y}}](../I/m/0180edc7112b9b28674769e10574486a.png) | Elasticity | ||
![F[y]={y''' \over y'}-{3\over 2}\left({y''\over y'}\right)^2](../I/m/35079918636de33b40dc61e517450075.png) | Schwarzian derivative | ||
![F[y]=\int_a^t |y'| \,dt](../I/m/01f779edce31f5f0438763b3575d319c.png) | Total variation | ||
![F[y]=\frac{1}{t-a}\int_a^t y\,dt](../I/m/7a6653583ea941e99e751998426851a0.png) | Arithmetic mean | ||
![F[y]=\exp \left( \frac{1}{t-a}\int_a^t \ln y\,dt \right)](../I/m/4df1cc08b4304136736fadd9088a192a.png) | Geometric mean | ||
![F[y]= -\frac{y}{y'}](../I/m/771799ab1e4c1fa679c92f4354f09e1e.png) | Cartesian | 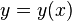 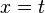 | Subtangent |
![F[x,y]= -\frac{yx'}{y'}](../I/m/279255dd9a83486684b89e1c3b950863.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 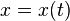 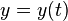 | |
![F[r]= -\frac{r^2}{r'}](../I/m/1988acc2b720ea4fd5cc128262e1e8d5.png) | Polar | 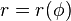 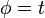 | |
![F[r]=\frac{1}{2}\int_a^t r^2 dt](../I/m/2e47e425be100da3ae1396dd619658e3.png) | Polar | 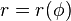 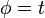 | Sector area |
![F[y]= \int_a^t \sqrt { 1 + y'^2 }\, dt](../I/m/daf0aa41502f6f4ae687a782c9fd0a2b.png) | Cartesian | 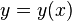 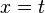 | Arc length |
![F[x,y]= \int_a^t \sqrt { x'^2 + y'^2 }\, dt](../I/m/fabb6d0bb97bc4746e9ad20e5d10e570.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 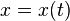 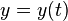 | |
![F[r]= \int_a^t \sqrt { r^2 + r'^2 }\, dt](../I/m/b62a2fd149b52d43ac452927bbf55d59.png) | Polar | 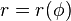 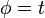 | |
![F[x,y] = \int_a^t\sqrt[3]{y''}\, dt](../I/m/2568479d543c616fedb6184035a22735.png) | Cartesian | 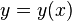 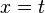 | Affine arc length |
![F[x,y] = \int_a^t\sqrt[3]{x'y''-x''y'}\, dt](../I/m/b7a12af03c9c48f00602194879527e00.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 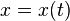 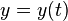 | |
![F[x,y,z]=\int_a^t\sqrt[3]{z'''(x'y''-y'x'')+z''(x'''y'-x'y''')+z'(x''y'''-x'''y'')}](../I/m/6f6580ef6791ea75d5361daef3ef6dc0.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 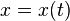 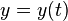 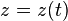 | |
![F[y]=\frac{y''}{(1+y'^2)^{3/2}}](../I/m/e0ea1ae833565d4b1b41c41382e4b53d.png) | Cartesian | 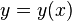 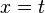 | Curvature |
![F[x,y]= \frac{x'y''-y'x''}{(x'^2+y'^2)^{3/2}}](../I/m/4f78f09209d07999a9e9f96767e8c3c9.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 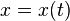 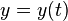 | |
![F[r]=\frac{r^2+2r'^2-rr''}{(r^2+r'^2)^{3/2}}](../I/m/7ee9b3616fc7f4889af9f93fd1e13f3b.png) | Polar | 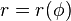 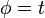 | |
![F[x,y,z]=\frac{\sqrt{(z''y'-z'y'')^2+(x''z'-z''x')^2+(y''x'-x''y')^2}}{(x'^2+y'^2+z'^2)^{3/2}}](../I/m/6f358023a9da4d45f759a823ee27c90a.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 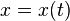 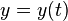 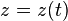 | |
![F[y]=\frac{1}{3}\frac{y''''}{(y'')^{5/3}}-\frac{5}{9}\frac{y'''^2}{(y'')^{8/3}}](../I/m/e19db1fb34c57c0a767bc2c6f886daf5.png) | Cartesian | 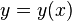 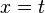 | Affine curvature |
![F[x,y]= \frac{x''y'''-x'''y''}{(x'y''-x''y')^{5/3}}-\frac{1}{2}\left[\frac{1}{(x'y''-x''y')^{2/3}}\right]''](../I/m/d89e28c9d6be339ff06c761f788deb09.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 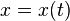 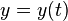 | |
![F[x,y,z]=\frac{z'''(x'y''-y'x'')+z''(x'''y'-x'y''')+z'(x''y'''-x'''y'')}{(x'^2+y'^2+z'^2)(x''^2+y''^2+z''^2)}](../I/m/c52fa64348864d2ee2565431b3f139a9.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 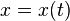 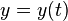 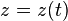 | Torsion of curves |
![X[x,y]=\frac{y'}{yx'-xy'}](../I/m/e194332d41ee7f040451d40342960eea.png) ![Y[x,y]=\frac{x'}{xy'-yx'}](../I/m/451f8ceefba3042f3e6119278270d864.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 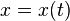 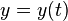 | Dual curve (tangent coordinates) |
![X[x,y]=x+\frac{ay'}{\sqrt {x'^2+y'^2}}](../I/m/647b764f6b1bdc007709689a57500cc5.png) ![Y[x,y]=y-\frac{ax'}{\sqrt {x'^2+y'^2}}](../I/m/79df52cae371e456b786179d5725f7b1.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 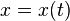 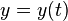 | Parallel curve |
![X[x,y]=x+y'\frac{x'^2+y'^2}{x''y'-y''x'}](../I/m/c8e238b46813629cab3df47183a5bd50.png) ![Y[x,y]=y+x'\frac{x'^2+y'^2}{y''x'-x''y'}](../I/m/c94a285074edb6fc5f149c3d16c39551.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 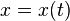 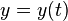 | Evolute |
![F[r]=t (r'\circ r^{[-1]})](../I/m/e28dedddc22aa666b049846271ec95ea.png) | Intrinsic | 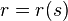 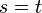 | |
![X[x,y]=x-\frac{x'\int_a^t \sqrt { x'^2 + y'^2 }\, dt}{\sqrt { x'^2 + y'^2 }}](../I/m/50c28b1f60a9fad0c7a43dd62c931a1f.png) ![Y[x,y]=y-\frac{y'\int_a^t \sqrt { x'^2 + y'^2 }\, dt}{\sqrt { x'^2 + y'^2 }}](../I/m/2ed0da6a13e5d3743ee25347536281f3.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 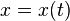 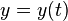 | Involute |
![X[x,y]=\frac{(xy'-yx')y'}{x'^2 + y'^2}](../I/m/d7dcadaecf9caf291dce86f89aad5327.png) ![Y[x,y]=\frac{(yx'-xy')x'}{x'^2 + y'^2}](../I/m/a358f788b739ad1ad4f44358213a6c4e.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 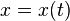 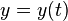 | Pedal curve with pedal point (0;0) |
![X[x,y]=\frac{(x'^2-y'^2)y'+2xyx'}{xy'-yx'}](../I/m/a588ce2e39ab0f23e1d64d2fa9212179.png) ![Y[x,y]=\frac{(x'^2-y'^2)x'+2xyy'}{xy'-yx'}](../I/m/96ea79b8881ea384ebba265a2ed407db.png) | Parametric Cartesian | 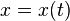 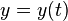 | Negative pedal curve with pedal point (0;0) |
![X[y] = \int_a^t \cos \left[\int_a^t \frac{1}{y} \,dt\right] dt](../I/m/7388111d1347030ae66786d61ee5114f.png) ![Y[y] = \int_a^t \sin \left[\int_a^t \frac{1}{y} \,dt\right] dt](../I/m/12fa1a381840f1a9e2d482727f4e517d.png) | Intrinsic | 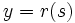 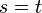 | Intrinsic to Cartesian transformation |
| Metric functionals | |||
![F[y]=||y||=\sqrt{\int_E y^2 \, dt}](../I/m/7c8219d9bf7d64cf9956cd7aedff42d6.png) | Norm | ||
![F[x,y]=\int_E xy \, dt](../I/m/5f07dba271068316a463b2d579c631a1.png) | Inner product | ||
![F[x,y]=\arccos \left[\frac{\int_E xy \, dt}{\sqrt{\int_E x^2 \, dt}\sqrt{\int_E y^2 \, dt}}\right]](../I/m/649a78875da76bdf112111a8239831cc.png) | Fubini–Study metric (inner angle) | ||
| Distribution functionals | |||
![F[x,y] = x * y = \int_E x(s) y(t - s)\, ds](../I/m/02fd75ea1f0e9e10d4cf9b0953ea90b2.png) | Convolution | ||
![F[y] = \int_E y \ln y \, dy](../I/m/bded6b0422d94f0ffc8c832f9282cedc.png) | Differential entropy | ||
![F[y] = \int_E yt\,dt](../I/m/f81088dcd35f4a5f4b8a21b5d81eed73.png) | Expected value | ||
![F[y] = \int_E (t-\int_E yt\,dt)^2y\,dt](../I/m/7d0076a25484b91fbb18fce89d075edc.png) | Variance | ||
See also
- List of transforms
- List of Fourier-related transforms
- Transfer operator
- Fredholm operator
- Borel transform
- Table of mathematical symbols
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/13/2014. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.