Major duodenal papilla
| Major duodenal papilla | |
|---|---|
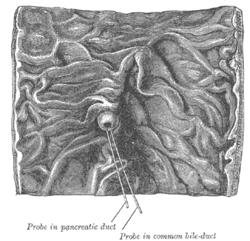 Interior of the descending portion of the duodenum, showing bile papilla. | |
 The pancreatic duct. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | papilla duodeni major |
| TA | A05.6.02.015 |
| FMA | 15074 |
The major duodenal papilla is an opening of the pancreatic duct into the duodenum. The major duodenal papilla is, in most people, the primary mechanism for the secretion of bile and other enzymes that facilitate digestion.
Structure

9. Gallbladder, 10–11. Right and left lobes of liver. 12. Spleen.
13. Esophagus. 14. Stomach. 15. Pancreas: 16: Accessory pancreatic duct, 17: Pancreatic duct.
18. Small intestine: 19. Duodenum, 20. Jejunum
21–22: Right and left kidneys (silhouette).
The anterior border of the liver is lifted upwards (brown arrow). Gallbladder with Longitudinal section, pancreas and duodenum with frontal one. Intrahepatic ducts and stomach in transparency.
The major duodenal papilla is situated in the second part of the duodenum, 7-10 cm from the pylorus, at the level of the second or third lumbar vertebrae. It is surrounded by the sphincter of Oddi, and receives a mixture of pancreatic enzymes and bile from the Ampulla of Vater, which drains both the pancreatic duct and biliary system.[1] The junction between the foregut and midgut occurs directly below the major duodenal papilla.[2] :274
The major duodenal papilla is seen from the duodenum as lying within a mucosal fold. The minor duodenal papilla is situated 2cm proximal.[1]
Variation
The major duodenal papilla is occasionally found in the third part of the duodenum, the level of the vertebrae may be L2-3, and in about 10% of people, it may not receive bile. Additionally, in a small number of people, the primary papilla for draining the pancreas may in fact be the accessory pancreatic duct.[1]
History
The major duodenal papilla was first illustrated by Gottfreid Bidloo in 1685, although is sometimes called the papilla of Vater, after German anatomist Abraham Vater.[1]
See also
External links
- pancreas at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- digest-019—Embryo Images at University of North Carolina
- Swiss embryology (from UL, UB, and UF) sdigestive/pankreas01
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- 1 2 3 4 Skandalakis, editor in chief John E. (2004). Skandalakis' surgical anatomy : the embryologic and anatomic basis of modern surgery. Athens, Greece: PMP. pp. Chapter 16: Small Intestine; Chapter 21:Pancreas, sections titled "Major duodenal papilla". ISBN 9603990744.
- ↑ Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.