Mapanuepe Lake
| Mapanuepe Lake | |
|---|---|
 The lake in 1992 with the three settlements already submerged | |
.svg.png) Mapanuepe Lake Location within the Philippines | |
| Location | Zambales, Luzon Island |
| Coordinates | 14°59′0″N 120°17′30″E / 14.98333°N 120.29167°ECoordinates: 14°59′0″N 120°17′30″E / 14.98333°N 120.29167°E |
| Type | Lahar-dammed lake |
| Primary inflows | Mapanuepe and Marella River |
| Primary outflows | Santo Tomas River[1] |
| Basin countries | Philippines |
| First flooded | 1991-1992 |
| Max. length | 4.1 kilometres (2.5 mi) |
| Max. width | 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi) |
| Surface area | 648 hectares (1,600 acres) |
| Max. depth | 25 metres (82 ft) |
| Shore length1 | 33 kilometres (21 mi) |
| Surface elevation | 129 metres (423 ft) |
| Islands | Ten small islets |
| Settlements | San Marcelino |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Mapanuepe Lake is a freshwater lake located in the province of Zambales in the Philippines. The lake was created after the cataclysmic eruption of Mount Pinatubo in 1991. Lahars following the eruption blocked the drainage of Mapanuepe River, south of the volcano, flooding Mapanuepe Valley together with its settlements. Only the steeple of the church protruding out of the water remained on one of the villages.[2]
History
Mapanuepe lake is located at the confluence of Marella and Mapanuepe Rivers as the two rivers merge to become the Santo Tomas River. The subsequent rains following the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo produced lahar that dumped volcanic debris on the Marella River, one of the major drainages of the mountain, aggrading the river that eventually dammed the Mapanuepe River. The rising waters submerged the Mapanuepe Valley including the barangays of Aglao (lower), Buhawen and Pili of San Marcelino, Zambales. During the development of the lake, breaching and reforming of the debris dam occurred following each lahar episode. At its maximum extent, the lake grew to an area of 670 hectares (1,700 acres) and had a stored water volume of 75 x 106 cubic meters (98,000,000 cu yd) before reaching its current state. The only structure that remains is a church tower with a huge metal cross right in the middle of the lake.[3] Prior to the 1991 eruption, studies of geologic formations and sediments of Mapanuepe Valley showed that the area was the site of a similar lahar-formed lake from old eruptions.[2]
Water quality
The lake water is reportedly contaminated with mercury leaking from the abandoned Dizon Copper Mine which is located on the east shore of the lake.
Popular culture
- The lake was featured on Episode 10 in the second season of Destination Truth, an American TV show on SyFy channel, titled Ahool and Pinatubo Monsters . The Destination Truth team made an investigation following reports by local fishermen of mysterious, giant, and black fish-like creatures swimming on the lake labeled as the "Pinatubo Monster" by the show.[4]
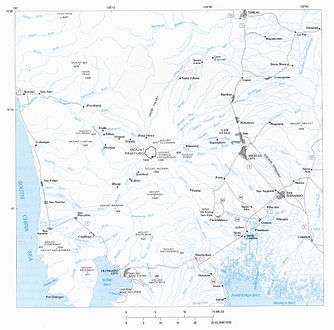 Map of the major rivers originating from Mount Pinatubo
Map of the major rivers originating from Mount Pinatubo Mapanuepe Lake before the eruption and after the formation in 1991
Mapanuepe Lake before the eruption and after the formation in 1991 A closer look at the confluence of Marella and Mapanuepe Rivers before the eruption with the location of the old settlements that were submerged
A closer look at the confluence of Marella and Mapanuepe Rivers before the eruption with the location of the old settlements that were submerged
See also
References
- ↑ Rodolfo, Kelvin S.; Umbal, Jesse V. "Two Years of Lahars on the Western Flank of Mount Pinatubo". U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved on 2011-06-17.
- 1 2 "The 1991 Lahars of Southwestern Mount Pinatubo and Evolution of the Lahar-Dammed Mapanuepe Lake". U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved on 2011-06-17.
- ↑ "The World Behind My Wall: Look Ma, No Mutation". theworldbehindmywall.com. 2011-04-11. Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- ↑ "Destination Truth - Ahool and Pinatubo Episode". SyFy Channel. Retrieved on 2011-06-17.