Metagonimus yokogawai
| Metagonimus yokogawai | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Metagonimus yokogawai | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Trematoda |
| Subclass: | Digenea |
| Order: | Opisthorchiida |
| Family: | Heterophyidae |
| Genus: | Metagonimus |
| Species: | M. yokogawai |
| Binomial name | |
| Metagonimus yokogawai (Katsurada, 1912)[1] | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
Heterophyes yokogawai Katsurada, 1912 | |
Metagonimus yokogawai is a species of a trematode, or fluke worm, in the family Heterophyidae.
It is a human parasite causing metagonimiasis.
Distribution
This species occurs in Korea, China, Taiwan, Japan, Russia, Indonesia, Israel, and Spain.[3]
Description
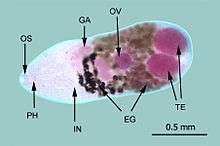
Life cycle
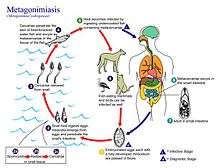
The first intermediate hosts of Metagonimus yokogawai include freshwater snails Semisulcospira libertina, Semisulcospira coreana,[3] and Semisulcospira reiniana.[2]
The second intermediate host include freshwater fish: Plecoglossus altivelis, Tribolodon hakonensis, Tribolodon ezoe, and Lateolabrax japonicus.[2][3]
Natural definitive hosts are: dogs, cats, rats, and humans.[3] Experminetal type hosts are: Syrian golden hamster.[2]
Here, the life cycle of Metagonimus yokogawai will be examined, however, it should be noted Metagonimus takahashii and Metagonimus miyatai follow similar life cycle pattern. All three species are hermaphroditic and capable of self-fertilization. Embryonated eggs are passed into an aquatic environment (fresh or brackish water) each containing a fully developed larva, called a miracidium. Development can’t proceed past this stage unless the eggs are ingested by the first intermediary host, freshwater snails. After the snail host ingests the eggs, miracidia emerge and penetrate the snail’s intestines. In the snail tissue, mircadia develop into sporocysts, then rediae, and finally emerge from the snail as cercariae. The cercariae then penetrate the skin or go under the scale of a fresh or brackish water fish and encyst as metacercariae in the tissue. The type of fish that serves as secondary host varies based on location. The host then becomes infected by consuming undercooked, raw, or pickled fish containing the infectious metacercariae. The metacercariae then excyst in the small intestine of the host (human, mammal or bird), and develop into adults. In the small intestine, the adults attach to the walls and develop new eggs.
References
- ↑ (Japanese) Katsurada F. (1912). "Heterophyes in Japan. II. Creation of a new genus Metagonimus". Okayama Igakkai Zasshi 273: 768–778.
- 1 2 3 4 Shimazu T. & Kino H. (2015). "Metagonimus yokogawai (Trematoda: Heterophyidae): From Discovery to Designation of a Neotype". The Korean Journal of Parasitology 53(5): 627-639. doi:10.3347/kjp.2015.53.5.627.
- 1 2 3 4 Chai J. Y., Darwin Murrell K. & Lymbery A. J. (2005). "Fish-borne parasitic zoonoses: Status and issues". International Journal for Parasitology 35(11-12): 1233-1254. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2005.07.013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Metagonimus yokogawai. |