White flight
| Part of a series of articles on Racial segregation | |
|---|---|
 | |
| South Africa | |
| United States | |
White flight is a term that originated in the United States, starting in the mid-20th century, and applied to the large-scale migration of people of various European ancestries from racially mixed urban regions to more racially homogeneous suburban or exurban regions. The term has more recently been applied to other migrations by whites, from older, inner suburbs to rural areas, as well as from the US Northeast and Midwest to the milder climate in the Southeast and Southwest.[1][2][3] The term has also been used for large-scale post-colonial emigration of whites from Africa, or parts of that continent,[4][5][6][7][8] driven by levels of violent crime and anti-colonial state policies.[9]
Migration of middle-class white populations was observed during the 1950s and 1960s out of cities such as Cleveland, Detroit, and Oakland, although racial segregation of public schools had ended there long before the U.S. Supreme Court's decision Brown v. Board of Education in 1954. In the 1970s, attempts to achieve effective desegregation by means of forced busing in some areas led to more families' moving out of former areas.[10][11] More generally, some historians suggest that white flight occurred in response to population pressures, both from the large migration of blacks from the rural South to northern cities in the Great Migration and the waves of new immigrants from southern and eastern Europe.[12] However, some historians have challenged the phrase "white flight" as a misnomer whose use should be reconsidered. In her study of Chicago's West Side during the post-war era, historian Amanda Seligman argues that the phrase misleadingly suggests that whites immediately departed when blacks moved into the neighborhood, when in fact, many whites defended their space with violence, intimidation, or legal tactics.[13]
The business practices of redlining, mortgage discrimination, and racially restrictive covenants contributed to the overcrowding and physical deterioration of areas where minorities chose to congregate. Such conditions are considered to have contributed to the emigration of other populations. The limited facilities for banking and insurance, due to a perceived lack of profitability, and other social services, and extra fees meant to hedge against perceived profit issues increased their cost to residents in predominantly non-white suburbs and city neighborhoods.[14][15] According to the environmental geographer Laura Pulido, the historical processes of suburbanization and urban decentralization contribute to contemporary environmental racism.[16]
United States
In the United States during the 1940s, for the first time a powerful interaction between segregation laws and race differences in terms of socioeconomic status enabled white families to abandon inner cities in favor of suburban living. The eventual result was severe levels of urban decay that, by the 1960s, resulted in the crumbling urban "ghettos". Prior to national data obtained by the 1950 U.S. census, the migration pattern of disproportionate numbers of whites moving from cities to suburban communities was merely anecdotal. Because urban populations in the United States were still substantially growing, a relative decrease in one racial or ethnic component remained very difficult to prove statistically to the satisfaction of national policy makers. Data on urban population changes had not been broken into what are now familiarly called its "components." The first data set that potentially could prove "white flight" was the 1950 census data. But the original processing of this data, on older-style tabulation machine by the U.S. Census Bureau, failed to attain any such level of statistical proof. It was a rigorous reprocessing of the same mass of raw data, on a UNIVAC I by Donald J. Bogue of the Scripps Foundation, that scientifically proved the reality of white flight.[17]
During the later 20th century, industrial restructuring led to major losses of jobs, leaving formerly middle-class working populations suffering poverty, with some unable to move away and seek employment elsewhere. Real estate prices often fall in areas of economic erosion, allowing persons with lower income to establish homes in such areas. Since the 1960s and changed immigration laws, the United States has received immigrants from Mexico, Central and South America, Asia, and Africa. Immigration has changed the demographics of both cities and suburbs, and the US become a largely suburban nation, with the suburbs becoming more diverse. In addition, Latinos, the fastest growing minority group in the US, began to migrate away from traditional entry cities and to cities in the Southwest, such as Phoenix and Tucson. In 2006, the increased number of Latinos had made whites a minority group in some western cities.[18]
Catalysts
Legal exclusion
In the 1930s, states outside the South (where racial segregation was legal) practiced unofficial segregation via exclusionary covenants in title deeds and real estate neighborhood redlining[19][20] – explicit, legally sanctioned racial discrimination in real property ownership and lending practices. Blacks were effectively barred from pursuing homeownership, even when they were able to afford it.[21] Suburban expansion was reserved for middle-class and working-class white people, facilitated by their increased wages incurred by the war effort and by subsequent federally guaranteed mortgages (VA, FHA, HOLC) available only to whites to buy new houses, such as those created by the Federal Housing Administration.[22]
Roads
After World War II, aided by the construction of the Interstate Highway System, many White Americans began leaving industrial cities for new housing in suburbs.[21] The roads served to transport suburbanites to their city jobs, facilitating the development of suburbs, and shifting the tax base away from the city. This may have exacerbated urban decay.[23] In some cases, such as in the Southern United States, local governments used highway road constructions to deliberately divide and isolate black neighborhoods from goods and services, often within industrial corridors. In Birmingham, Alabama, the local government used the highway system to perpetuate the racial residence-boundaries the city established with a 1926 racial zoning law. Constructing interstate highways through majority-black neighborhoods eventually reduced the populations to the poorest proportion of people financially unable to leave their destroyed community.[24]
Blockbusting
The real estate business practice of "blockbusting" was a for-profit catalyst for white flight and a means to control non-white migration. By subterfuge, real estate agents would facilitate black people buying a house in a white neighborhood, either by buying the house themselves, or via a white proxy buyer, and then re-selling it to the black family. The remaining white inhabitants (alarmed by real estate agents and the local newsmedia),[25] fearing devalued residential property, would quickly sell, usually at a loss. Losses happened when they sold en masse, and would sell the properties to the incoming black families, profiting from price arbitrage and the sales commissions from both the blacks and the whites. By such tactics, the racial composition of a neighborhood population often changed completely in a few years.[26]
Association with urban decay

Urban decay is the sociological process whereby a city, or part of a city, falls into disrepair and decrepitude. Its characteristics are depopulation, economic restructuring, abandoned buildings, high local unemployment (and thus poverty),[27] fragmented families, political disenfranchisement, crime, and a desolate, inhospitable city landscape. White flight contributed to the draining of cities' tax bases when middle-class people left. Abandoned properties attracted criminals and street gangs, contributing to crime.[27]
In the 1970s and 1980s, urban decay was associated with Western cities, especially in North America and parts of Europe. In that time, major structural changes in global economies, transportation, and government policy created the economic, then social, conditions resulting in urban decay.[28]
White flight in North America started to reverse in the 1990s, when the rich suburbanites returned to cities, gentrifying the decayed urban neighborhoods.[21][29]
Government-aided white flight
New municipalities were established beyond the abandoned city's jurisdiction to avoid the legacy costs of maintaining city infrastructures; instead new governments spent taxes to establish suburban infrastructures. The federal government contributed to white flight and the early decay of non-white city neighborhoods by withholding maintenance capital mortgages, thus making it difficult for the communities to either retain or attract middle-class residents.[30]
The new suburban communities limited the emigration of poor and non-white residents from the city by restrictive zoning; thus, few lower-middle-class people could afford a house in the suburbs. Many all-white suburbs were eventually annexed to the cities their residents had left. For instance, Milwaukee, Wisconsin partially annexed towns such as Granville; the (then) mayor, Frank P. Zeidler, complained about the socially destructive "Iron Ring" of new municipalities incorporated in the post–World War II decade.[31] Analogously, semi-rural communities, such as Oak Creek, South Milwaukee, and Franklin, formally incorporated as discrete entities to escape urban annexation. Wisconsin state law had allowed Milwaukee's annexation of such rural and suburban regions that did not qualify for discrete incorporation per the legal incorporation standards.[32][33]
Desegregation of schools
In some areas, the post–World War II racial desegregation of the public schools catalyzed white flight. In 1954, the US Supreme Court case Brown v. Board of Education (1954) ordered the de jure termination of the "separate, but equal" legal racism established with the Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) case in the 19th century. It declared that segregation of public schools was unconstitutional. Many southern jurisdictions mounted massive resistance to the policy. In some cases, white parents withdrew their children from public schools and established private religious schools instead. These schools, termed segregation academies, sprung up in the American South between the late 1950s and mid-1970s and allowed parents to prevent their children from being enrolled in racially mixed schools.[34]
Upon desegregation in 1957 in Baltimore, Maryland, the Clifton Park Junior High School had 2,023 white students and 34 black students; ten years later, it had twelve white students and 2,037 black students. In northwest Baltimore, Garrison Junior High School's student body declined from 2,504 whites and twelve blacks to 297 whites and 1,263 blacks in that period.[35] At the same time, the city's working class population declined because of the loss of industrial jobs as heavy industry restructured.
In Swann v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education (1971), the Supreme Court ordered the desegregation busing of poor black students to suburban white schools, and suburban white students to the city to try to integrate student populations. In Milliken v. Bradley (1974), the dissenting Justice William Douglas observed, "The inner core of Detroit is now rather solidly black; and the blacks, we know, in many instances are likely to be poorer." Likewise, in 1977, the Federal decision in Penick v. The Columbus Board of Education (1977) accelerated white flight from Columbus, Ohio. Although the racial desegregation of schools affected only public school districts, the most vehement opponents of racial desegregation have sometimes been whites whose children attended private schools.[36][37]
A secondary, non-geographic consequence of school desegregation and busing was "cultural" white flight: withdrawing white children from the mixed-race public school system and sending them to private schools unaffected by US federal integration laws. In 1970, when the United States District Court for the Central District of California ordered the Pasadena Unified School District desegregated, the proportion of white students (54%) reflected the school district's proportion of whites (53%). Once the federally ordered school desegregation began, whites who could afford private schools withdrew their children from the racially diverse Pasadena public school system. By 2004, Pasadena had 63 private schools educating some 33% of schoolchildren, while white students made up only 16% of the public school populace. The Pasadena Unified School District superintendent characterized public schools as "like the bogey-man" to whites. He implemented policies to attract white parents to the racially diverse Pasadena public school district.[38]
Checkerboard and tipping models
In studies in the 1980s and 1990s, blacks said they were willing to live in neighborhoods with 50/50 ethnic composition. Whites were also willing to live in integrated neighborhoods, but preferred proportions of more whites. Despite this willingness to live in integrated neighborhoods, the majority still live in largely segregated neighborhoods, which have continued to form.[39]
In 1969, Nobel Prize-winning economist Thomas Schelling published "Models of Segregation", a paper in which he demonstrated through a "checkerboard model" and mathematical analysis, that even when every agent prefers to live in a mixed-race neighborhood, almost complete segregation of neighborhoods emerges as individual decisions accumulate. In his "tipping model", he showed that members of an ethnic group do not move out of a neighborhood as long as the proportion of other ethnic groups is relatively low, but if a critical level of other ethnicities is exceeded, the original residents may make rapid decisions and take action to leave. This tipping point is viewed as simply the end-result of domino effect originating when the threshold of the majority ethnicity members with the highest sensitivity to sameness is exceeded. If these people leave and are either not replaced or replaced by other ethnicities, then this in turn raises the level of mixing of neighbors, exceeding the departure threshold for additional people.[40]
Africa
South Africa
About 800,000 out of an earlier total population of 5.2 million whites have left South Africa since 1995, according to a report from 2009. (Apartheid, a system of segregation of whites, blacks, and people of other races, had ended in 1994.) The country has suffered a high rate of violent crime, a primary stated reason for emigration. Other causes include attacks against white farmers, concern about being excluded by affirmative action programs, rolling blackouts in electrical supplies, and worries about corruption and autocratic political tendencies among new leaders. Since many of those who leave are highly educated, there are shortages of skilled personnel in the government, teaching, and other professional areas. Some observers fear the long-term consequences, as South Africa's labor policies make it difficult to attract skilled immigrants. The migration of whites in South Africa was facilitated by the creation of immigration routes into European countries for people with European ancestry. For instance, the British government introduced the notion of patriality to ensure white people of British ancestry from Africa could settle in the UK. In the global economy, some professionals and skilled people have been attracted to work in the US and European nations.[9][41]
Zimbabwe (Rhodesia)
Until 1980, the former British dependency of Rhodesia held a well-publicised image as being one of two nations in sub-Saharan Africa where a white minority of European descent and culture held political, economic, and social control over a preponderantly black African majority.[42] Nevertheless, unlike white South Africans a significant percentage of white Rhodesians represented recent immigrants. Initially, about three-fourths of resident whites were of British origin, with those from England and Wales predominating.[42] After World War II there was a substantial influx of the British diaspora, including former colonials from India, Pakistan, and other British possessions in Africa. Also represented were working-class Englishmen responding to economic opportunities.[42] In 1969 only 41% of Rhodesia's white community had been nationals since birth, or 93,600 persons. It was estimated that half of the remainder held British passports (approximately 67,000 persons), with a smaller number having South African passports.[42]
During the Rhodesian Bush War, almost the entire white male population between eighteen and fifty-eight was affected by various military commitments, and individuals spent up to five or six months of the year on combat duty away from their normal occupations in the civil service, commerce, industry, or agriculture.[43] These long periods of service in the field led to an increased emigration of men of military age. In November 1963, state media cited the chief reasons for emigration as uncertainty about the future, economic decline due to embargo and war, and the heavy commitments of national service, which was described as "the overriding factor causing people to leave".[43] Of the male emigrants in 1976 about half fell into the 15 to 39 age bracket. Between 1960 and 1976 160,182 whites immigrated, while 157,724 departed. This dynamic turnover rate led to depressions in the property market, a slump in the construction industry, and a decline in retail sales.[43] The number of white Rhodesians peaked in 1975 at 278,000 and rapidly declined as the bush war intensified. Disfavour with the biracial Zimbabwe Rhodesia administration in 1979 also contributed to a mass exodus.[42]
The establishment of the new Republic of Zimbabwe in 1980 sounded the death knell for white political power and ushered in a new era of self-determination for the black majority.[42] White emigration peaked between 1980 and 1982 at 53,000 persons, with the breakdown of law and order, an increase in crime in the rural areas, and the provocative attitude of Zimbabwean officials being cited as the main causes.[44] Political conditions typically had a greater impact on the decision to migrate among white than black professionals.[45] Between 1982 and 2000 Zimbabwe registered a net loss of 100,000 whites, or an average of 5,000 departures per year.[46] A second wave of white emigration was sparked by President Robert Mugabe's violent land reform programme after 2000.[45] Popular destinations included South Africa and Australia, which emigrants perceived to be geographically, culturally, or sociopolitically similar to their home country.[46]
From a strictly economic point of view, the departure figures were not as significant as the loss of the skills of those leaving.[42] A disproportionate number of white Zimbabwean emigrants were well educated and highly skilled. Among those living in the United States, for example, 53.7% had a bachelor's degree, while only 2% had not completed secondary school.[46] Most (52.4%) had occupied technical or supervisory positions of critical importance to the modern sector of the economy.[46] Inasmuch as black workers did not begin making large inroads into apprenticeships and other training programs until the 1970s, few were in a position to replace their white colleagues in the 1980s.[42]
Europe
Denmark
A study of school choice in Copenhagen found that an immigrant proportion of below 35% in the local schools did not affect parental choice of schools. If the percentage of immigrant children rose above this level, native Danes are far more likely to choose other schools. Immigrants who speak Danish at home also opt out. Other immigrants, often more recent ones, stay with local schools.[47]
Ireland
A 2007 government report stated that immigration in Dublin has caused "dramatic" white flight from elementary schools in a studied area (Dublin 15). 27% of residents were foreign-born immigrants. The report stated that Dublin was risking creating immigrant-dominated banlieues, on the outskirts of a city, similar to such areas in France. The immigrants in the area included Eastern Europeans (such as those from Poland), Asians, and Africans (mainly political refugees from Nigeria).[48]
Norway
White flight in Norway has increased in the 1970s with the immigration of non-Scandinavians from (in numerical order, starting with the largest): Poland, Pakistan, Iraq, Somalia, Vietnam, Iran, Turkey, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Russia, Sri Lanka, the Philippines, the former Yugoslavia, Thailand, Afghanistan, and Lithuania. By June 2009, more than 40% of Oslo schools had an immigrant majority, with some schools having a 97% immigrant share.[49] Schools in Oslo are increasingly divided by ethnicity.[50][51] For instance, in the Groruddalen (Grorud valley), four boroughs which currently has a population of around 165,000, the ethnic Norwegian population decreased by 1,500 in 2008, while the immigrant population increased by 1,600.[52] In thirteen years, a total of 18,000 ethnic Norwegians have moved from the borough.[53]
In January 2010, a news feature from Dagsrevyen on the public Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation said, "Oslo has become a racially divided city. In some city districts the racial segregation starts already in kindergarten." Reporters said, "In the last years the brown schools have become browner, and the white schools whiter," a statement which caused some minor controversy.[53][54]
Sweden
After World War II, immigration into Sweden occurred in three phases. The first was a direct result of the war, with refugees from concentration camps and surrounding countries in Scandinavia and Northern Europe. The second, prior to 1970, involved immigrant workers, mainly from Finland, Italy, Greece, and Yugoslavia. In the most recent phase, from the 1970s onwards, refugees immigrated from the Middle East, Africa, and Latin America, joined later by their relatives.[55]
A study which mapped patterns of segregation and congregation of incoming population groups[56] found that, if a majority group is reluctant to accept a minority influx, they may leave the district, avoid the district, or use tactics to keep the minority out. The minority group in turn react by either dispersing or congregating, avoiding certain districts in turn. Detailed analysis of data from the 1990s onwards indicates that the concentration of immigrants in certain city districts, such as Husby in Stockholm and Rosengård in Malmö, is in part due to immigration influx, but primarily due to white flight.[57][58]
United Kingdom
For centuries, London was the destination for refugees and immigrants from continental Europe. Although all the immigrants were European, neighborhoods showed ethnic succession over time, as older residents (in some cases, ethnic British) moved out and new immigrants moved in, an early case of white flight (though the majority of London's population was still ethnic British).[59]
In the 2001 census, the London boroughs of Newham and Brent were found to be the first areas to have non-white majorities.[60] The 2011 census found that, for the first time, less than 50% of London's population were white British, and that in some areas of London white British people make up less than 20% of the population. A 2005 report stated that white migration within the UK is mainly from areas of high ethnic minority population to those with predominantly white populations. White British families have moved out of London as many immigrants have settled in the capital. The report's writers expressed concern about British social cohesion and stated that different ethnic groups were living "parallel lives"; they were concerned that lack of contact between the groups could result in fear more readily exploited by extremists. The London School of Economics in a study found similar results.[61]
Researcher Ludi Simpson says that the growth of ethnic minorities in Britain is due mostly to natural population growth (births outnumber deaths) rather than immigration. Both white and non-white Britons who can do so economically are equally likely to leave mixed-race inner-city areas. In his opinion, these trends indicate counter urbanisation rather than white flight.[62][63]
Oceania
Australia
In Sydney, the poorer suburbs that attracted migrants were in the Greater Western Sydney region, away from the city and the harbor. Those areas popular with European and Asian migrants experienced a degree of white flight, with a concentration of Anglo-Celtic people in certain areas, such as Penrith in far-western Sydney, the Sutherland Shire and the Gosford–Wyong area of the Central Coast, north of Sydney. These suburbs remain predominantly European-Australian.[64]
According to the New South Wales Secondary Principals Council and the University of Western Sydney, public schools in that state have experienced white flight to private and Catholic schools wherever there is a large presence of Aboriginal and Middle Eastern students.[65]
New Zealand
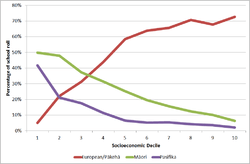
White flight has been observed in low socioeconomic decile schools in New Zealand. Data from the Ministry of Education found that 60,000 New Zealand European students attended low-decile schools (situated in the poorest areas) in 2000, and had fallen to half that number in 2010. The same data also found that high-decile schools (which are in the wealthiest areas) had a corresponding increase in New Zealand European students.[66] The Ministry claimed demographic changes were behind the shifts, but teacher and principal associations have attributed white flight to racial and class stigmas of low-decile schools, which commonly have majority Maori and Pacific Islander rolls.[67]
In one specific case, white flight has significantly affected Sunset Junior High School in a suburb of the city of Rotorua, with the total number of students reduced from 700 to 70 in the early 1980s. All but one of the 70 students are Maori. The area has a concentration of poor, low-skilled people, with struggling families, and many single mothers. Related to the social problems of the families, student educational achievement is low on the standard reading test.[68]
See also
References
Notes
- ↑ Schaefer, Richard T., ed. (2008). The Encyclopedia of Race, Ethnicity, and Society. SAGE publications.
- ↑ "white flight". Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
- ↑ Armor, David J. (1986). Forced Justice: School Desegregation and the Law. Oxford University Press US.
- ↑ Joshua Hammer (May–June 2010). "(Almost) Out of Africa: The White Tribes". World Affairs Journal.
- ↑ Johnson, RW (October 19, 2008). "Mosiuoa 'Terror' Lekota threatens to topple the ANC". The Times. London.
- ↑ Christopher, A. J. (2000). The atlas of changing South Africa (2nd ed.). Routledge. p. 213. ISBN 9780203185902.
- ↑ Bradshaw, York W.; Ndegwa, Stephen N., eds. (2001). The uncertain promise of Southern Africa. Indiana University Press. p. 6.
- ↑ Reinhardt, Steven G.; Reinhartz, Dennis P., eds. (2006). Transatlantic history (1st ed.). Texas A&M University Press. pp. 149–150. ISBN 9781585444861.
- 1 2 "White flight from South Africa: Between staying and going". The Economist. September 25, 2008.
- ↑ Clotfelter, Charles T. (2004). After Brown: The Rise and Retreat of School Desegregation. Princeton University Press.
- ↑ Ravitch, Diane (1983). The Troubled Crusade: American Education, 1945–1980. New York City: Basic books. ISBN 9780465087570.
- ↑ Boustan, L. P. (2010). "Was Postwar Suburbanization "White Flight"? Evidence from the Black Migration*". Quarterly Journal of Economics. 125: 417–443. doi:10.1162/qjec.2010.125.1.417.
- ↑ Seligman, Amanda (2005). Block by block : neighborhoods and public policy on Chicago's West Side. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 213–14. ISBN 978-0-226-74663-0.
- ↑ Kruse, Kevin M. (2007). White Flight: Atlanta and the Making of Modern Conservatism. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-13386-7.
- ↑ Thabit, Walter (2003). How East New York Became a Ghetto. New York: New York University Press. p. 42. ISBN 0-8147-8267-1.
- ↑ Pulido, Laura (Mar 2000). "Rethinking Environmental Racism: White Privilege and Urban Development in Southern California" (PDF). Annals of the Association of American Geographers. 90 (1): 12–40. doi:10.1111/0004-5608.00182.
- ↑ Bogue, Donald J. (1957) Components of Population Change, 1940–1950 published jointly by Scripps Foundation for Research in Population Problems: Miami University, and Population Research and Training Center: University of Chicago.
- ↑ Asthana, Anushka (August 21, 2006). "Changing Face of Western Cities: Migration Within U.S. Makes Whites a Minority in 3 More Areas". Washington Post.
- ↑ Crossney, Kristen; Bartelt, David (December 1, 2005). "Residential Security, Risk, and Race: The Home Owners' Loan Corporation and Mortgage Access in Two Cities". Urban Geography. 26 (8): 707–736. doi:10.2747/0272-3638.26.8.707.
- ↑ Crossney; Bartelt. "2006 Housing Policy Debate" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on April 14, 2008.
- 1 2 3 Jackson, Kenneth T. (1985), Crabgrass Frontier: The Suburbanization of the United States, New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-504983-7
- ↑ "Racial" Provisions of FHA Underwriting Manual, 1938
- "Recommended restrictions should include provisions for: prohibition of the occupancy of properties except by the race for which they are intended. ... Schools should be appropriate to the needs of the new community, and they should not be attended in large numbers by inharmonious racial groups." —Federal Housing Administration, Underwriting Manual: Underwriting and Valuation Procedure Under Title II of the National Housing Act With Revisions to February, 1938 (Washington, D.C.), Part II, Section 9, Rating of Location.
- ↑ Wheeler, James O. (1976). "Locational Dimensions of Urban Highway Impact: An Empirical Analysis". Geografiska Annaler. Series-B, Human Geography. 58 (2): 67–78. JSTOR 490613.
- ↑ Connerly, C. E. (December 1, 2002). "From Racial Zoning to Community Empowerment: The Interstate Highway System and the African American Community in Birmingham, Alabama". Journal of Planning Education and Research. 22 (2): 99–114. doi:10.1177/0739456X02238441.
- ↑ Ford, Richard Thompson (2008). The Race Card: How Bluffing about Bias Makes Race Relations Worse (1st ed.). New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. pp. 290–291. ISBN 9780374245757.
- ↑ Hirsch, Arnold R. "Blockbusting". Encyclopedia of Chicago History.
- 1 2 Caro, Robert. The Power Broker: Robert Moses and the Fall of New York. p.522. "The construction of the Gowanus Parkway, laying a concrete slab on top of lively, bustling Third Avenue, buried the avenue in shadow, and when the parkway was completed, the avenue was cast forever into darkness and gloom, and its bustle and life were forever gone. ISBN 0-394-72024-5
- ↑ Andersen, Hans Skifter (2003). Urban Sores: On the Interaction Between Segregation, Urban Decay, and Deprived Neighbourhoods. Burlington, VT: Ashgate. ISBN 0-7546-3305-5.
- ↑ Proscio, Tony; Grogan, Paul S. (2000). Comeback Cities: A Blueprint for Urban Neighborhood Revival. Boulder, CO: Westview Press. pp. 139–145. ISBN 0-8133-3952-9.
The 1965 law brought an end to the lengthy and destructive – at least for cities – period of tightly restricted immigration a spell born of the nationalism and xenophobia of the 1920s. [p.140]
- ↑ Wilson, William Julius (1997). When Work Disappears: The World of the New Urban Poor. New York City: Vintage Books. ISBN 0-679-72417-6.
- ↑ Borsuk, by Alan J. (July 8, 2006). "Mayor served 'the public welfare': Longtime city icon known for integrity, energy, principles]". Journal Sentinel. Archived from the original on July 11, 2006.
- ↑ Rast, J. (1 September 2006). "Governing the Regimeless City: The Frank Zeidler Administration in Milwaukee, 1948-1960". Urban Affairs Review. 42 (1): 81–112. doi:10.1177/1078087406289734.
- ↑ Curran, Donald J. Curran (February 1964). "Infra-Metropolitan Competition". Land Economics. 40 (1): 94–99. doi:10.2307/3144466.
- ↑ Clotfelter, Charles T. (2004). After Brown: The Rise and Retreat of School Desegregation. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. pp. 101–109.
- ↑ "From the Old Order to the New Order–Reasons and Results, 1957-1997". Baltimore City Public School System. Archived from the original on January 2, 2004.
- ↑ Jacobson, Cardell K. "Desegregation Rulings and Public Attitude Changes: White Resistance or Resignation?". American Journal of Sociology. 84 (3): 698–705. doi:10.1086/226833. JSTOR 2778261.
- ↑ Nevius, C.W. (September 9, 2007). "Racism alive and well in S.F. schools – here's proof". San Francisco Chronicle.
- ↑ Ryan, John. "Tackling Local Resistance to Public Schools" (PDF). Daily Journal.
- ↑ Zhang, J. (2011). "Tipping and Residential Segregation: A Unified Schelling Model". Journal of Regional Science. 51: 167–193. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9787.2010.00671.x.
- ↑ Schelling, T. (1969). "Models of segregation". The American Economic Review. 59 (2): 488–493.
- ↑ Johnson, Scott (February 14, 2009). "Fleeing From South Africa". Newsweek. Archived from the original on July 28, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Nelson, Harold D, ed. (1983). Zimbabwe, a Country Study. Area Handbook Series (Second ed.). Washington, D.C.: Department of the Army, American University. OCLC 227599708.
- 1 2 3 Raeburn, Michael. We are everywhere: Narratives from Rhodesian guerillas. pp. 200–209.
- ↑ Smith, Ian (1997). The Great Betrayal. London: Blake Publishing Ltd. pp. 368–409. ISBN 1-85782-176-9.
- 1 2 Driouchi, Ahmed (2014). Labor and Health Economics in the Mediterranean Region: Migration and Mobility of Medical Doctors. Hershey: IGI Global. pp. 340–345. ISBN 978-1466647237.
- 1 2 3 4 Helen Marrow, The new Americans: a guide to immigration since 1965 // Mary C. Waters, Reed Ueda, Helen B. Marrow (eds.), Harvard University Press, 2007, pp. 309-317
- ↑ Rangvid, B. S. (2009). "School Choice, Universal Vouchers and Native Flight from Local Schools". European Sociological Review. 26 (3): 319–335. doi:10.1093/esr/jcp024.
- ↑ "Report finds evidence of 'white flight' from immigrants in northwest Dublin". International Herald Tribune. October 19, 2007. Archived from the original on October 24, 2007. Retrieved April 20, 2011.
- ↑ "40 prosent av Osloskolene har innvandrerflertall" (in Norwegian).
- ↑ Bredeveien, Jo Moen (June 2, 2009). "Rømmer til hvitere skoler" [Escaping the whiter schools]. Dagsavisen (in Norwegian).
- ↑ Lundgaard, Hilde (August 22, 2009). "Foreldre flytter barna til 'hvitere' skoler" [Parents moving kids to 'whiter' schools]. Aftenposten (in Norwegian).
- ↑ Slettholm, Andreas (December 15, 2009). "Ola og Kari flytter fra innvandrerne". Aftenposten (in Norwegian).
- 1 2 "Noen barn er brune". Nettavisen. January 15, 2010.
- ↑ Ringheim, Gunnar; Fransson, Line; Glomnes, Lars Molteberg (January 14, 2010). "Et stort flertall av barna er brune". Dagbladet (in Norwegian).
- ↑ Andersson 2007, p. 64
- ↑ Andersson 2007, p. 68
- ↑ Andersson 2007, pp. 74–75
- ↑ Bråmå, Åsa (2006). "'White flight'? The production and reproduction of immigrant concentration areas in Swedish cities, 1990–2000". Urban Studies. 43 (7): 1127–1146. doi:10.1080/00420980500406736.
- ↑ Porter, Roy (1994). London: A Social History. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. pp. 132, 140.
- ↑ "Census 2001: Ethnicity". BBC News.
- ↑ Johnston, Philip (February 10, 2005). "Whites 'leaving cities as migrants move in'". The Telegraph.
- ↑ Dominic Casciani (September 4, 2006). "So who's right over segregation?". BBC News Magazine. Retrieved September 21, 2006.
- ↑ Finney & Simpson 2009, Myths and counterarguments: a quick reference summary.
- ↑ Birrell, Bob, and Seol, Byung-Soo. "Sydney's Ethnic Underclass", People and Place, vol. 6, no. 3, September 1998. Archived October 2, 2006, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "'White flight' from Aussie public schools". Sydney Morning Herald. March 10, 2008.
- ↑ Garret-Walker, Hana (June 18, 2012). "Claim of 'white flight' from low decile schools". The New Zealand Herald.
- ↑ "Some Pakeha parents stereotyping Maori pupils – principals". Radio New Zealand. June 19, 2012.
- ↑ Collins, Simon (July 24, 2006). "'White flight' threatens school". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved September 22, 2011.
Bibliography
- Andersson, Roger (2007). Schönwälder, Karen, ed. "Ethnic residential segregation and integration processes in Sweden" (PDF). Residential Segregation and the Integration of Immigrants: Britain, the Netherlands and Sweden. Social Science Research Center Berlin: 61–90.
- Avila, Eric (2005). Popular Culture in the Age of White Flight: Fear and Fantasy in Suburban Los Angeles. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-24811-3.
- Finney, Nissa; Simpson, Ludi (2009). 'Sleepwalking to segregation'?: Challenging myths about race and migration. Bristol: Policy Press. ISBN 9781847420077.
- Gamm, Gerald (1999). Urban Exodus: Why the Jews Left Boston and the Catholics Stayed. Harvard University Press.
- Kruse, Kevin M. White Flight: Atlanta and the Making of Modern Conservatism. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0691133867.
- Lupton, R.; Power, A. (2004). "Minority Ethnic Groups in Britain" (PDF). CASE-Brookings Census Brief. London (2).
- Pietila, Antero (2010). Not in My Neighborhood: How Bigotry Shaped a Great American City. Chicago: Ivan R. Dee. ISBN 978-1566638432.
- Schneider, J. (30 May 2008). "Escape From Los Angeles: White Flight from Los Angeles and Its Schools, 1960-1980". Journal of Urban History. 34 (6): 995–1012. doi:10.1177/0096144208317600.
- Seligman, Amanda I. (2005), Block by Block: Neighborhoods and Public Policy on Chicago's West Side Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Sugrue, Thomas J. (2005). The Origins of the Urban Crisis: Race and Inequality in Postwar Detroit. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-12186-4.
- Tarasawa, Beth (January 19, 2009). "New Patterns of Segregation: Latino and African American Students in Metro Atlanta High Schools]". Southern Spaces.
- Wiese, Andrew (2006). "African American Suburban Development in Atlanta". Southern Spaces.