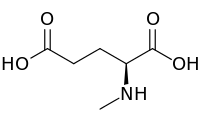
N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-2-(Methylamino)pentanedioic acid | |
| Other names
N-Methylglutamic acid; Methylglutamic acid; Methylglutamate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 6753-62-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16440 |
| ChemSpider | 388497 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 161.16 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid (methylglutamate) is a chemical derivative of glutamic acid in which a methyl group has been added to the amino group. It is an intermediate in methane metabolism. Biosynthetically, it is produced from methylamine and glutamic acid by the enzyme methylamine—glutamate N-methyltransferase.[1] It can also be demethylated by methylglutamate dehydrogenase to regenerate glutamic acid.[2]
References
- ↑ Shaw, WV; Tsai, L; Stadtman, ER (1966). "The enzymatic synthesis of N-methylglutamic acid". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 241 (4): 935–45. PMID 5905132.
- ↑ Hersh, LB; Stark, MJ; Worthen, S; Fiero, MK (1972). "N-methylglutamate dehydrogenase: Kinetic studies on the solubilized enzyme". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 150 (1): 219–26. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(72)90029-X. PMID 5028076.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/13/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.