Neutralisation (immunology)
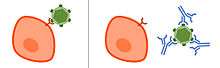
Covering an antigen in antibodies make it less infectious and less pathogenic.
Neutralisation or neutralization in the immunological sense refers to the ability of specific antibodies to block the site(s) on bacteria and their toxins or viruses that they use to enter their target cell. The effect of an neutralizing antibody can be negligible even with large excesses of antibody production if they lack specificity to this antigen. The production of specific antibodies can be learned for a faster response at next exposition.[1]
The reduction or destruction of a homologous infectious agent can be partial or complete and can make it no longer infectious or pathogenic to other cells.[2]
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/5/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.