Niobium(V) bromide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
niobium pentabromide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 13748-45-0 NbBr5 17633-68-0 Nb2Br10 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 19388901 |
| EC Number | 236-778-5 |
| PubChem | 83517 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NbBr5 | |
| Molar mass | 492.430 g/mol |
| Appearance | wine red to black crystals |
| Density | 4.417 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 254 °C (489 °F; 527 K) |
| Boiling point | 364 °C (687 °F; 637 K) |
| soluble | |
| Structure | |
| orthorhombic | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
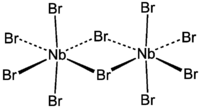
Niobium(V) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula Nb2Br10. Its name comes from the compound's empirical formula, NbBr5. It is a diamagnetic, orange solid that hydrolyses readily. The compound adopts an edge-shared bioctahedral structure, which means that two NbBr5 units are joined by a pair of bromide bridges.[1] The pentachloride and pentaiodides of Nb and Ta share this structural motif. There is no bond between the Nb centres. It is prepared by the reaction of bromine with niobium metal at high temperature in a tube furnace.[2]
References
- ↑ Hönle, Wolfgang; Furuseth, Sigrid; von Schnering, Hans Georg "Synthesis and crystal structure of ordered, orthorhombic α-NbBr5" Zeitschrift für Naturforschung, B: Chemical Sciences 1990, vol. 45, pp. 952-6. doi:10.1515/znb-1990-0706
- ↑ Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.