Peanut oil

Peanut oil, also known as groundnut oil or arachis oil, is a mild-tasting vegetable oil derived from peanuts. The oil is available with a strong peanut flavor and aroma, analogous to sesame oil.[1][2]
It is often used in Chinese, South Asian and Southeast Asian cuisine, both for general cooking, and in the case of roasted oil, for added flavor. Peanut oil has a high smoke point relative to many other cooking oils, so is commonly used for frying foods. Its major component fatty acids are oleic acid (46.8% as olein), linoleic acid (33.4% as linolein), and palmitic acid (10.0% as palmitin).[3] The oil also contains some stearic acid, arachidic acid, behenic acid, lignoceric acid and other fatty acids.[4]
Antioxidants such as vitamin E are sometimes added to improve the shelf life of the oil.[5]
History
Shortage of whale oil in the Confederacy made peanut oil an attractive alternative during the Civil War.[6] The oil had increased use in the United States during World War II, because of war shortages of other oils.[7]
Nutritional content
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 3,699 kJ (884 kcal) |
|
0 g | |
|
100 g | |
| Saturated | 17 g |
| Monounsaturated | 46 g |
| Polyunsaturated | 32 g |
|
0 g | |
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin E |
(105%) 15.7 mg |
| Minerals | |
| Zinc |
(0%) 0.01 mg |
| Other constituents | |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg |
| Selenium | 0.0 mcg |
|
Fat percentage can vary. | |
| |
|
Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database | |
According to the USDA data upon which the following table is based, 100 g of peanut oil contains 17.7 g of saturated fat, 48.3 g of monounsaturated fat, and 33.4 g of polyunsaturated fat.[3]
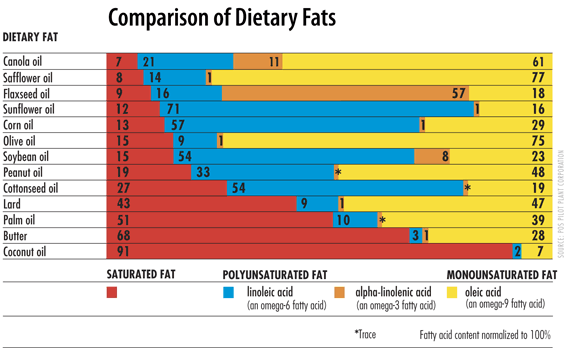
| Type of fat | Total fat (g) | Saturated fat (g) | Monounsaturated fat (g) | Polyunsaturated fat (g) | Smoke point |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunflower oil | 100 | 11 | 20 | 69 | 225 °C (437 °F)[8] |
| Sunflower oil (high oleic) | 100 | 12 | 84 [9] | 4 [9] | |
| Soybean oil | 100 | 16 | 23 | 58 | 257 °C (495 °F)[8] |
| Canola oil | 100 | 7 | 63 | 28 | 205 °C (401 °F)[9][10] |
| Olive oil | 100 | 14 | 73 | 11 | 190 °C (374 °F)[8] |
| Corn oil | 100 | 15 | 30 | 55 | 230 °C (446 °F)[8] |
| Peanut oil | 100 | 17 | 46 | 32 | 225 °C (437 °F)[8] |
| Rice bran oil | 100 | 25 | 38 | 37 | 250 °C (482 °F)[11] |
| Vegetable shortening (hydrogenated) | 71 | 23 | 8 | 37 | 165 °C (329 °F)[8] |
| Lard | 100 | 39 | 45 | 11 | 190 °C (374 °F)[8] |
| Suet | 94 | 52 | 32 | 3 | 200 °C (392 °F) |
| Butter | 81 | 51 | 21 | 3 | 150 °C (302 °F)[8] |
| Coconut oil | 100 | 86 | 6 | 2 | 177 °C (351 °F) |
Allergens and toxins

Most highly refined peanut oils remove the peanut allergens and have been shown to be safe for "the vast majority of peanut-allergic individuals".[12] However, cold-pressed peanut oils may not remove the allergens and thus could be highly dangerous to people with peanut allergy.[13] Since the degree of processing for any particular product is often unclear, "avoidance is prudent."[14][15] If quality control is neglected, peanuts that contain the mold that produces highly toxic aflatoxin can end up contaminating the oil derived from them.[16]
Other uses

Peanut oil, as with other vegetable oils, can be used to make soap by the process of saponification.[17] The oil is safe for use as a massage oil. Peanut researcher George Washington Carver marketed a peanut massage oil.[18][19]
Biodiesel
At the 1900 Paris Exhibition, the Otto Company, at the request of the French Government, demonstrated that peanut oil could be used as a source of fuel for the diesel engine; this was one of the earliest demonstrations of biodiesel technology.[20]
Suspension agent
Some medicines and vitamins use arachis oil as a suspension agent.
References
- ↑ Liu, Xiaojun; Jin, Qingzhe; Liu, Yuanfa; Huang, Jianhua; Wang, Xingguo; Mao, Wenyue; Wang, Shanshan (2011). "Changes in Volatile Compounds of Peanut Oil during the Roasting Process for Production of Aromatic Roasted Peanut Oil". Journal of Food Science. 76 (3): C404–12. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02073.x. PMID 21535807.
- ↑ "USA-Grown Peanut Sources - Peanut Oil". National Peanut Board.
- 1 2 "USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference". Nutrient Data Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 3 August 2011. Choose peanut oil and then "Oil, peanut, salad or cooking".
- ↑ Anyasor, G.N.; Ogunwenmo, K.O.; Oyelana, O.A.; Ajayi, D.; Dangana, J. (2009). "Chemical Analyses of Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) Oil". Pakistan Journal of Nutrition. 8 (3): 269–272. doi:10.3923/pjn.2009.269.272.
- ↑ Chu, Yan-Hwa; Hsu, Hsia-Fen (1999). "Effects of antioxidants on peanut oil stability". Food Chemistry. 66: 29–34. doi:10.1016/S0308-8146(98)00082-X.
- ↑ http://www2.uttyler.edu/vbetts/savannah_republican_1862.htm, 16 January, p.1., c.5
- ↑ "The Peanut Situation" (Dec 12, 1942) The Billboard
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The Culinary Institute of America (2011). The Professional Chef (9th ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-42135-2. OCLC 707248142.
- 1 2 3 "Nutrient database, Release 25". United States Department of Agriculture.
- ↑ Katragadda, H. R.; Fullana, A. S.; Sidhu, S.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á. A. (2010). "Emissions of volatile aldehydes from heated cooking oils". Food Chemistry. 120: 59. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.09.070.
- ↑ http://alfaone.ca/rice-bran-oil-faq/
- ↑ Crevel, R.W.R; Kerkhoff, M.A.T; Koning, M.M.G (2000). "Allergenicity of refined vegetable oils". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 38 (4): 385–93. doi:10.1016/S0278-6915(99)00158-1. PMID 10722892.
- ↑ Hourihane, J. O'B; Bedwani, S. J; Dean, T. P; Warner, J. O (1997). "Randomised, double blind, crossover challenge study of allergenicity of peanut oils in subjects allergic to peanuts". BMJ. 314 (7087): 1084–8. doi:10.1136/bmj.314.7087.1084. PMC 2126478
 . PMID 9133891.
. PMID 9133891. - ↑ "Peanut Allergy". Food Allergy Initiative. Retrieved 3 August 2011.
- ↑ Carlson, Margaret (13 January 2012). "Deaths Show Schools Need Power of the EpiPen: Margaret Carlson". Bloomberg.
- ↑ "Aflatoxin suspected in cooking oil". United Press International. 29 December 2011.
- ↑ "Saponification Table Plus The Characteristics of Oils in Soap", Soap Making Resource
- ↑ "Peanut Oil", Meridian Institute
- ↑ "Oil Treatment for the Hands Gaining Favor" (Jun 24, 1939) Spokane Daily Chronicle
- ↑ "Peanut Biodiesel". Boiled Peanut World. 2010. Retrieved 3 August 2011.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Peanut oil. |