Philippine nationality law

The Philippine nationality law is based upon the principles of jus sanguinis (Latin for right of blood) and therefore descent from a parent who is a citizen or national of the Republic of the Philippines is the primary method of acquiring Philippine citizenship. This is contrasted with the legal principle of jus soli where being born on the soil of a country, even to foreign parents, grants one citizenship. For those born in the Philippines to non-Filipino parents, the Administrative Naturalization Law of 2000 (R.A. 9139) provides a path for administrative naturalization for those who qualify.[1][2]
Citizenship by birth
As of 2010, with no significant changes expected, Philippine nationality law provides that a person becomes a Philippine citizen by birth if
- that person was born on or after October 15, 1986 and at least one parent was a Philippine citizen on the birthdate;[3]
- that person was born on or after January 17, 1973 and both parents were Philippine citizens on the birthdate or the person elected Philippine citizenship pursuant to the provisions of the 1935 Constitution;[4]
- or the person was born on or after May 14, 1935 and the father was a Philippine citizen or, if the father was not, the mother was a Philippine citizen and the person elected Philippine citizenship pursuant to the provisions of the 1935 Constitution;[5]
- or that person was born on or after August 29, 1916 and prior to May 14, 1935 and at least one parent was an inhabitant and resident of the Philippine Islands and a Spanish subject on April 11, 1899, or that person was an inhabitant and resident of the Philippine Islands and a Spanish subject on April 11, 1899, except in certain specific cases.[6]
Citizenship by naturalization
Commonwealth Act No. 473, approved June 17, 1939, provided that persons having certain specified qualifications may become a citizen of the Philippines by naturalization.[7]
Republic Act No. 9139, approved June 8, 2001, provided that aliens under the age of 18 who were born in the Philippines, who have resided in the Philippines and have resided therein since birth, and who possess other specified qualifications may be granted Philippines citizenship by administrative proceeding subject to certain requirements.[1][2]
Under Section 2 of the Revised Naturalization Law the applicant must possess the following qualifications:
- He/she must not be less than twenty-one (21) years of age on the day of the hearing of the petition;
- He/she must have resided in the Philippines for a continuous period of not less than ten (10) years;
- He/she must be of good moral character and believes in the principles underlying the Philippine Constitution, and must have conducted himself in a proper and irreproachable manner during the entire period of his residence in the Philippines in his relation with the constituted government as well as with the community in which he is living;
- He/she must own real estate in the Philippines worth not less than five thousand (5000) pesos, Philippine currency, or must have some known lucrative trade, profession, or lawful occupation;[lower-alpha 1]
- He/she must be able to speak or write English or Spanish or any one of the principal languages;[lower-alpha 2]
- He/she must have enrolled his minor children of school age in any of the public or private schools recognized by the Bureau of Public Schools of the Philippines where Philippine history, government and civics are taught or prescribed as part of the school curriculum, during the entire period of the residence in the Philippines required of him prior to the hearing of the petition for naturalization as Philippine citizen.[8]
Loss and reacquisition of Philippine citizenship
Commonwealth Act No. 36, dated 20 October 1936, provides that Philippine citizens may lose citizenship in any of the following ways or events:[9]
- By naturalization in a foreign country;
- By express renunciation of citizenship;
- By subscribing to an oath of allegiance to support the constitution or laws of a foreign country upon attaining twenty-one years of age or more: Provided, however, That a Filipino may not divest himself of Philippine citizenship in any manner while the Republic of the Philippines is at war with any country.
- By rendering services to, or accepting commission in, the armed forces of a foreign country, and the taking of an oath of allegiance incident thereto, except in certain specified cases;
- By cancellation of the certificates of naturalization;
- By having been declared by competent authority, a deserter of the Philippine armed forces in time of war, unless subsequently, a plenary pardon or amnesty has been granted; and
- In the case of a woman, upon her marriage to a foreigner if, by virtue of the laws in force in her husband's country, she acquires his nationality.
Republic Act No. 8171, approved 23 October 1995, provided a mechanism allowing Filipino women who have lost their Philippine citizenship by marriage to aliens and natural-born Filipinos who have lost their Philippine citizenship, including their minor children, on account of political or economic necessity, to reacquire Philippine citizenship.[10]
Republic Act No. 9225, approved 29 August 2003, provided that natural-born citizens of the Philippines who had lost their Philippine citizenship by reason of their naturalization as citizens of a foreign country would be deemed to have re-acquired Philippine citizenship upon taking an oath of allegiance to the Republic, and that their children whether legitimate, illegitimate or adopted, below eighteen (18) years of age, shall be deemed citizens of the Philippines.[11]
Travel freedom
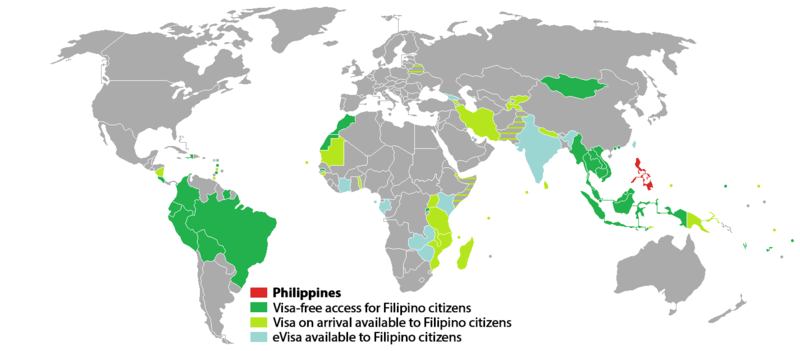
In 2016, Filipino citizens had visa-free or visa on arrival access to 29 countries and territories, ranking the Philippine passport 103rd in the world according to the Visa Restrictions Index.
See also
- Constitution of the Philippines
- Nationality law
- Nationality
- Citizenship
- Oath of Allegiance (Philippines)
- Philippine passport
- Visa requirements for Filipino citizens
Notes
- ↑ In 1939, when CA473 was enacted, real estate in the Philippines was available for acquisition by foreigners. Article XII Section 7 of the 1987 Philippine constitution limits acquisition of real estate by foreigners to cases of hereditary succession.[3]
- ↑ the language used here is based on a Philippine Bureau of Immigration web page on Philippine citizenship.[8] This language differs from the language in CA473, which reads, "He must be able to speak and write English or Spanish and any one of the principal Philippine languages" (emphasis added).[7]
References
- 1 2 The Administrative Naturalization Law of 2000, Chan Robles Law Library, 8 June 2001, retrieved 2006-12-19.
- 1 2 Rules and Regulations Implementing Republic Act No. 9139, Chan Robles Law Library, retrieved 2006-12-19.
- 1 2 1987 Constitution of the Republic of the Philippines, Chan Robles Law Library, 15 October 1986, retrieved 2008-10-06.
- ↑ 1973 Constitution of the Republic of the Philippines, SChan Robles Law Library, 17 January 1973, retrieved 2014-06-29.
- ↑ 1935 Constitution of the Republic of the Philippines, Chan Robles Law Library, 14 May 1935, retrieved 2008-10-06.
- ↑ The Philippine Autonomy Act (Jones Law), Chan Robles Law Library, August 29, 1916, retrieved 2008-10-06.
- 1 2 Commonwealth Act No. 473 : Revised Naturalization Law, LAWPHIL Project, Arellano Law Foundation, 17 June 1939, retrieved 2008-10-06
- 1 2 Philippine Citizenship, The Bureau of Immigration, archived from the original on 2010-09-25, retrieved 3 July 2011
- ↑ An act providing for the ways in which Philippine citizenship may be lost or reacquired, Chan Robles Law Library, 20 October 1939, retrieved 2008-10-06.
- ↑ An act providing for the repatriation of Filipino women who have lost their Philippine citizenship by marriage to aliens and natural-born Filipinos, Chan Robles Law Library, 23 October 1995, retrieved 2008-10-06.
- ↑ Citizenship Retention and Re-acquisition Act of 2003, Chan Robles Law Library, 29 August 2003, retrieved 2008-10-06.
Further reading
- Cortes, Irene R; Lotilla, Raphael Perpetuo M (1990), "Nationality and International Law from the Philippine Perspective", in Ko, Swan Sik, Nationality and International Law in Asian Perspective, Martinus Nijhoff, pp. 335–422, ISBN 0-7923-0876-X
- Cornelius J. Peck (1965), "Nationalistic Influences on the Philippine Law of Citizenship", The American Journal of Comparative Law, The American Journal of Comparative Law, Vol. 14, No. 3, 14 (3): 459–478, doi:10.2307/838452, JSTOR 838452.