Procolophonoidea
| Procolophonoidea Temporal range: 259.8–201.3 Ma Mid Wuchiapingian - Rhaetian | |
|---|---|
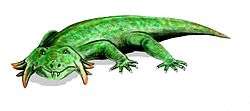 | |
| Hypsognathus fenneri | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | †Parareptilia |
| Order: | †Procolophonomorpha |
| Clade: | †Procolophonia |
| Superfamily: | †Procolophonoidea Broom, 1939 |
| Families | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Procolophonoidea is an extinct superfamily of procolophonian parareptiles. Members were characteristically small, stocky, and lizard-like in appearance. Fossils have been found worldwide from many continents including Antarctica.[1] The first members appeared during the Late Permian in the Karoo Basin of South Africa.[2]
Taxonomy
Procolophonoidea includes the families Owenettidae and Procolophonidae. Sclerosaurus, which is placed within its own family Sclerosauridae, may be a member of the superfamily as well. In 1997, De Braga and Rieppel defined this same taxon (the oldest common ancestor of Procolophonidae and Owenettidae and all its descendants) using the name Procolophoniformes.[3]
When the superfamily was constructed in 1956, it was thought to be within the anthracosaur suborder Diadectomorpha.[4] Since then it has been placed within the suborder Procolophonia along with the pareiasaurs, a group of large herbivorous Permian parareptiles.[5][6][7][8]
- Procolophonia
- Procolophonoidea
- Family Owenettidae
- Species "Owenetta" kitchingorum
- Genus Barasaurus
- Genus Candelaria
- Genus Owenetta
- Genus Ruhuhuaria
- Genus Saurodektes
- Family Procolophonidae
- ? Genus Gomphiosauridion
- ? Genus Kinelia
- ? Genus Spondylolestes
- ? Genus Xenodiphyodon
- Genus Coletta
- Genus Kitchingnathus
- Genus Lasasaurus
- Genus Phaanthosaurus
- Genus Pintosaurus
- Genus Sauropareion
- Genus Tichvinskia
- Subfmily Leptopleuroninae
- Subfmily Procolophoninae
- Subfmily Theledectinae
- Family Owenettidae
- Procolophonoidea
| Cladogram of Procolophonoidea, excluding members of Procolophonidae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cisneros et al. 2004[9] |
| Cladogram of Procolophonidae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Modesto et al. 2001[10] |
References
- ↑ Colbert, E. H. and Kitching, J. W. (1975). The Triassic reptile Procolophon in Antarctica. American Museum Novitates 2566:1-23.
- ↑ Broom, R. (1939). A new type of cotylosaurian, Owenetta rubidgei. Annals of the Transvaal Museum 19:319–321.
- ↑ Jalil, N. E., & Janvier, P. (2005). Les pareiasaures (Amniota, Parareptilia) du Permien supérieur du Bassin d’Argana, Maroc. Geodiversitas, 27(1), 35-132.
- ↑ Romer, A. S. (1956). Osteology of the Reptiles. University of Chicago Press. 772 pp.
- ↑ Daly, E. (1973). A Lower Permian vertebrate fauna from southern Oklahoma. Journal of Paleontology 47(3):562-589.
- ↑ Carroll, R. L. (1988). Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution. WH Freeman and Company, New York ISBN 0-7167-1822-7.
- ↑ Lee, M. S. Y. (1997). Pareisaur phylogeny and the origin of turtles. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 120(3):197-280.
- ↑ Modesto, S. P. and Damiani, R. (2007). The procolophonoid reptile Sauropareion anoplus from the lowermost Triassic of South Africa. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 27(2):337-349.
- ↑ Cisneros, J. C., Damiani, R., Schultz, C., da Rosa, A., Schwanke, C., Neto, L. W. and Aurélio, P. L. P. (2004) A procolophonoid reptile with temporal fenestration from the Middle Triassic of Brazil. Proceedings of the Royal Society Series B 271(1547):1541–1546.
- ↑ Modesto, S. Sues, H.-D. and Damiani, R. (2001). A new Triassic procolophonoid reptile and its implications for procolophonoid survivorship during the Permo-Triassic extinction event. Proceedings of the Royal Society Series B 268(2001):2047–2052.
External links
- Introduction to Procolophonoidea University of California Museum of Paleontology (UCMP)
- Procolophonoidea in the Paleobiology Database
