Proteus mirabilis
| Proteus mirabilis | |
|---|---|
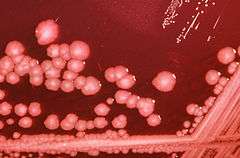 | |
| P. mirabilis on an XLD agar plate. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Proteobacteria |
| Class: | Gamma Proteobacteria |
| Order: | Enterobacteriales |
| Family: | Enterobacteriaceae |
| Genus: | Proteus |
| Species: | P. mirabilis |
| Binomial name | |
| Proteus mirabilis Hauser 1885 | |
Proteus mirabilis is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It shows swarming motility and urease activity. P. mirabilis causes 90% of all Proteus infections in humans. It is widely distributed in soil and water.[1]
Diagnosis
An alkaline urine sample is a possible sign of P. mirabilis. It can be diagnosed in the lab due to characteristic swarming motility, and inability to metabolize lactose (on a MacConkey agar plate, for example). Also P. mirabilis produces a very distinct fishy odor.
Disease
This rod-shaped bacterium has the ability to produce high levels of urease, which hydrolyzes urea to ammonia (NH3), so makes the urine more alkaline. If left untreated, the increased alkalinity can lead to the formation of crystals of struvite, calcium carbonate, and/or apatite, which can result in kidney stones. The bacteria can be found throughout the stones, and these bacteria lurking in the kidney stones can reinitiate infection after antibiotic treatment. Once the stones develop, over time they may grow large enough to cause obstruction and renal failure. Proteus species can also cause wound infections, septicemia, and pneumonia, mostly in hospitalized patients.[2]
Treatment
P. mirabilis is generally susceptible to most antibiotics apart from tetracycline and nitrofurantoin,[3] but 10–20% of P. mirabilis strains are also resistant to first-generation cephalosporins and ampicillin.[4]
Characteristics
P. mirabilis can use urea. It can produce hydrogen sulfide gas, and forms clear films on growth media. It is motile, possessing peritrichous flagella, and is known for its swarming ability. It is commonly found in the intestinal tracts of humans. P. mirabilis is not pathogenic in guinea pigs or chickens. Noteworthy is the ability of this species to inhibit growth of unrelated strains, resulting in a macroscopically visible line of reduced bacterial growth where two swarming strains intersect. This line is named the Dienes line after its discoverer Louis Dienes.
The micro-organism tests:
- Indole-negative and nitrate reductase-positive (no gas bubbles produced)
- Methyl red-positive and Voges-Proskauer negative (Can be both MR- and V-P-positive)
- Catalase positive and cytochrome oxidase-negative
- Phenylalanine deaminase-positive
- Tryptophan test-negative
- Urea test- positive
- Casein test-negative
- Starch test- negative
- Hydrogen sulfide test-positive
- Citrate agar test-positive
- Ornithine decarboxylase-positive
- Lysine decarboxylase-positive
References
- ↑
- Bacteria of the species Proteus mirabilis are widely distributed in soil and water in the natural environment. In humans, Proteus is found as part of the normal flora of the gut....from BioMedHTC
- ↑ Proteus mirabilis and Urinary Tract Infection .
- ↑ O'hara CM, Brenner FW, Miller JM. Classification, identification, and clinical significance of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2000;13(4):534-46. .
- ↑ Gonzalez, Gus; et al. "Proteus Infections Medication". Medscape. Retrieved 30 October 2015.
External links
- Proteus Genome Projects from Genomes OnLine Database
- Type strain of Proteus mirabilis at BacDive - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase
Further reading
- Esipov, Sergei E.; Shapiro, J. A. (1998). "Kinetic model of Proteus mirabilis swarm colony development". Journal of Mathematical Biology. 36 (3): 249–268. doi:10.1007/s002850050100.
- Frénod, Emmanuel (2006). "Existence result for a model of Proteus mirabilis swarm". Differential and Integral Equations. 19 (6): 697–720. arXiv:math.FA/0702761
 .
. - Gué, Michaël; Dupont, Virginie; Dufour, Alain; Sire, Olivier (2001). "Bacterial swarming: A biological time-resolved FTIR-ATR study of Proteus mirabilis swarm-cell differentiation". Biochemistry. 40 (39): 11938–45. doi:10.1021/bi010434m. PMID 11570895.
- Rauprich, O.; Matsushita, M.; Weijer, C. J.; Siegert, F.; Esipov, S. E.; Shapiro, J. A. (1 November 1996). "Periodic phenomena in Proteus mirabilis swarm colony development". Journal of Bacteriology. 178 (22): 6525–38. PMC 178539
 . PMID 8932309.
. PMID 8932309. - "Proteus mirabilis". NCBI Taxonomy Browser. 584.